Dog Ears Anatomy
Beyond the ear flap is the ear canal and the eardrum. Both have an eardrum or tympanic membrane.
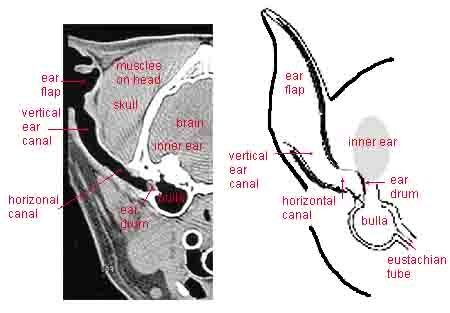 Canine Ear Problems Symptoms Treatment And Cleaning
Canine Ear Problems Symptoms Treatment And Cleaning
It is composed of a cartilage core and skin.

Dog ears anatomy. The anatomy of a dogs ears. The ear is turned parallel to the side of the face not back or forward and pulled to the head. Unlike humans that have a very short ear canal dogs have a long narrow ear canal that makes almost a 90 degree bend as it travels to the deeper parts of the ear.
Moreover associated anatomical bodies such as cartilages nerves vascular supply glands and the ear cavity assists in the normal functioning of ear and helps the body to maintain balance. There are three parts to the ear. Both species also have ossicles or little bones in the inner ear that vibrate and send signals along the auditory nerve to the brain.
In some dogs it is of the floppy variety and in others it is straight or upright. Pinched ears usually happen when a dog is very stressed or fearful. The ear flap is part of the outer ear and stands up tall in some dog breeds or flops over in others.
They can be long short curly or flat. The membranous labyrinth is an interconnected group of fluid filled membranous sacs. Pinched ears are only visible in floppy eared dogs like goldens labs or hounds.
The outer ear middle ear and inner ear. When sound waves hit these layers and the inner ear which is the major functional part of a dogs ear the brain assesses and coordinates the identification of the sound wave. The middle ear includes the eardrum and a small air filled chamber that contains 3 tiny bones.
The outer ear cannel is separated from the middle ear by a thin membrane called the eardrum or tympanic membrane. The inner ear contains the membranous labyrinth which is surrounded by the bony labyrinth. The tail is an extension of the spine so any injuries to the tail can be quite serious.
The fluid is endolymph. Dog tail anatomy the tail of a dog serves many functions such as non verbal communication and as a rudder in water. The tail isnt just something which wags to show you theyre happy it serves a much bigger function.
Ear structure and function in dogs. The anatomy of the middle and inner ear is relatively the same in humans and dogs. Ear anatomy anatomy of the normal dog ear.
It also includes 2 muscles the oval window and the eustachian tube a small tube that connects the middle ear with the back of the nose allowing air to enter. The inner ear is located within the petrous temporal bone. The hammer anvil and stirrup.
This is the external most visual portion of the canine ear.
 How To Draw Animals Dogs And Wolves And Their Anatomy
How To Draw Animals Dogs And Wolves And Their Anatomy
 Dog Behavior And Training Cleaning Ears Vca Animal Hospital
Dog Behavior And Training Cleaning Ears Vca Animal Hospital
How Do I Clean My Dog S Ears Lakes Veterinary Hospital
 Pdf Practical Otic Anatomy And Physiology Of The Dog And Cat
Pdf Practical Otic Anatomy And Physiology Of The Dog And Cat
 Structure Of The Canine Ear Whole Dog Journal
Structure Of The Canine Ear Whole Dog Journal
 Evolution Of Facial Muscle Anatomy In Dogs Pnas
Evolution Of Facial Muscle Anatomy In Dogs Pnas
 6 Easy Dog Ear Cleaning Tips You Should Try
6 Easy Dog Ear Cleaning Tips You Should Try
 Ears 101 Anatomy Hearing Development In Dogs Petcoach
Ears 101 Anatomy Hearing Development In Dogs Petcoach
Cleaning Your Dog S Ears Animal Hospital Of Hasbrouck Heights
 5 Best Dog Ear Cleaners W Free Dog Ear Cleaning Guide
5 Best Dog Ear Cleaners W Free Dog Ear Cleaning Guide
 Ear Nose And Throat Diseases Of The Dog And Cat
Ear Nose And Throat Diseases Of The Dog And Cat
 2019 Ultimate Veterinary Guide To Dog Anatomy With Images
2019 Ultimate Veterinary Guide To Dog Anatomy With Images
 Dog Ear Infection Treament Tips Cimarron Animal Hospital
Dog Ear Infection Treament Tips Cimarron Animal Hospital
Total Ear Canal Ablation Dogs Teca Michigan Ave Animal
 Examining And Medicating The Ears Of Your Dog
Examining And Medicating The Ears Of Your Dog
 Dog Ear Canal Diagram Dog Anatomy Ear Canal Diagram Anatomy
Dog Ear Canal Diagram Dog Anatomy Ear Canal Diagram Anatomy
Cleaning Your Dog S Ears Piney Mountain Foster Care
 5 Best Dog Ear Cleaners In 2019
5 Best Dog Ear Cleaners In 2019
 Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Senses Wikibooks
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Senses Wikibooks
Total Ear Canal Ablation Dogs Teca Michigan Ave Animal
Anatomical Studies Of Canine Vascular And Ligamentous Ear
 Cleaning Your Dogs Ears Canine Ear Diagram Ear Cleaning
Cleaning Your Dogs Ears Canine Ear Diagram Ear Cleaning
 Cleaning Your Dog S Ears Dogtopia
Cleaning Your Dog S Ears Dogtopia
A Beginner S Guide To Ear Anatomy And Physiology

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-clean-your-dogs-ears-1118393_final-4de719c48db14bf591e6d2d9c1002819.gif)


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Dog Ears Anatomy"
Posting Komentar