Internal Anatomy Of Chicken
The thigh ends at the lower leg drumstick. When food enters the beak of a chicken it immediately begins being broken down by saliva chickens dont have teeth.
Nervous Systems Important Sensory Organs Poultry Hub
This provides a strong and rigid union in conjunction with powerful muscles.

Internal anatomy of chicken. It is one of the most common and widespread domestic animals with a total population of more than 19 billion as of 2011. The skull of the chicken consists of many small bones and the face is made up of the nasal and the premaxillary bone. There are no vocal cords in mammals.
Chickens stand and walk on their toes. The leg of the chicken is similar to the human anatomy except that the hip bone is fused with the backbone. Table of contents digestion female reproduction precocial versus altricial sex reversal in chickens poultry genetics sexing day old.
The next place that the food enters after the tongue pushes the food down the throat is the esophagus. Play this quiz called internal anatomy of a chicken and show off your skills. They make up the cranium which is the back of the chicken head.
This is a quiz called internal anatomy of a chicken and was created by member geographonic login. Y shaped organ located at the base of the trachea that appears as a pinched in part of the trachea. Vocalization in birdssound is produced by syringeal muscles and tympanic membranes in conjunction with the clavicular air sar.
There is also a jaw bone which is called a mandible. The chicken gallus gallus domesticus is a type of domesticated fowl a subspecies of the red junglefowl. A normal bursa is a small grape like pouch with a wrinkled cream colored interior.
The thigh is connected to the shank foot at the hock joint which is the equivalent of the ankle in humans. The white pasty material that commonly coats chicken fecal material is uric acid the avian form of urine and is normal see figure 34. There are more chickens in the world than any other bird or domesticated fowl.
The largest bones in a chickens face are called frontal parietal and temporal bones. This provides a strong and rigid union in conjunction with powerful muscles. In a chicken less than 4 months old you may be able to find this important organ of the growing birds immune system when you cut through the cloaca at the end of the digestive tract.
From the esophagus the food then enters the chickens crop. The thigh of a chicken is the upper part of the leg attached to the body of the bird.
 Chicken Hen Anatomy Model 6 Parts
Chicken Hen Anatomy Model 6 Parts
 Chicken Organs Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Chicken Organs Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Reproductive System Poultry Hub
 Eggs Building Up To A Grand Finish Recreation
Eggs Building Up To A Grand Finish Recreation
 Amazon Com Hen Showing Muscular System Chicken Body 3d
Amazon Com Hen Showing Muscular System Chicken Body 3d
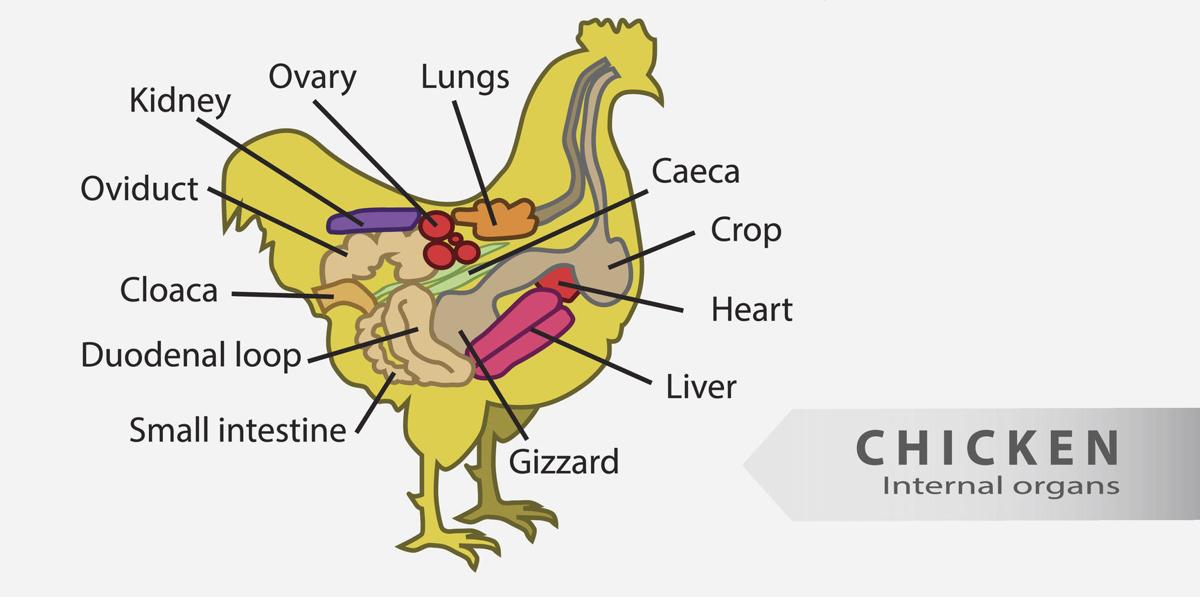
 Chicken Internal Anatomy Diagram Chicken Gizzard Internal
Chicken Internal Anatomy Diagram Chicken Gizzard Internal
Everything You Need To Know About How A Chicken Lays Eggs
 Chicken Organs Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Chicken Organs Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Chicken Anatomy Tiny Eggs Forming
Chicken Anatomy Tiny Eggs Forming
Definitions Genetic Load And Others The Classroom The Coop
Six Things You Didn T Know About Chicken Reproduction
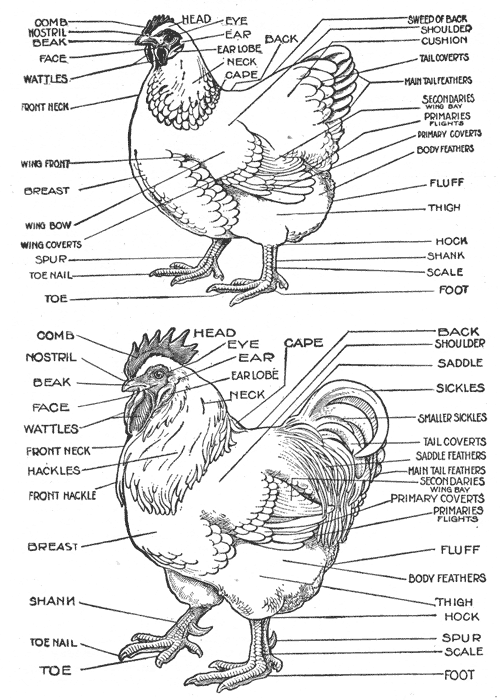
 Chicken Body Parts Diagram Reading Industrial Wiring Diagrams
Chicken Body Parts Diagram Reading Industrial Wiring Diagrams
Chicken Internal Anatomy Poster 18 X 24
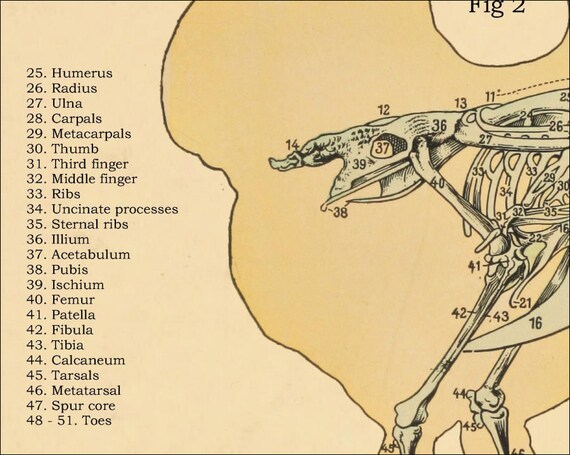 Chicken Skeletal Internal Anatomy Poster 18 X 24
Chicken Skeletal Internal Anatomy Poster 18 X 24
 Chicken Internal Anatomy Labels Stock Vector Royalty Free
Chicken Internal Anatomy Labels Stock Vector Royalty Free
 Chicken Diagram And Anatomy Of A Chicken Pictures And Labels
Chicken Diagram And Anatomy Of A Chicken Pictures And Labels
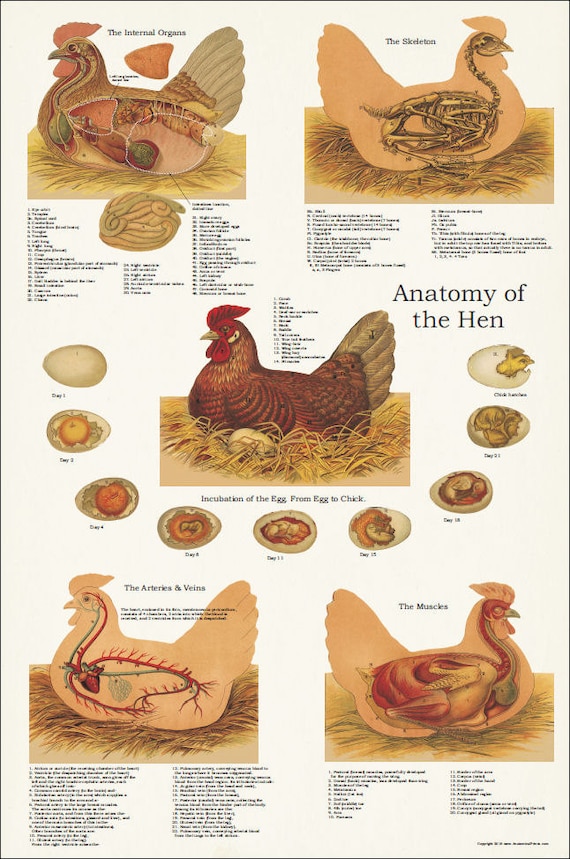 Chicken Hen Muscle Skeletal Anatomy Poster 24 X 36 Veterinary Chart
Chicken Hen Muscle Skeletal Anatomy Poster 24 X 36 Veterinary Chart
 Twin Tier Poultry Club Poultry Knowledge
Twin Tier Poultry Club Poultry Knowledge
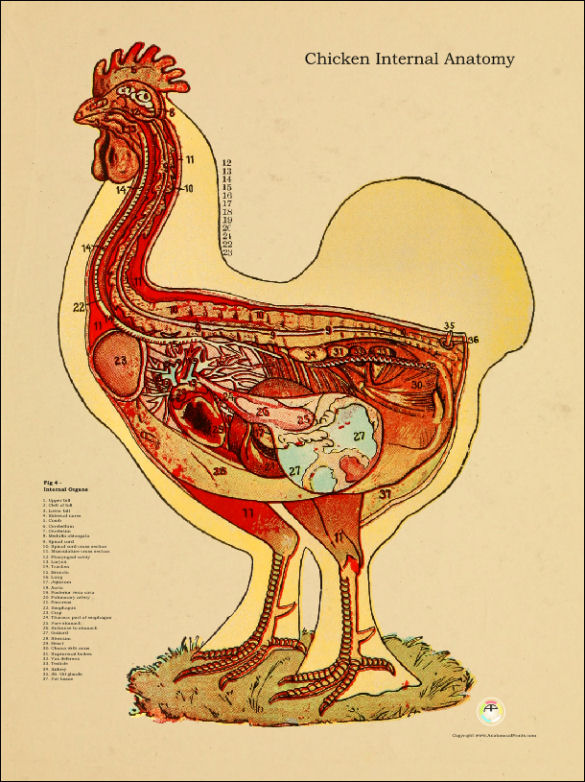 Chicken Internal Anatomy Poster 18 X 24
Chicken Internal Anatomy Poster 18 X 24
 Chicken Anatomy 101 Everything You Need To Know
Chicken Anatomy 101 Everything You Need To Know
 Details About Chicken Poultry Anatomy Model Organs Heart Wing Muscle Veterinary Study Animal T
Details About Chicken Poultry Anatomy Model Organs Heart Wing Muscle Veterinary Study Animal T
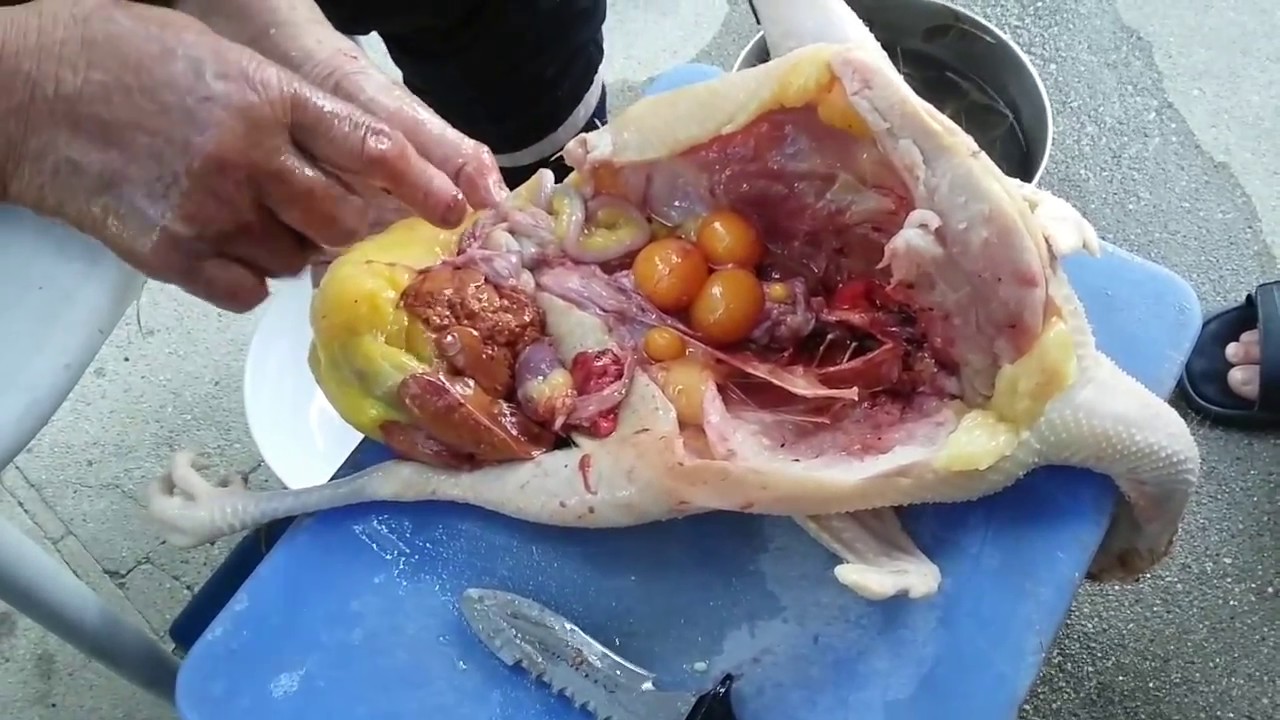
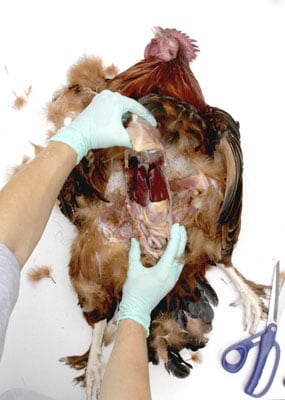 Necropsying A Chicken The Internal Organs Dummies
Necropsying A Chicken The Internal Organs Dummies

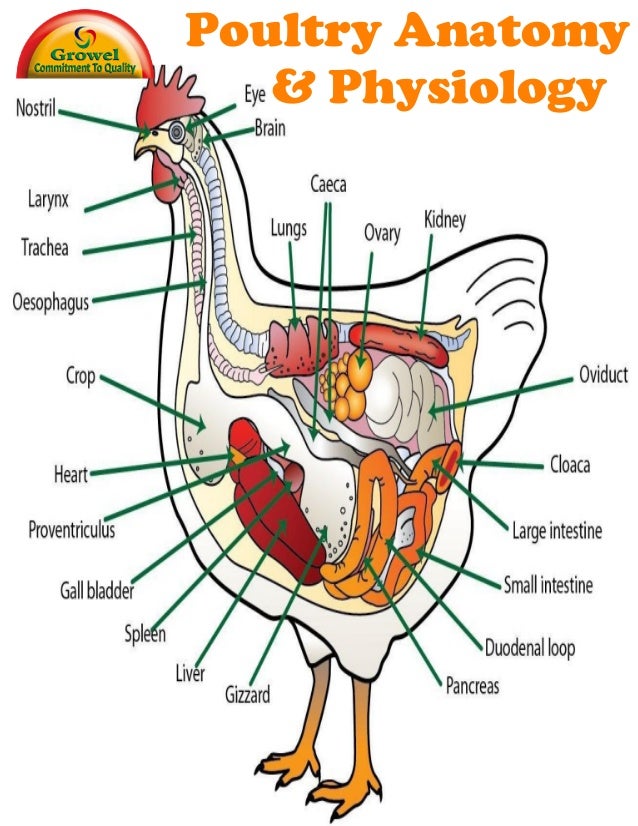

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Internal Anatomy Of Chicken"
Posting Komentar