Myosin Definition Anatomy
Myosin binds to actin and slides it pulling 2 lines closer together and reducing the width on the i band spaces between the filaments that is shortened sliding filament mechanism in contracting muscles. Actomyosin a protein complex in muscle fibers.
 10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology
10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology
A threadlike filament of actin or myosin that is a component of a myofibril.
Myosin definition anatomy. This will result in a contraction and expansion movement. Shortens when stimulated and causes muscle contractions. Depicted is a basic illustration of skeletal muscles underlying components down to the sarcomere.
Myosin is a special protein that converts adenosine triphosphate. Each myosin filament is surrounded by six actin filaments. A globular protein present in muscle and in nonmuscle cells that has an atpase activity.
Myosin the commonest protein in muscle. Any of the ultramicroscopic filaments made up of actin and myosin that are the structural units of a myofibril. Myosin filament one of the contractile elements in skeletal cardiac and smooth muscle fibers.
Myosin and the protein actin form the contractile units sarcomeres of skeletal muscle. Mīə sĭn a protein found in muscle tissue as a thick filament made up of an aggregate of similar proteins. Myosin is a motor molecule that works to move the cell.
Myosin filament one of the thick contractile filaments in a myofibril composed mainly of myosin. In combination with actin it forms actomyosin. Myofibril definition a myofibril is a component of the animal skeletal muscle.
Globulin a family of proteins found in blood and milk and muscle and in plant seed. In the sarcomere actin and myosin filaments slide past each other to cause the shortening of a muscle fiber. Size of the filament actin.
It works closely with a globular protein called actin that polymerizes to create actin filaments. Myosin forms the thick filaments in muscle. Myofibrils are long filaments that run parallel to each other to form muscle my.
Composed of myosin and actin. In skeletal muscle the filament is about 15 nm thick and 15 mcm long. Myosin refers to a protein that forms the thick contractile filaments in muscle cells.
Myosin is a thick fiber with a globular head and actin is a thinner filament that interacts with myosin when we flex. A globulin that combines with actin to form actomyosin. Actin forms a thin 0005 μm short 2 26 μm filament.
 Human Muscle Cell Types Interactive Anatomy Guide
Human Muscle Cell Types Interactive Anatomy Guide
 The Anatomy Of Myosin Ii A Basic Domain Structure Of A
The Anatomy Of Myosin Ii A Basic Domain Structure Of A
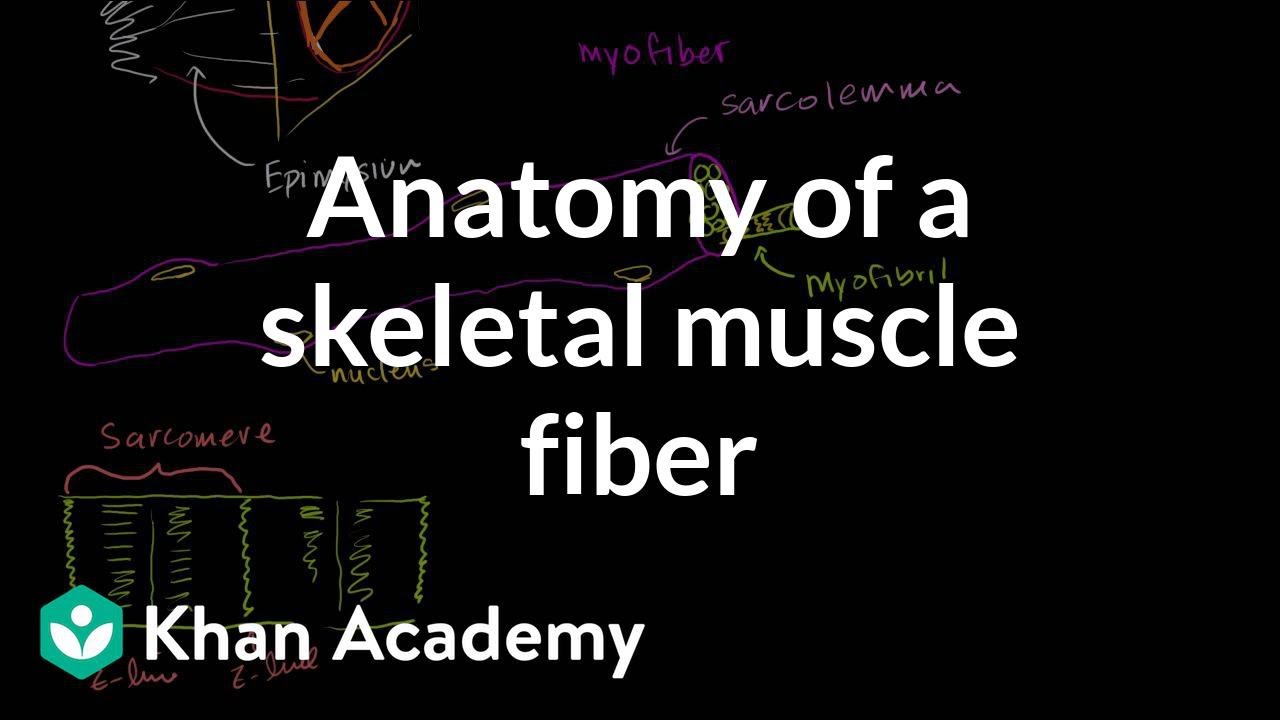 Anatomy Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Video Khan Academy
Anatomy Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Video Khan Academy
 Myosin Light Chain Kinase Wikipedia
Myosin Light Chain Kinase Wikipedia
 Interacting Heads Motif Has Been Conserved As A Mechanism Of
Interacting Heads Motif Has Been Conserved As A Mechanism Of
Mesomechanical Model And Analysis Of An Artificial Muscle
 What Is Axon Guidance And The Growth Cone Mbinfo
What Is Axon Guidance And The Growth Cone Mbinfo
 Myosin Gene Mutation Correlates With Anatomical Changes In
Myosin Gene Mutation Correlates With Anatomical Changes In
 Muscle Biology Physiology Basic Science Orthobullets
Muscle Biology Physiology Basic Science Orthobullets
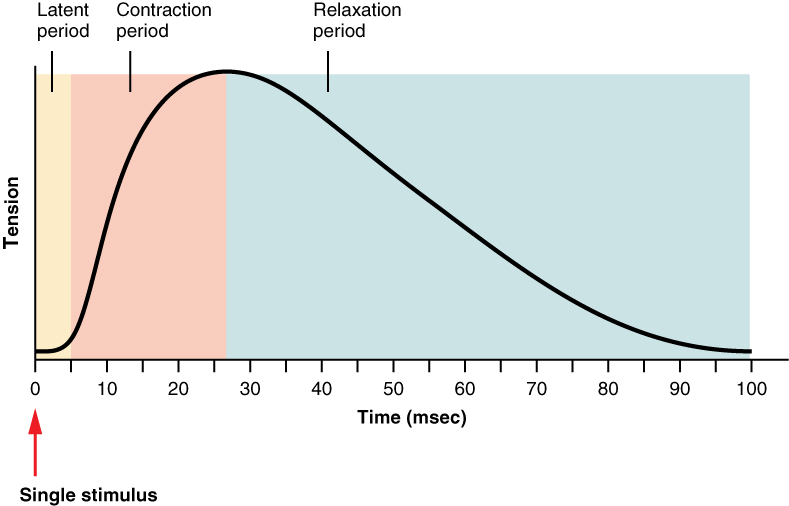 10 4 Nervous System Control Of Muscle Tension Anatomy And
10 4 Nervous System Control Of Muscle Tension Anatomy And
 Muscle Fiber Type Diversity Revealed By Anti Myosin Heavy
Muscle Fiber Type Diversity Revealed By Anti Myosin Heavy
 Muscle Contraction Actin And Myosin Bonding Video
Muscle Contraction Actin And Myosin Bonding Video
 Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Theory Teachpe Com
Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Theory Teachpe Com
 Muscle Anatomy Structure Jen Reviews
Muscle Anatomy Structure Jen Reviews
 Bio 101 Simons Human Biology Part 1 Lecture Notes
Bio 101 Simons Human Biology Part 1 Lecture Notes
 Sarcomere Definition Structure Function And Quiz
Sarcomere Definition Structure Function And Quiz
 Skeletal Mybp C Isoforms Tune The Molecular Contractility Of
Skeletal Mybp C Isoforms Tune The Molecular Contractility Of
 Ib Sports Exercise And Health Science Sub Topics Anatomy
Ib Sports Exercise And Health Science Sub Topics Anatomy
 Muscle Tissue Term Definition Types Of Muscle Tissue
Muscle Tissue Term Definition Types Of Muscle Tissue
 Muscle Contraction Actin And Myosin Bonding Video
Muscle Contraction Actin And Myosin Bonding Video
 Anatomy And Physiology Test 3 At Camden County College
Anatomy And Physiology Test 3 At Camden County College
 Sliding Filament Model Of Contraction Biology For Majors Ii
Sliding Filament Model Of Contraction Biology For Majors Ii
 Sliding Filament Theory Sarcomere Muscle Contraction
Sliding Filament Theory Sarcomere Muscle Contraction
 Structure Of The Rigor Actin Tropomyosin Myosin Complex Cell
Structure Of The Rigor Actin Tropomyosin Myosin Complex Cell
 Muscular Contraction Cross Bridge Formation
Muscular Contraction Cross Bridge Formation
 6 Anatomy Of A Muscle Fiber Muscle Cell Actin And Myosin
6 Anatomy Of A Muscle Fiber Muscle Cell Actin And Myosin
 Myofibril Definition Function And Structure Biology
Myofibril Definition Function And Structure Biology
 Sarcomere An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Sarcomere An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7006/Muscles.png) Muscles And Muscle Tissue Types And Functions Kenhub
Muscles And Muscle Tissue Types And Functions Kenhub
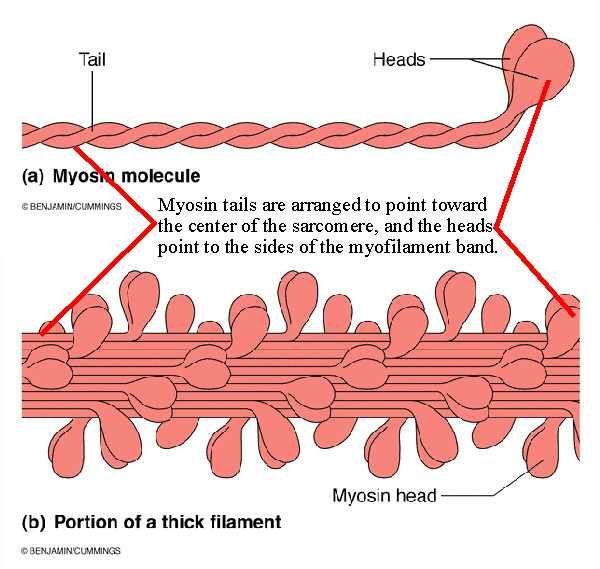 Biol 237 Class Notes Muscle Cells Muscle Physiology
Biol 237 Class Notes Muscle Cells Muscle Physiology



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Myosin Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar