Sural Nerve Anatomy
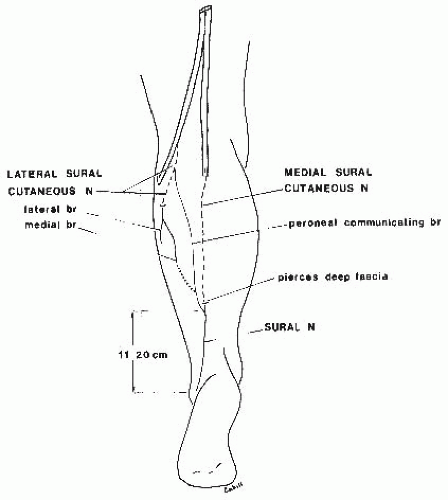
Sural nerve formation at the distal third of the gastrocnemius both sural cutaneous branches join to become the sural nerve. High in the popliteal fossa the sciatic nerve divides into its two main branches on route to serve the leg namely the tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve.
%20nerve,superficial%20fibular%20(peroneal)%20nerve,fibula,talus,inferior%20extensor%20retinaculum,fibularis%20(peroneus)%20longus%20muscle,fibularis%20(peroneus)%20brevis%20muscle,calcaneus,abductor%20digiti%20minimi%20muscle,peroneus%20tertius%20muscle,extensor%20digitorum%20brevis%20muscle) Sural Nerve Distal Tibia Deep Fibular Peroneal Nerv Open I
Sural Nerve Distal Tibia Deep Fibular Peroneal Nerv Open I
The nerve is comprised of spinal nerve roots from s1 and s2.

Sural nerve anatomy. Sural nerve anatomy as aforesaid it is purely a sensory nerve and does not consist of motor fibers. The sural nerve supplies the dorsal cutaneous area of the lateral 2 and half toes in some cases. Functions the sural nerve supplies skin at the lower posterolateral side of the leg as well as the lateral aspect of the foot and little toe.
It travels within subcutaneous tissue adjacent to the small saphenous vein in the lower posterolateral calf. Clinical relevance damage to the sural nerve due to injury can occur as a result of trauma fractured calcaneus damage from surgery in the region. The sural nerve is a sensory nerve of the lower limb formed by the union of branches from the tibial nerve as well as common fibular nerve supplying sensation to the lower lateral aspect of the calf and foot.
Travels posterior to lateral malleolus and deep to fibularis tendon sheath. The sural nerve is a sensory nerve of the lower limb that supplies the lower posterolateral part of the leg and lateral part of the dorsum of the foot. The sural nerve is a sensory nerve made up of collateral branches off of the common tibial and common fibular nerve.
It is generally described as a sensory nerve but may contain motor fibres discussed later in this article 14 16. Descends on the posterolateral aspect of leg. The short saphenous nerve initially courses posterior between the heads of the gastrocnemius muscle.
It is made up of branches of the tibial nerve and common fibular nerve the medial cutaneous branch from the tibial nerve and the lateral cutaneous branch from the common fibular nerve. The sural nerve is a sensory nerve of the lower lateral leg and lateral aspect of the foot. It can end at the lateral border of the foot without.
The sural nerve is a sensory nerve in the calf region of the leg. The sural nerve is purely sensory and it supplies sensation to the lower lateral leg lateral heel ankle and dorsal lateral foot. In the posterior calf the sural nerve emerges from between the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle and runs with the small saphenous vein inferiorly to curve under the lateral malleolus.
Sural Nerve Location Origin Function Nerve Block
 Midfoot Approach Dorsolateral To The Cuboid Ao Surgery
Midfoot Approach Dorsolateral To The Cuboid Ao Surgery
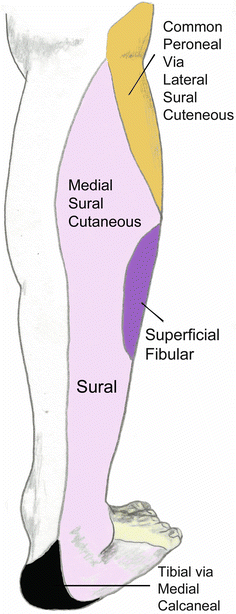 Sural Nerve Entrapment Springerlink
Sural Nerve Entrapment Springerlink
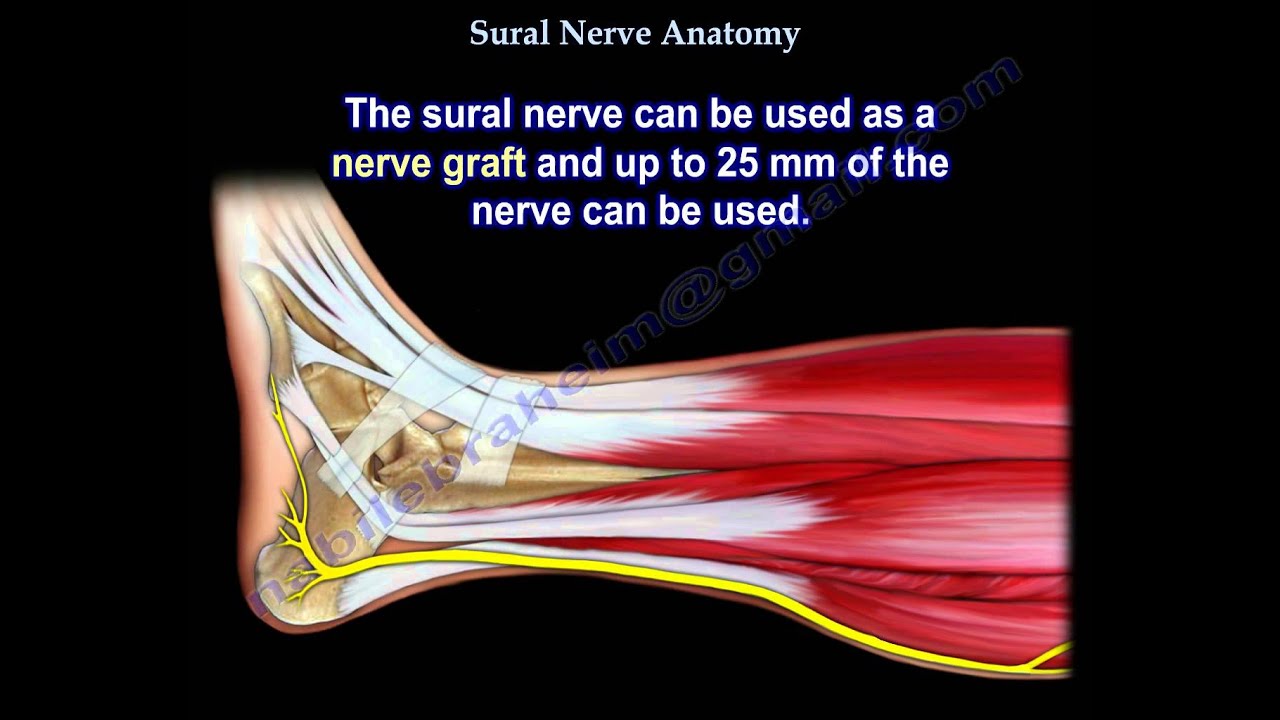 Sural Nerve Anatomy Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Sural Nerve Anatomy Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
 A New Pattern Of The Sural Nerve Added To Anatomy Of The Su
A New Pattern Of The Sural Nerve Added To Anatomy Of The Su
Sural Nerve Location Function Anatomy And Pictures
 Lower Extremity Innervation Msk Medbullets Step 1
Lower Extremity Innervation Msk Medbullets Step 1
 Sural Nerve Block Sciencedirect
Sural Nerve Block Sciencedirect
 Sural Nerve Entrapment Springerlink
Sural Nerve Entrapment Springerlink
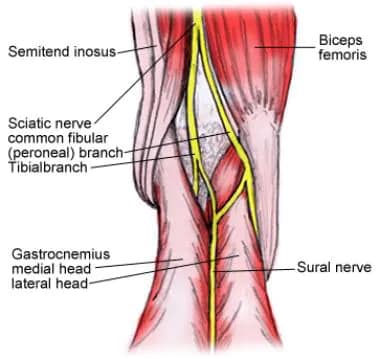 Popliteal Nerve Block Background Indications
Popliteal Nerve Block Background Indications
 The Tibial Nerve Course Motor Sensory Teachmeanatomy
The Tibial Nerve Course Motor Sensory Teachmeanatomy
Sural Nerve Lipoma An Anatomy Review
 Figure 3 From Late Estimation Of Sensibility Loss After
Figure 3 From Late Estimation Of Sensibility Loss After
 Sural Nerve In The Calf Sonoanatomy For Anaesthetists
Sural Nerve In The Calf Sonoanatomy For Anaesthetists
 Uncommon Injuries Sural Nerve Neuropathy
Uncommon Injuries Sural Nerve Neuropathy
 Ankle Block Hadzic S Peripheral Nerve Blocks And Anatomy
Ankle Block Hadzic S Peripheral Nerve Blocks And Anatomy
Irritation Or Neuroma Of The Sural Nerve Posterior Foot Pain
Medical Exhibits Demonstrative Aids Illustrations And Models
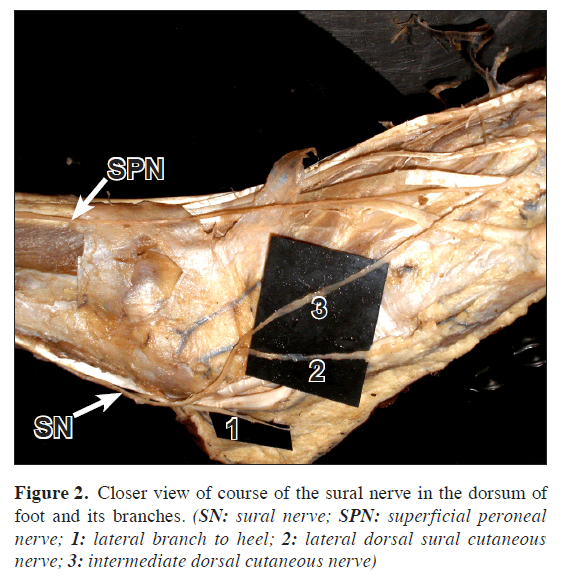 Variant Formation Of Sural Nerve And Its Distribution At The
Variant Formation Of Sural Nerve And Its Distribution At The
Sural Nerve Graft Harvest Iowa Head And Neck Protocols
 Estimation Of Ultrasound Reference Values For The Lower Limb
Estimation Of Ultrasound Reference Values For The Lower Limb
 The Sural Nerve Anatomy And Entrapment Functional
The Sural Nerve Anatomy And Entrapment Functional
 Sural Nerve Entrapment Springerlink
Sural Nerve Entrapment Springerlink
Bats Better Anaesthesia Through Sonography
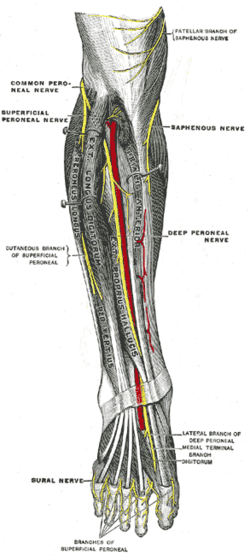 Superficial Peroneal Nerve Wikipedia
Superficial Peroneal Nerve Wikipedia
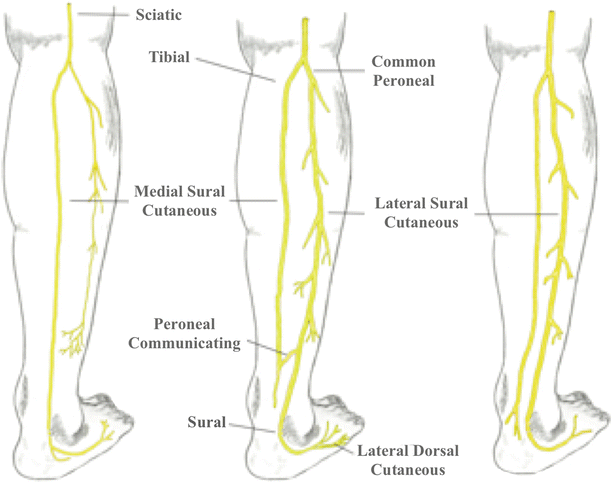 Sural Nerve Entrapment Springerlink
Sural Nerve Entrapment Springerlink
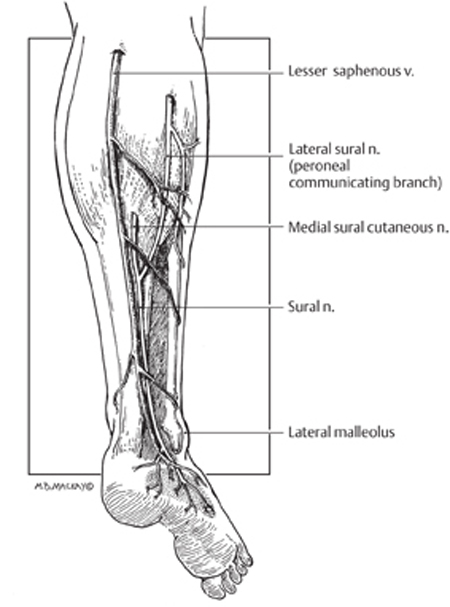 Sural Nerve Injury And Neuroma Neupsy Key
Sural Nerve Injury And Neuroma Neupsy Key
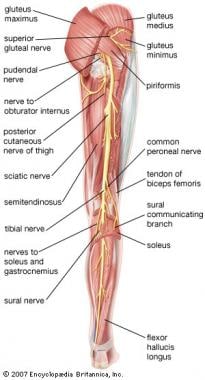 Sciatic Nerve Decompression Background Indications
Sciatic Nerve Decompression Background Indications
 Uncommon Injuries Sural Nerve Neuropathy
Uncommon Injuries Sural Nerve Neuropathy
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Sural Nerve Anatomy"
Posting Komentar