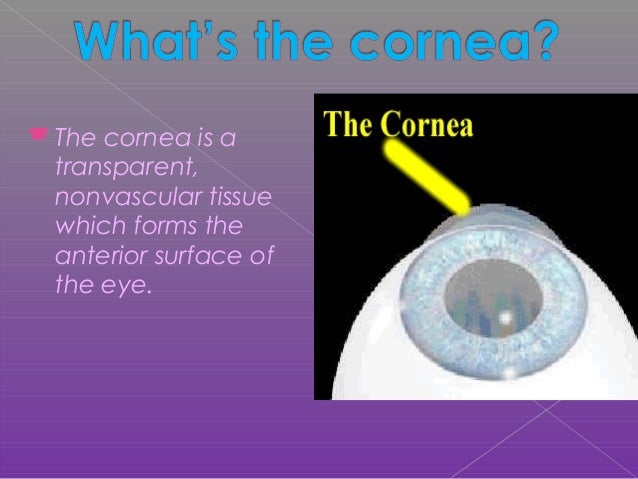
Cornea Anatomy
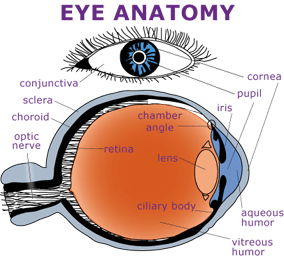
The front part what you see in the mirror includes. Is made up of the cornea and the sclera.
The area where the edge of the cornea meets the conjunctiva and sclera.
Cornea anatomy. The epithelium or outer covering. The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris pupil and anterior chamber. The cornea is 0506 mm thick in the dog and cat and about 1 mm in horses.
The cornea composes the outermost layer of the eye. It covers the pupil the opening at the center of the eye iris the colored part of the eye and anterior chamber the fluid filled inside of the eye. When blood vessels invade the cornea they begin from the limbus.
Yet without its clarity the eye would not be able to perform its necessary functions. A thin layer of tissue that covers the entire front of your eye except. The cornea is the transparent part of the eye that covers the front portion of the eye.
This magnified image of a section of the eye demonstrates the structure of the cornea and the limbus. The stroma or supporting structure. The cornea is a transparent structure that together with the lens provides the refractive power of the eye.
A clear dome over the iris. The black circular opening in the iris that lets light in. With corneal edema the thickness of the cornea can substantially increase in the area of edema.
Part of the undergraduates course of ophthalmology. Please try again later. The cornea with the anterior chamber and lens refracts light with the cornea accounting for approximately two thirds of the eyes total optical power.
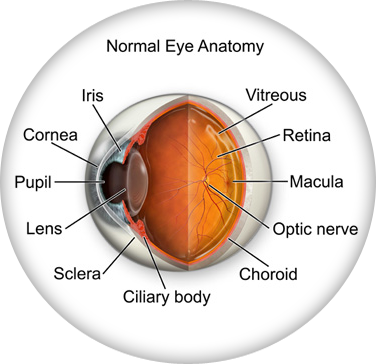
The anatomy and structure of the adult human cornea. The white of your eye. It contains five distinguishable layers.
Corneal anatomy the cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris pupil and anterior chamber. This feature is not available right now. Anchoring fibers type vii collagen penetrate into anterior stroma and attach with anchoring plaques type iv collagen to the stroma and to reticular fibers type iii collagen deep to the basement membrane.
The cornea is the transparent window of the eye. Anatomy and physiology of the cornea. The cornea lacks the neurobiological sophistication of the retina and the dynamic movement of the lens.
Together with the lens the cornea refracts light accounting for approximately two thirds of the eyes total optical power. The complexity of structure and function necessary to maintain such elegant simplicity is the wonder. The corneas main function is to refract or bend light.
And the endothelium or inner lining.
 Keratitis A Clinical Approach Intechopen
Keratitis A Clinical Approach Intechopen
 Vision And The Eye S Anatomy Healthengine Blog
Vision And The Eye S Anatomy Healthengine Blog
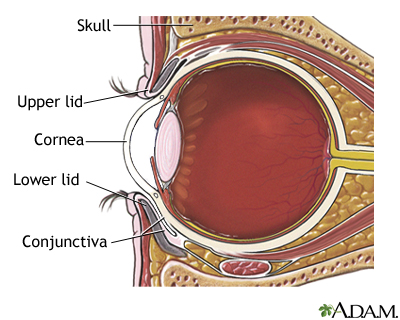
 Anatomy Of The Eye Kellogg Eye Center Michigan Medicine
Anatomy Of The Eye Kellogg Eye Center Michigan Medicine
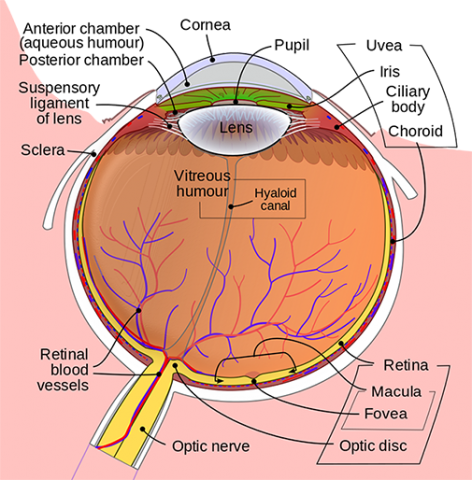
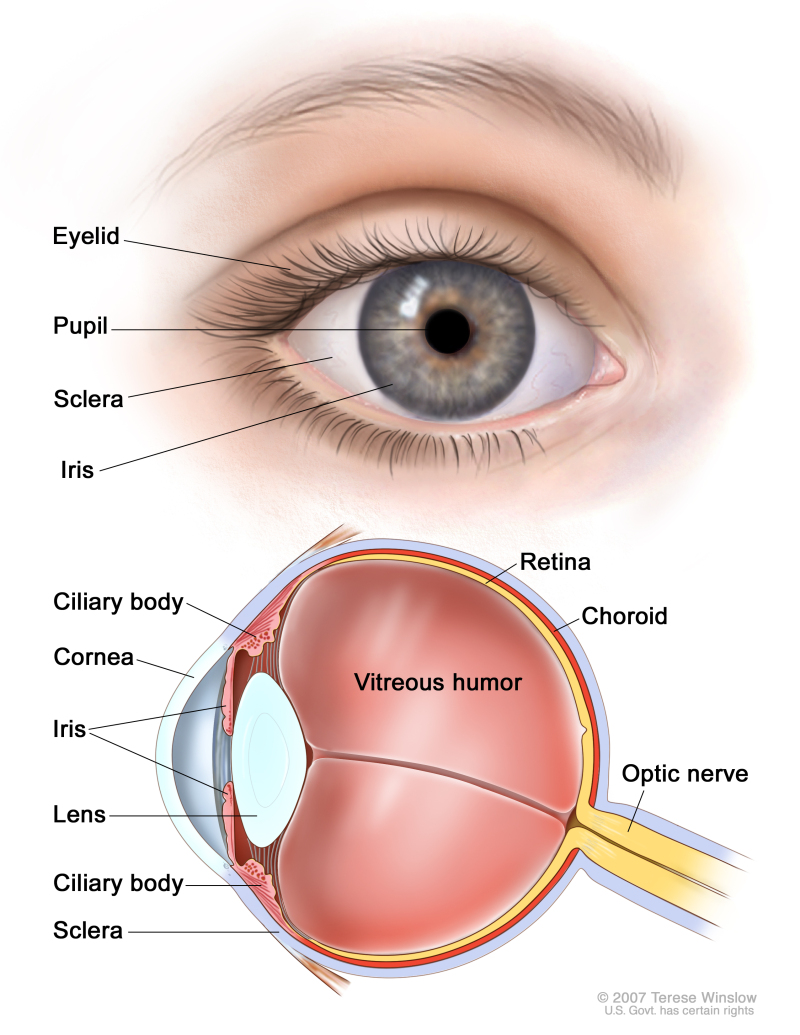 Figure Anatomy Of The Eye Showing Pdq Cancer
Figure Anatomy Of The Eye Showing Pdq Cancer
 Anatomy Of The Eye Hummel Eye Associates Oklahoma City
Anatomy Of The Eye Hummel Eye Associates Oklahoma City
Optimed Eye And Laser Clinic Anatomy The Cornea The
 Amazon Com Ambesonne Educational License Plate Human Eye
Amazon Com Ambesonne Educational License Plate Human Eye
 Eye Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Eye Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
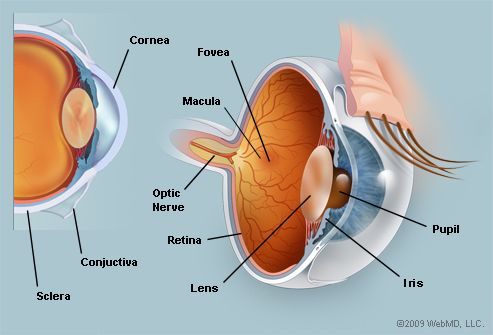 The Eyes Human Anatomy Diagram Optic Nerve Iris Cornea
The Eyes Human Anatomy Diagram Optic Nerve Iris Cornea
Eye In Cross Section Anatomy The Eyes Have It
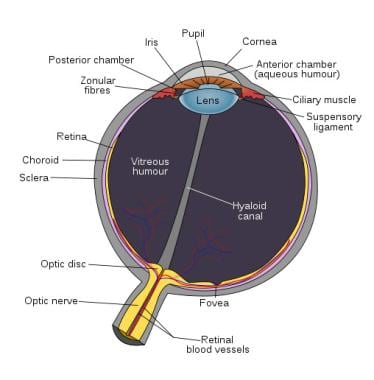 Bacterial Keratitis Background Pathophysiology Epidemiology
Bacterial Keratitis Background Pathophysiology Epidemiology
 The Cornea And Its Highlights Part 2 Anatomy Of The
The Cornea And Its Highlights Part 2 Anatomy Of The
Cornea Anatomy Functions Linkocare
The Anatomy Of The Eye Anterior Segment Precision Family
 The Anatomy And Physiology Of Cornea Download Scientific
The Anatomy And Physiology Of Cornea Download Scientific
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Cornea Sciencedirect
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Cornea Sciencedirect
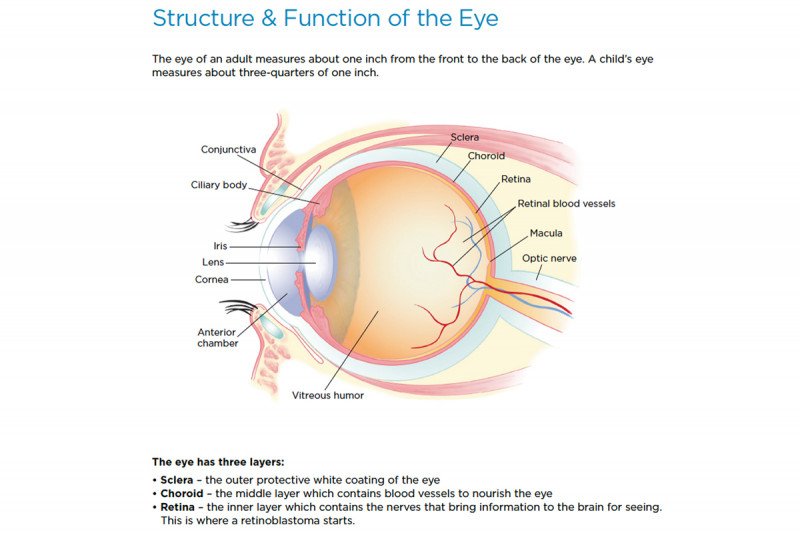 Retinoblastoma Anatomy Of The Eye Memorial Sloan
Retinoblastoma Anatomy Of The Eye Memorial Sloan
 Anatomy Of The Cornea A Section Of The Anterior Part Of
Anatomy Of The Cornea A Section Of The Anterior Part Of
 Eye Conditions Florida Eye Clinic
Eye Conditions Florida Eye Clinic
The Anatomy And Structure Of The Adult Human Cornea
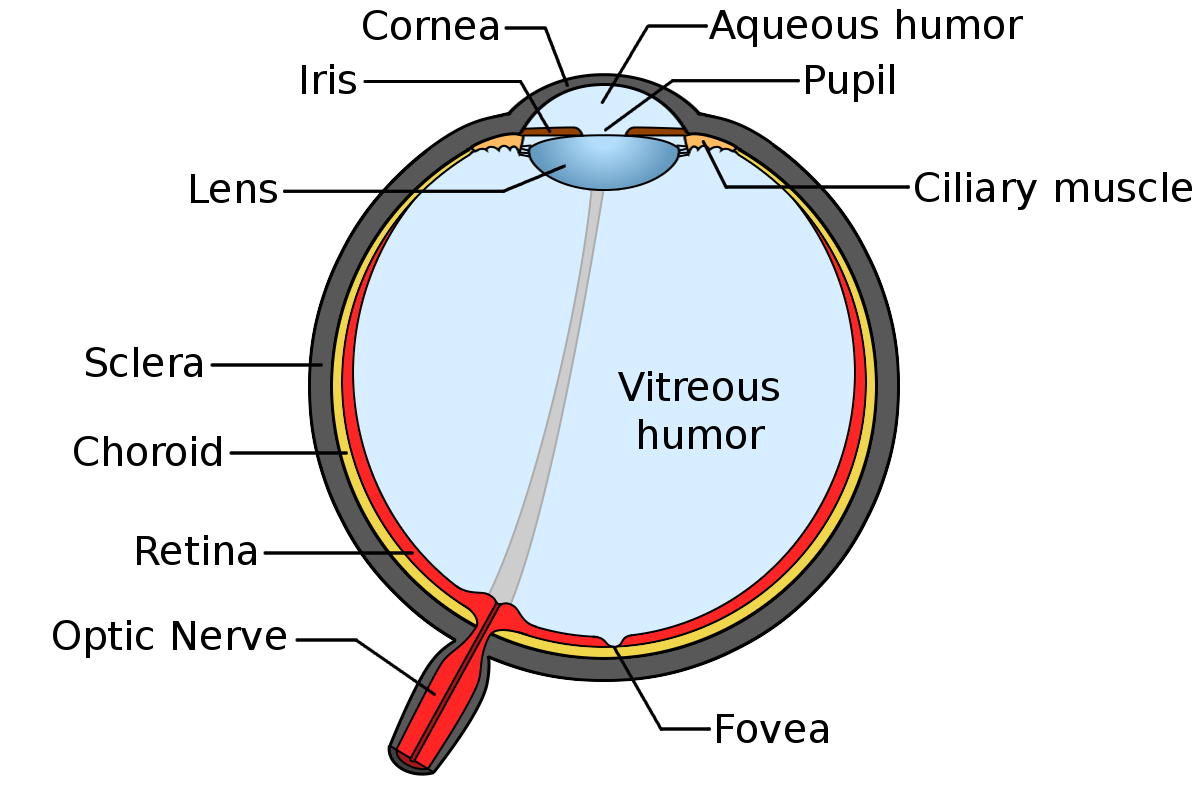 Are There Any Parts Of The Human Body That Get Oxygen
Are There Any Parts Of The Human Body That Get Oxygen
 Cornea Definition And Detailed Illustration
Cornea Definition And Detailed Illustration
 Royalty Free Cornea Anatomy Stock Images Photos Vectors
Royalty Free Cornea Anatomy Stock Images Photos Vectors
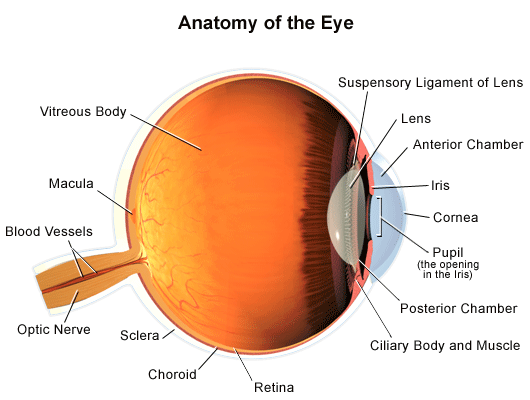


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Cornea Anatomy"
Posting Komentar