Superior Vena Cava Anatomy
The lung consists of five lobes. The anterior vena cava also known as the precava drains the head end of the body while the posterior vena cava or postcava drains the tail or rear end.
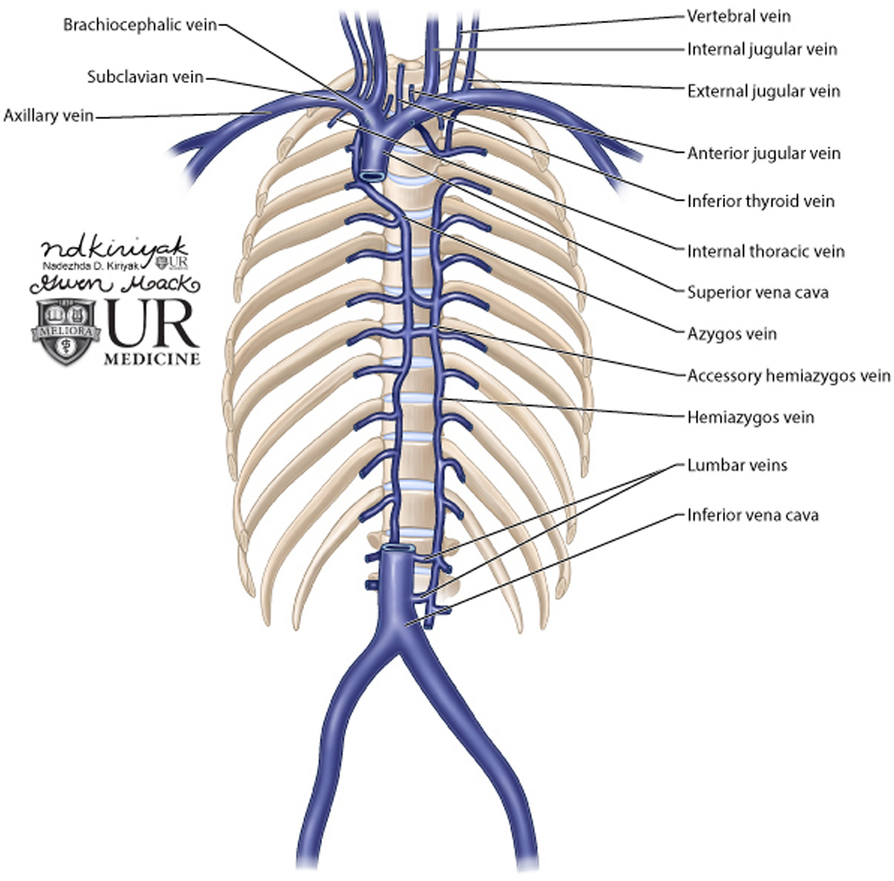 Blood Finds A Way Pictorial Review Of Thoracic Collateral
Blood Finds A Way Pictorial Review Of Thoracic Collateral
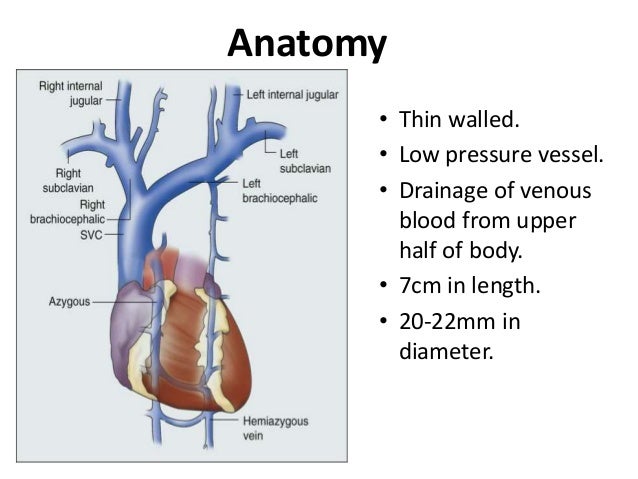
It is a large diameter 24 mm short length vein that receives venous return from the upper half of the body above the diaphragm.

Superior vena cava anatomy. The superior lobes of each lung are the uppermost pieces also called the upper lobes. This large vein brings de oxygenated blood from the head neck arm and chest regions of the body to the right atrium. The left lung has a superior and inferior lobe while the right lung has superior middle and inferior lobes.
The superior vena cava is a large significant vein responsible for returning deoxygenated blood collected from the body back into the heart. This vein brings de oxygenated blood from the lower body regions legs back abdomen and pelvis to the right. The superior vena cava svc is a large valveless venous channel formed by the union of the brachiocephalic veins.
The inferior vena cava forms at the superior end of the pelvic cavity when the common iliac veins unite to form a larger vein. The superior vena cava svc is the superior of the two venae cavae the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. Gross anatomy the svc be.
Its latin name is related to its large pipe appearance in cadavers cava meaning hollow. In humans these veins are respectively called the superior and inferior venae cavae. Thin walls of tissue called fissures separate the different lobes.
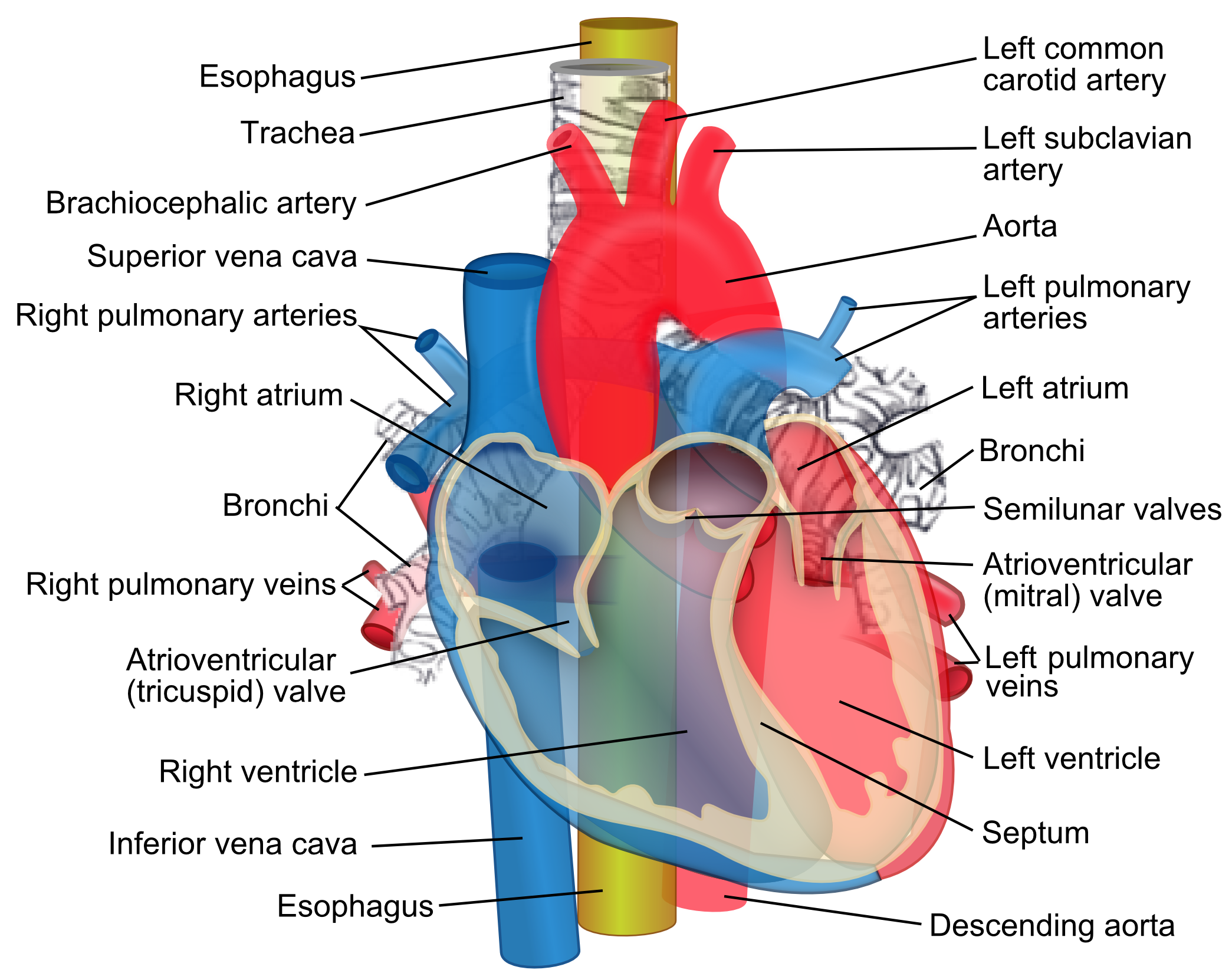
In this article we will look at the anatomy of the superior vena cava its position tributaries and clinical correlations. It is present within the superior and middle mediastinum. The superior vena cava handles the venous return of blood from structures located superior to the diaphragm.
Although the vena cava is very large in diameter its walls are incredibly thin due to the low pressure exerted by venous blood. The superior vena cava svc is a large valveless vein that conveys venous blood from the upper half of the body and returns it to the right atrium. It receives blood from the upper half of the body except the heart and returns it to the right atrium.
Function of the venae cavae superior vena cava. The superior vena cava svc also known as the cava or cva is a short but large diameter vein located in the anterior right superior mediastinum. Whereas many mammals including humans have only one anterior vena cava other animals have two.
The superior vena cava svc also known as the cava or cva is a short but large diameter vein located in the anterior right superior mediastinum.
 1000 Superior Vena Cava Stock Images Photos Vectors
1000 Superior Vena Cava Stock Images Photos Vectors
 Developmental Anatomy Of The Persistent Left Superior Vena
Developmental Anatomy Of The Persistent Left Superior Vena
Isolated Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava A Case Report
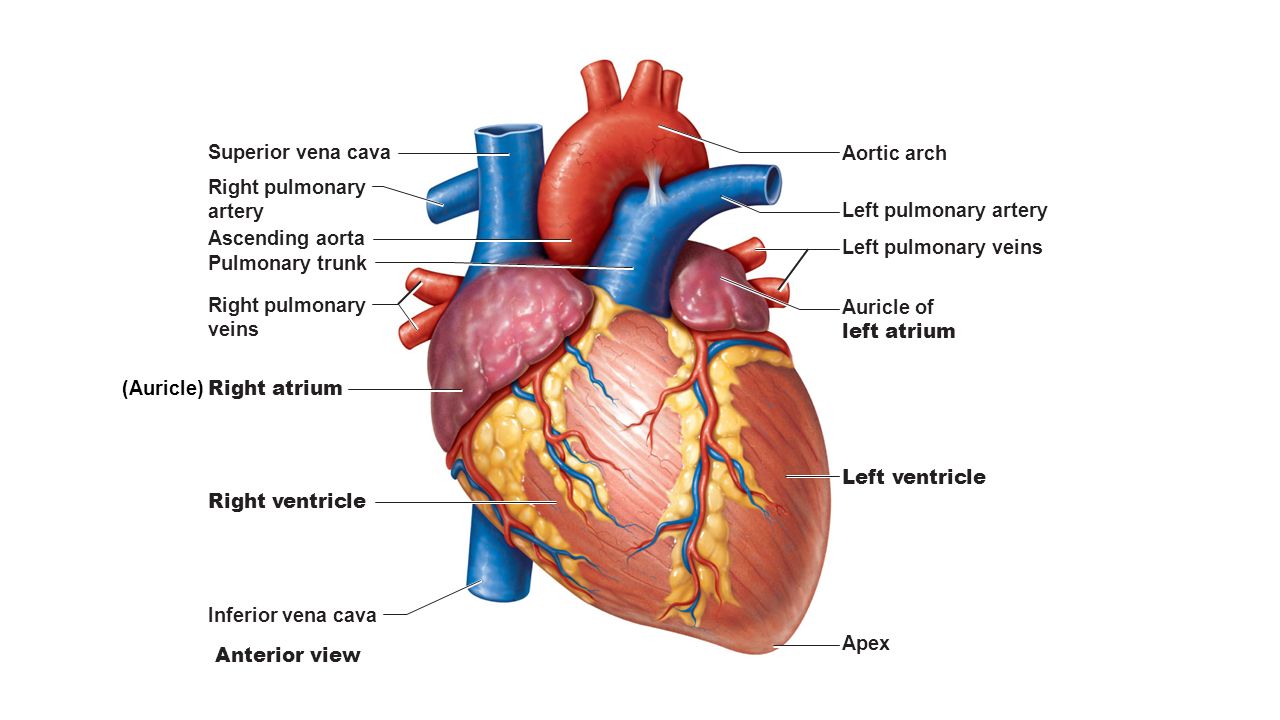 Superior Vena Cava Aorta Pulmonary Trunk Pericardium Cut
Superior Vena Cava Aorta Pulmonary Trunk Pericardium Cut
 Superior Vena Cava Cardiovascular System Human Anatomy Kenhub
Superior Vena Cava Cardiovascular System Human Anatomy Kenhub
 Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Occurs When The Svc Is
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Occurs When The Svc Is
Absent Superior Vena Cava In Tetralogy Of Fallot Shah Tr
Difference Between Superior And Inferior Vena Cava Pediaa Com
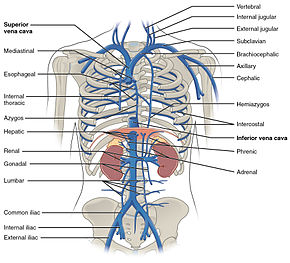 Brachiocephalic Vein Wikipedia
Brachiocephalic Vein Wikipedia

 Solved Correctly Label The Following External Anatomy Of
Solved Correctly Label The Following External Anatomy Of
 Figure 5 From 23 Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Semantic Scholar
Figure 5 From 23 Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Semantic Scholar
 Left Superior Vena Cava With Associated Venous Variations
Left Superior Vena Cava With Associated Venous Variations
 Upper Veins That Drain Into Superior Vena Cava Diagram Quizlet
Upper Veins That Drain Into Superior Vena Cava Diagram Quizlet
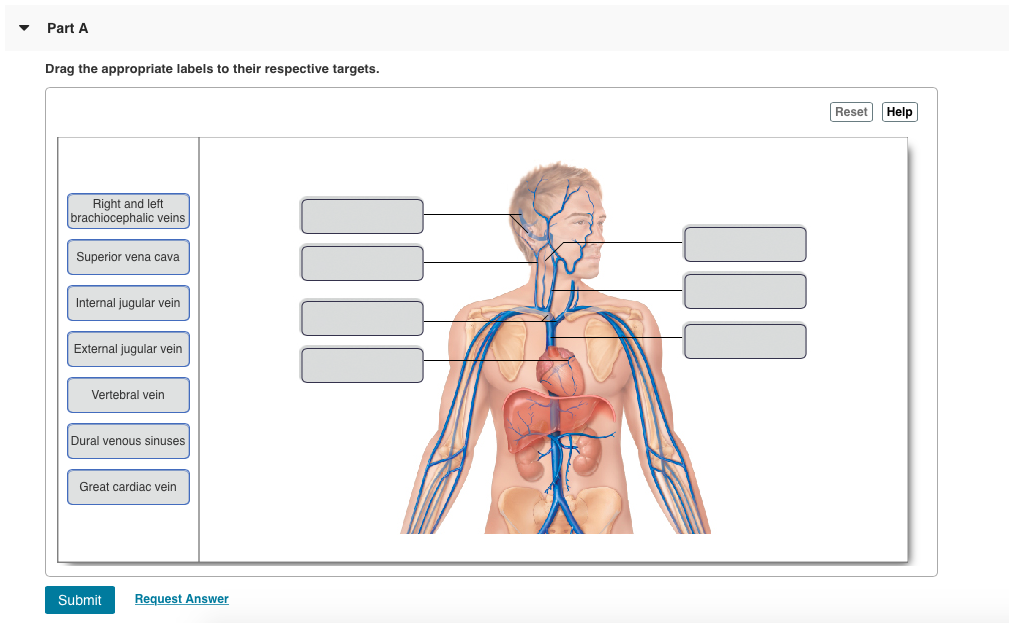 Solved Part A Drag The Appropriate Labels To Their Respec
Solved Part A Drag The Appropriate Labels To Their Respec
Thoracic And Abdominal Veins Course Hero
 Superior Vena Cava An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Superior Vena Cava An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
View Of Persistent Left Sided Superior Vena Cava The
 1000 Superior Vena Cava Stock Images Photos Vectors
1000 Superior Vena Cava Stock Images Photos Vectors
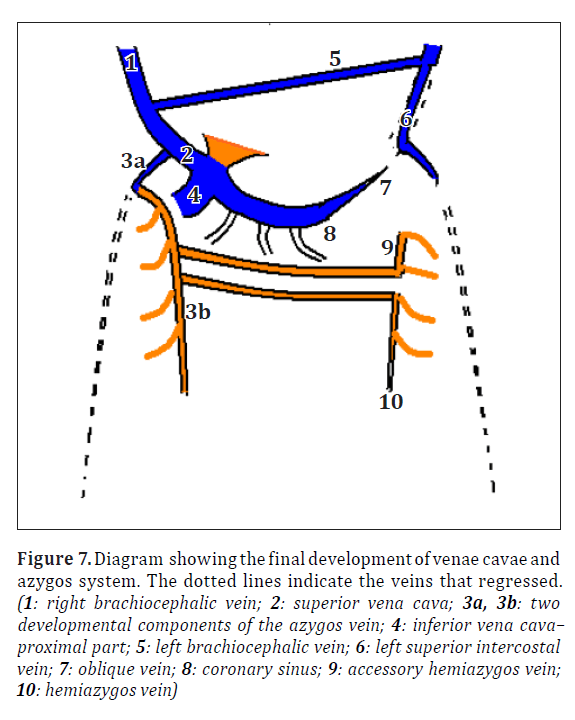
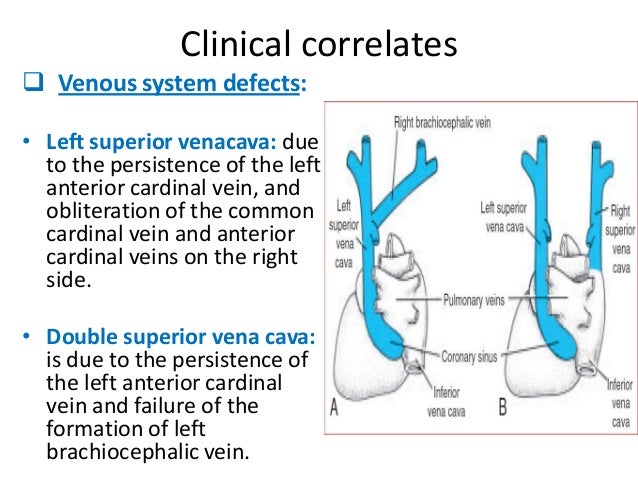 Development Of Superior Venacava And Azygous Vein
Development Of Superior Venacava And Azygous Vein
Chapter 125 Development Of The Venous System Primitive


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Superior Vena Cava Anatomy"
Posting Komentar