Insertion In Anatomy
Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. The opposite end of the muscle is called the origin.
 The Muscular System Origin Insertion Function Anatomy Unit
The Muscular System Origin Insertion Function Anatomy Unit
The first symptom is usually ptosis drooping eyelids.
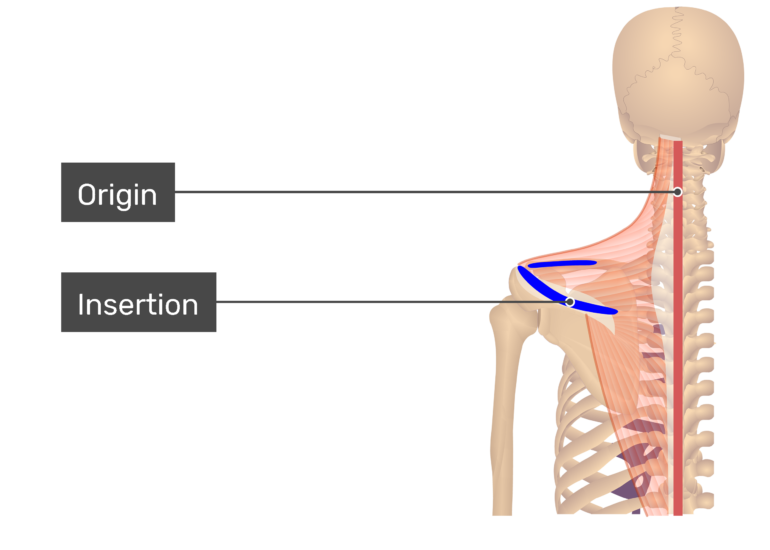
Insertion in anatomy. Genetics the addition as by mutation of one or more nucleotides to a chromosome. Conversely you can say the elbow is proximal to the wrist. The origin is the other point of attachment but it is usually more of an anchoring point than a point of movement.
In anatomy an insertion describes the point of attachment in a muscle where more movement occurs. Origin and insertion are two ends of a muscle that attach to a bone. Insertions are usually connections of muscle via tendon to bone.
The insertion of a muscle is the structure that it attaches to and tends to be moved by the contraction of the muscle. Origin is closer to the centre of the body while insertion is furthest to the centre of the body. Angle of mouth and upper lip.
An insertion is the point at which a muscle attaches to the skin a bone or another muscle. The act or process of inserting. Insert insertion the latin elements in and serere to join plant are part of insert and insertion.
The immune system seems to attack the neuromuscular junctions. Origin is the attachment end to the immovable bone while insertion is the attachment end to a more movable bone. The insertion attaches to the structure that will be moved by the contraction of the muscle.
Weakness in the jaw muscle will continue to the point where the patient cannot move their jaw. Elevates corners of mouth and lips. Muscular weakness due to a malfunction of the immune system.
So this is the key difference between origin and insertion. Anatomy muscles origin and insertion. Muscular contraction produces an action or a movement of the appendage.
For example one could say the wrist is distal to the elbow. Insertions are usually connections of muscle via tendon to bone. The insertion is usually distal or further away while the origin is proximal or closer to the body relative to the insertion.
This may be a bone a tendon or the subcutaneous dermal connective tissue.
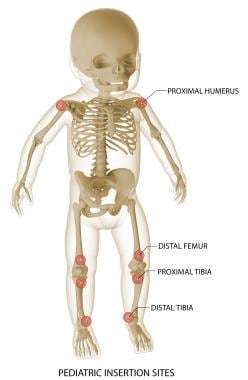 Intraosseous Cannulation Background Anatomy And
Intraosseous Cannulation Background Anatomy And
 Muscle Origin Insertion Complete Anatomy
Muscle Origin Insertion Complete Anatomy
 Muscle Anatomy Of The Peroneus Longus
Muscle Anatomy Of The Peroneus Longus
 Muscles Of The Arm Origin Insertion Innervation Human Anatomy Kenhub
Muscles Of The Arm Origin Insertion Innervation Human Anatomy Kenhub
 What Is An Insertion In Anatomy Education Seattle Pi
What Is An Insertion In Anatomy Education Seattle Pi
 Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Origin And Insertion Google Search
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Origin And Insertion Google Search
 Anatomy Of Greater Trochanter With Tendinous Insertion Sites
Anatomy Of Greater Trochanter With Tendinous Insertion Sites
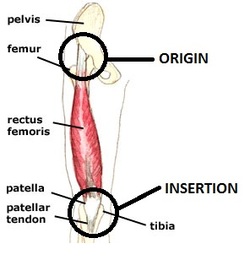 The Origin And Insertion Of Muscles Corewalking
The Origin And Insertion Of Muscles Corewalking
 Flexor Carpi Radialis Anatomy Origin Insertion Action
Flexor Carpi Radialis Anatomy Origin Insertion Action
 090 The Deltoideus Muscle Origin Insertion And Action
090 The Deltoideus Muscle Origin Insertion And Action
 Axis Scientific Mini Human Skeleton Model With Metal Stand 31 Tall With Removable Arms And Legs Painted And Numbered Muscle Insertion And Origin
Axis Scientific Mini Human Skeleton Model With Metal Stand 31 Tall With Removable Arms And Legs Painted And Numbered Muscle Insertion And Origin
 Muscles Origin And Insertion Lower Limb Muscle Origin And
Muscles Origin And Insertion Lower Limb Muscle Origin And
 Shoulder Subscapularis Muscle Origin And Insertion Scapula
Shoulder Subscapularis Muscle Origin And Insertion Scapula
 Adductor Brevis Origin And Insertion Google Search
Adductor Brevis Origin And Insertion Google Search
 Distal Biceps Avulsion Shoulder Elbow Orthobullets
Distal Biceps Avulsion Shoulder Elbow Orthobullets
What Is The Difference Between Origin And Insertion Pediaa Com
 L12 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy At University Of Michigan Ann
L12 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy At University Of Michigan Ann
 Supinator Origin Insertion Action Innervation The
Supinator Origin Insertion Action Innervation The
 Upper Trapezius Insertion And Origin Google Search Neck
Upper Trapezius Insertion And Origin Google Search Neck

 Muscle Origin Action Insertion Human Anatomy 35 With
Muscle Origin Action Insertion Human Anatomy 35 With
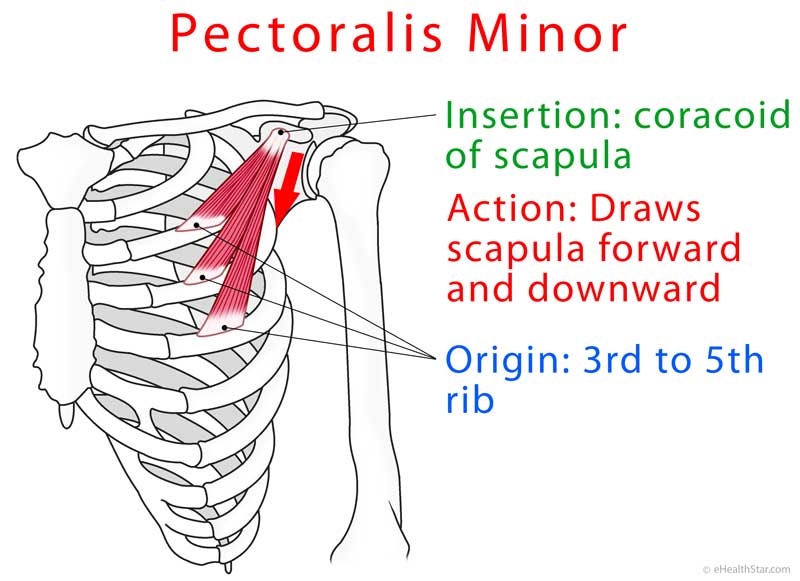 Pectoralis Minor Origin Insertion Action Nursing Anatomy
Pectoralis Minor Origin Insertion Action Nursing Anatomy
Anatomy And Physiology Muscles Location Action Origin And

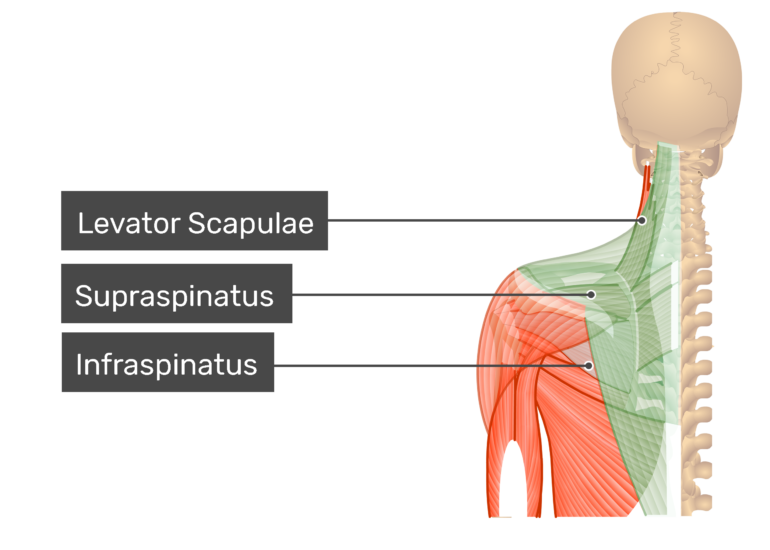


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Insertion In Anatomy"
Posting Komentar