Isotonic Definition Anatomy
In chemistry a solution is said to be isotonic when it has the same concentration of solutes as another solution across a semipermeable membrane. Of a motion in the direction of contraction of a muscle.
The distance between the origin and insertion becomes lessened.
Isotonic definition anatomy. Isotonic definition isotonic is a term used to describe solutions and chemistry and sometimes muscles in human biology. Postural contraction the state of muscular tension and contraction that just suffices to maintain the posture of the body. Isotonic of a fluid that exerts the same osmotic pressure as another especially as that of the body fluids.
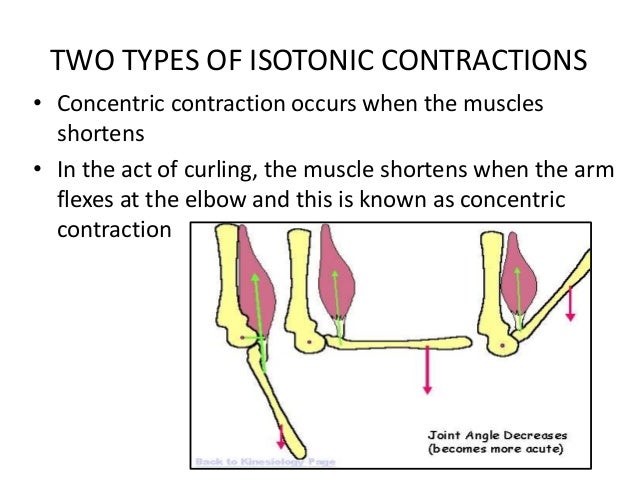
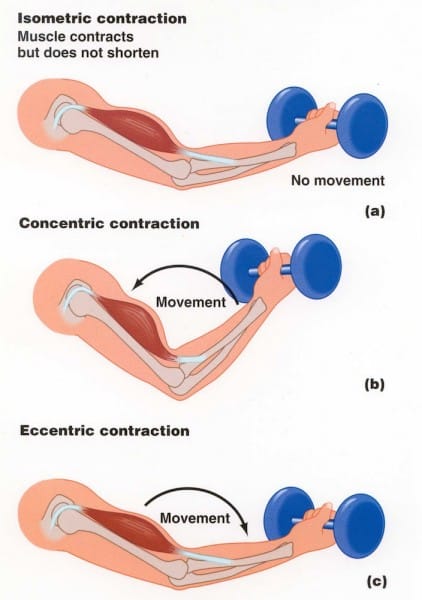
Isotonic exercise is one method of muscular exercise. Isotonic contractions are those where the muscle changes length as it contracts whilst the load or resistance remains the same. Isotonic contraction isotonic literally means same tension where iso means the same and tonic refers to tension or force in this case in the muscle.
As a result this causes movement of a body part. In contrast isometric exercise is when muscular contractions occur without movement of the involved parts of the body. Isotonic movements are either concentric working muscle shortens or eccentric working muscle lengthens.
There are two types of isotonic contraction. Start studying anatomy hypotonic isotonic hypertonic. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Lengthening contraction eccentric contraction. Water moves out of the cells. Of or involving muscular contraction against resistance in which the length of the muscle changes.
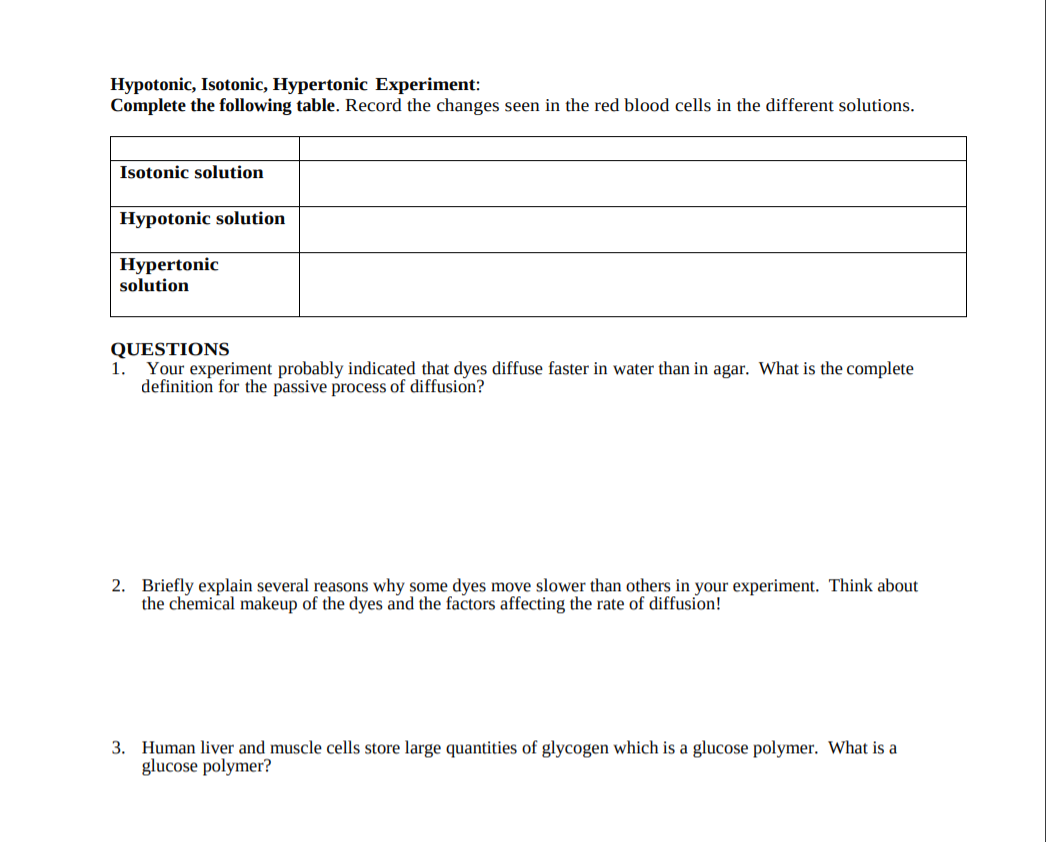
If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. Hypertonic isotonic and hypotonic solutions and their effect on cells. Water enters and exits the cells at the same rate equal solute concentration.
Isotonic contraction muscle contraction without appreciable change in the force of contraction. The outside of the cells have a lower concentration than on the inside which has a higher concentration. Body cells such as red blood cells can be immersed in an isotonic solution without being caused to change shape.
Isotonic comes from the greek iso equal tonos tone maintaining equal muscle tone.
 Study Sheet 1 Review Terms Study Sheet 2 Terminology Quiz
Study Sheet 1 Review Terms Study Sheet 2 Terminology Quiz
 Muscle Twitch And Tetanus Responses Britannica
Muscle Twitch And Tetanus Responses Britannica
 Isotonic Vs Hypotonic Vs Hypertonic Solution Biology
Isotonic Vs Hypotonic Vs Hypertonic Solution Biology
 Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
 Tonicity Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Solutions
Tonicity Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Solutions

 There Are Three Types Of Osmosis Hypotonic Hypertonic And
There Are Three Types Of Osmosis Hypotonic Hypertonic And
 Concentric Eccentric And Isometric Muscle Contractions
Concentric Eccentric And Isometric Muscle Contractions

 Learn What To Study For The Fsmtb Mblex Examination Pocket
Learn What To Study For The Fsmtb Mblex Examination Pocket
 Isotonic Solution Definition Example
Isotonic Solution Definition Example
 Isotonic Solution Definition Example Video Lesson
Isotonic Solution Definition Example Video Lesson
 What Is Isotonic Contraction What Does Isotonic Contraction Mean Issotonic Contraction Meaning
What Is Isotonic Contraction What Does Isotonic Contraction Mean Issotonic Contraction Meaning
 Solved Hypotonic Isotonic Hypertonic Experiment Comple
Solved Hypotonic Isotonic Hypertonic Experiment Comple
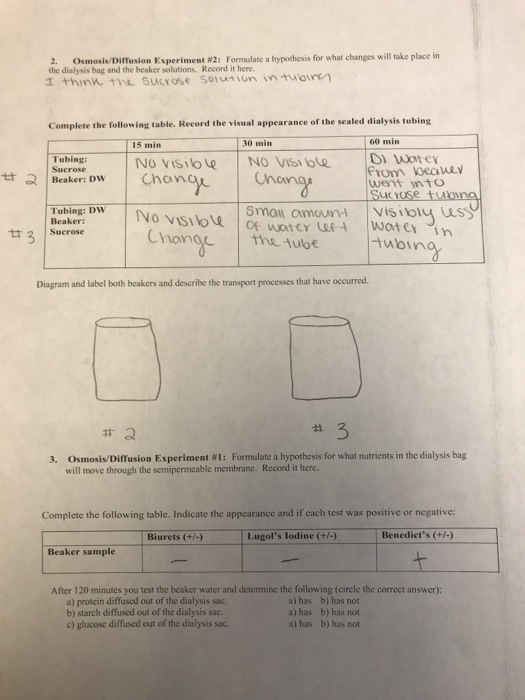
 4celltransport Doc Anatomy 30 Lab 4 Cell Transport
4celltransport Doc Anatomy 30 Lab 4 Cell Transport

Osmotic Solutions Ms Raeon S Biology Website
 Types Of Isotonic Contraction 1 Concentric Tension In
Types Of Isotonic Contraction 1 Concentric Tension In
 Solved Hypotonic Isotonic Hypertonic Experiment Comple
Solved Hypotonic Isotonic Hypertonic Experiment Comple
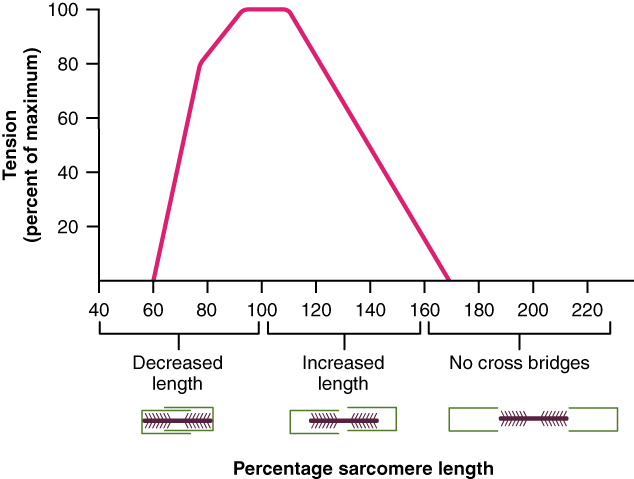 10 4 Nervous System Control Of Muscle Tension Anatomy And
10 4 Nervous System Control Of Muscle Tension Anatomy And
 Types Of Muscle Contraction Isotonic Concentric
Types Of Muscle Contraction Isotonic Concentric
 Tonicity Definition And Quiz Biology Dictionary
Tonicity Definition And Quiz Biology Dictionary
 Types Of Muscle Contraction Isotonic Concentric Eccentric
Types Of Muscle Contraction Isotonic Concentric Eccentric
What Do You Mean By Isotonic And Hypertonic Solution Quora
 Nervous System Control Of Muscle Tension Anatomy And
Nervous System Control Of Muscle Tension Anatomy And
 Isometric And Isotonic Contraction Definition And Examples
Isometric And Isotonic Contraction Definition And Examples
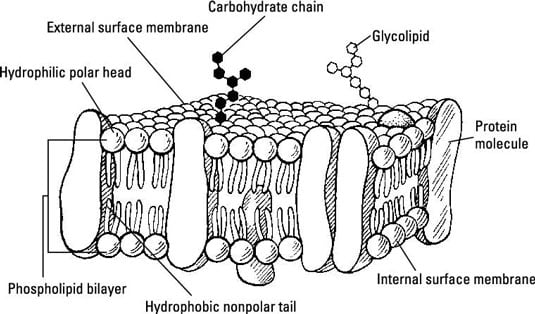 The Cell Membrane Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport
The Cell Membrane Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport
 Clinical Education Intravenous Therapy Skills
Clinical Education Intravenous Therapy Skills
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-85757775-5bbbd5a64cedfd00267868dd.jpg)
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Isotonic Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar