Buccal Anatomy
The angle of the mouth anteriorly the masseter muscle posteriorly the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the zygomaticus muscles superiorly the depressor anguli oris muscle and the attachment of the deep fascia to the mandible inferiorly the. Each space is enveloped by the superficial investing layer of the deep cervical fascia.
 Long Buccal Block Dental Injection Google Search Dental
Long Buccal Block Dental Injection Google Search Dental
Anatomy of the buccal mucosathe buccal mucosa is bordered vertically by the maxillary and mandibular vestibular folds whereas its anterior and posterior borders are formed by the outer commissure of the lips and the anterior tonsillar pillar respectively.

Buccal anatomy. The inflections of the voice are for sensations gesture is for sentiments. Anatomy of or relating to the cheek. It gives off a small cutaneous branch that supplies a small patch.
4 buccal cells symbolise a preferably first target site for early genotoxic events that are induced by carcinogenic agents entering the body. The buccal mucosa is primarily innervated by the long buccal nerve cn v3 and by the anterior middle and posterior superior alveolar nerves of the second division of the trigeminal nerve cn v2. The buccal spaces fig.
In buccal group three patients were found to have retained products of conception which were given repeat misoprostol 400 mcg. Anatomy of or relating to the mouth. It descends deep to temporalis muscle between it and the inferior head of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
The superficial branch passes sandwiched between the skin and the superficial muscles of the face. The buccal space or buccinator space is one of the seven suprahyoid deep compartments of the head and neck. The buccal spaces are paired fat contained spaces on each side of the face forming cheeks.
The buccal apparatus is for the expression of ideas. The buccal nerve has a superficial and deep branch. 1 anatomical boundaries are the buccinator muscle medially the superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia and the muscles of facial expression laterally and anteriorly and the masseter muscle mandible lateral and medial pterygoid muscles and the parotid gland posteriorly.
The boundaries of each buccal space are. It innervates the muscles at this site and anastomoses with the external nasal nerve and the infratrochlear nerves. Delsarte system of oratory various the two somites following the mandibular or first post oral or buccal somite carry appendages modified as maxillae.
The buccinator muscle originates from the alveolar processes of the maxilla and the mandible and it inserts into the pterygomandibular raphe. The buccal nerve divides off the anterior division and passes with the paired nerves to lateral pterygoid between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
 Duke Anatomy Lab 2 Pre Lab Exercise
Duke Anatomy Lab 2 Pre Lab Exercise
 Anatomy Of Buccal Cancer Mouth Cancer
Anatomy Of Buccal Cancer Mouth Cancer
 Micro Computed Tomographic Analysis Of A Maxillary Central
Micro Computed Tomographic Analysis Of A Maxillary Central
 Dental Buccal Space Medical Artist Com
Dental Buccal Space Medical Artist Com
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12550/HeadCadavar.png) Facial Nerve Origin Function Branches And Anatomy Kenhub
Facial Nerve Origin Function Branches And Anatomy Kenhub
 Diagrams Buccal Cavity Diagram Human Mouth Cavities
Diagrams Buccal Cavity Diagram Human Mouth Cavities
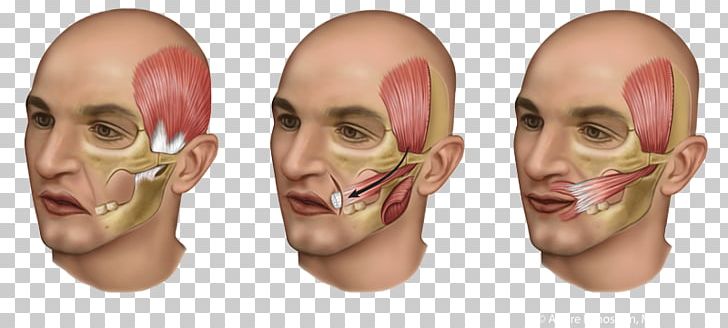 Temporal Muscle Surgery Tendon Buccal Fat Pad Png Clipart
Temporal Muscle Surgery Tendon Buccal Fat Pad Png Clipart
 Closure Of Oroantral Fistula By The Buccal Fat Pad Flap
Closure Of Oroantral Fistula By The Buccal Fat Pad Flap
Introduction To Dental Anatomy Dental Anatomy Physiology
 Management Of Cervicofacial Fat Plastic Surgery Key
Management Of Cervicofacial Fat Plastic Surgery Key
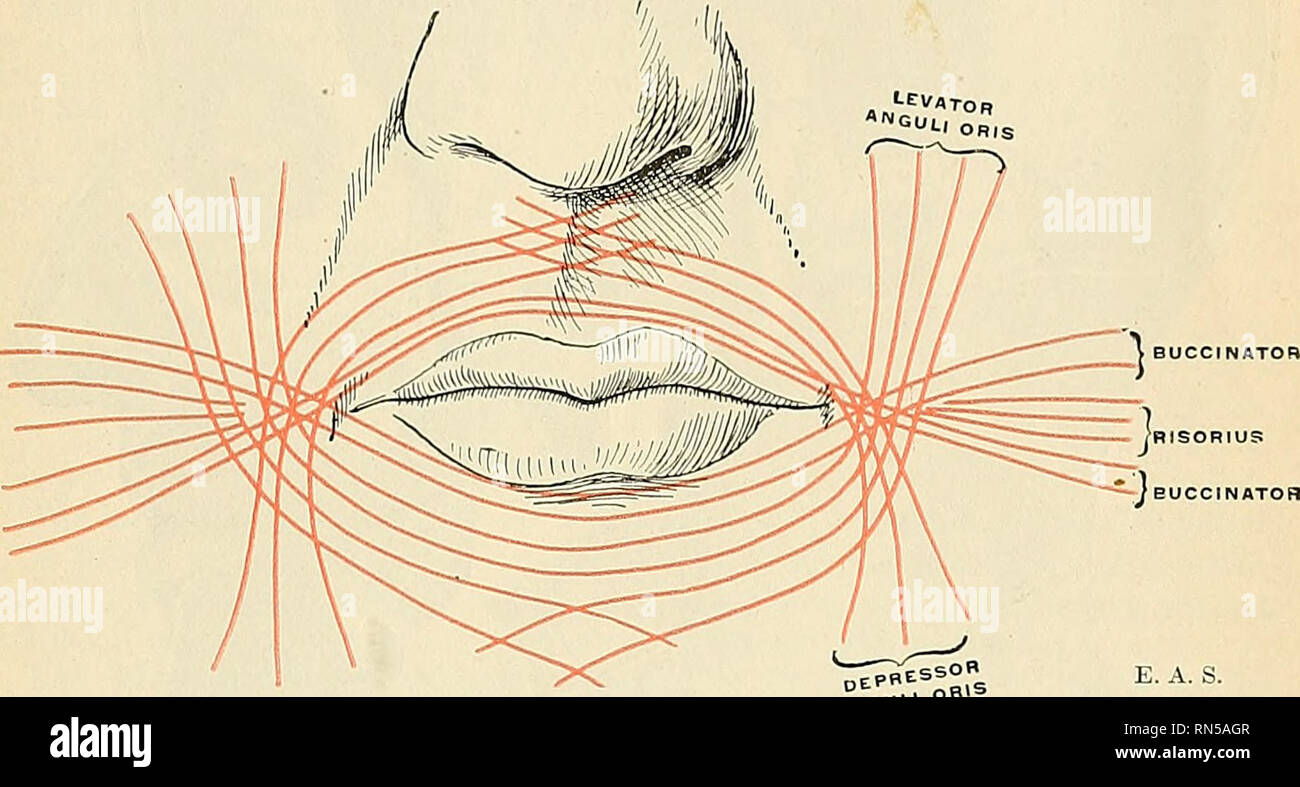 Anatomy Descriptive And Applied Anatomy The Buccal It Eg
Anatomy Descriptive And Applied Anatomy The Buccal It Eg
 Inferior Labial A Facial A Buccal A N35 Innervation Of Lips
Inferior Labial A Facial A Buccal A N35 Innervation Of Lips
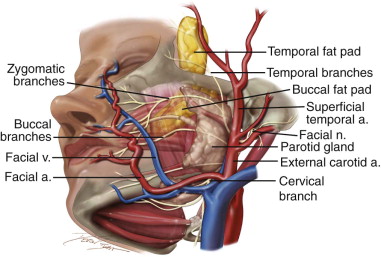 Buccal Fat Pad Flap Pocket Dentistry
Buccal Fat Pad Flap Pocket Dentistry
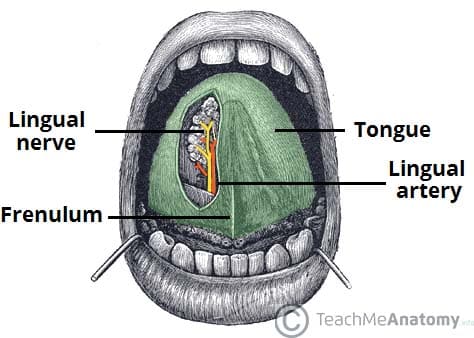 The Oral Cavity Divisions Innervation Teachmeanatomy
The Oral Cavity Divisions Innervation Teachmeanatomy
Parotid Region Anatomy The Head And Neck Flashcards
 Oral Cavity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Oral Cavity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/subclavian-vein-7/iQYJEaVqaBSFLBzbNUEqfA_T988_FINAL__2_.png) Head And Neck Regions And Anatomy Kenhub
Head And Neck Regions And Anatomy Kenhub
 Carcinoma Buccal Mucosa Anatomy To Management
Carcinoma Buccal Mucosa Anatomy To Management
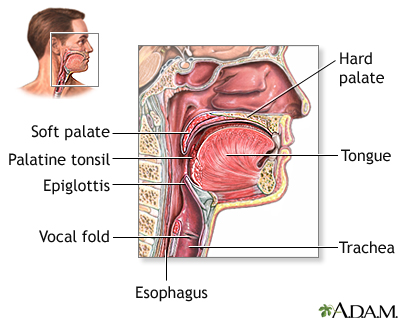 Buccal Smear Uf Health University Of Florida Health
Buccal Smear Uf Health University Of Florida Health
 Anatomy Of The Face For Cosmetic Purposes Springerlink
Anatomy Of The Face For Cosmetic Purposes Springerlink
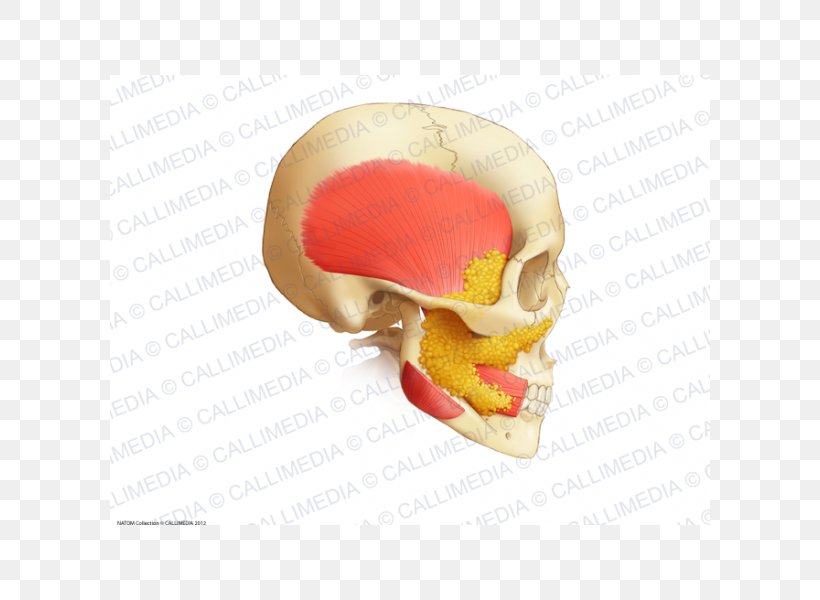 Human Anatomy Buccal Fat Pad Jaw Buccinator Muscle Png
Human Anatomy Buccal Fat Pad Jaw Buccinator Muscle Png



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Buccal Anatomy"
Posting Komentar