Arm Venous Anatomy
Upper arm veins brachial basilic the basilic vein is the larger and is more superficial. As you reach the proximal arm the axillary vein will divide into the basilic and brachial veins.
 Venipuncture Module 1 Anatomy Of The Arm And Vein Location
Venipuncture Module 1 Anatomy Of The Arm And Vein Location
The primary venous return from the arm is through the axillary vein which continues centrally as the subclavian and brachiocephalic innominate veins before emptying into the superior vena cava.
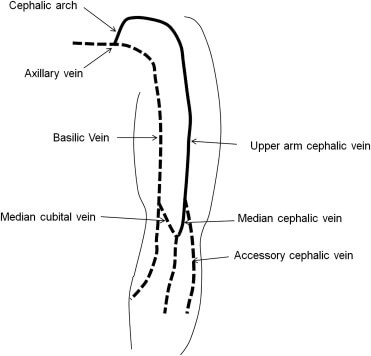
Arm venous anatomy. Continue from the axillary vein checking in transverse that the basilic and brachial veins of the upper arm are compressible. In common usage the arm extends to the hand. Deep veins and superficial veins.
The vessels of the arms are part of the circulatory system which provides nutrients to the tissues. The arteries deliver freshly oxygenated blood to muscles and bone. Each individual hands on training case is accompanied by image window specific expert instruction and probe positioning guidance.
Arm like in the forearm the arm is drained by the brachial veins deep veins that accompany the brachial artery and all its branches. Usually single but may be duplicated. Superficial veins of the upper limb in the cadaver.
In human anatomy the arm is the part of the upper limb between the glenohumeral joint shoulder joint and the elbow joint. In the hand forearm and upper arm the superficial system functions as the principal means for venous drainage. It can anatomically be divided into the superficial veins and the deep veins.
Anatomy physiology module provides a broad spectrum of adult male and female normal anatomy cases with varying body morphologies to maximize training efficacy. In common usage the arm extends to the hand. The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm forearm and hand.
The veins of the arm may be divided into two groups. As a result the caliber of the superficial veins is generally larger than the deep veins. The major superficial veins of the hand forearm and upper arm exist as single structures and infrequently have accessory veins.
Starting around the radial area of what is known as the dorsal venous network the cephalic vein continues towards the upper part of the body in a circular fashion throughout the forearm interacting with tributaries along the way.
 Arm Venous Anatomy Physiology Module Sonosim
Arm Venous Anatomy Physiology Module Sonosim
 Anatomy Of The Nerves Arteries And Veins Of The Arm Upper
Anatomy Of The Nerves Arteries And Veins Of The Arm Upper
 How To Draw Blood Like A Pro Nurse Org
How To Draw Blood Like A Pro Nurse Org
 Venous Hemodynamics What Happens When Flow Is Wrong
Venous Hemodynamics What Happens When Flow Is Wrong
 Clinical Education Intravenous Therapy Skills
Clinical Education Intravenous Therapy Skills
 Anatomy Of The Nerves Arteries And Veins Of The Arm Upper
Anatomy Of The Nerves Arteries And Veins Of The Arm Upper
 Us Iv Technique Proceduralist Org
Us Iv Technique Proceduralist Org
 Human Being Anatomy Blood Circulation Principal
Human Being Anatomy Blood Circulation Principal
 Anatomy 101 Arteries Of The Arm The Handcare Blog
Anatomy 101 Arteries Of The Arm The Handcare Blog
 Anatomy Atlases Anatomy Of First Aid A Case Study Approach
Anatomy Atlases Anatomy Of First Aid A Case Study Approach
 What Is A Vein Definition Types And Illustration
What Is A Vein Definition Types And Illustration
 Catheter Interventions For Hemodialysis Fistulas And Grafts
Catheter Interventions For Hemodialysis Fistulas And Grafts
 Basilic Vein An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Basilic Vein An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Brachial Vein Anatomy Course Tributaries Kenhub
Brachial Vein Anatomy Course Tributaries Kenhub
 Superficial Veins Of Forearm Mnemonic Epomedicine
Superficial Veins Of Forearm Mnemonic Epomedicine
 Superior Vena Cava And Right Arm Vein Anatomy
Superior Vena Cava And Right Arm Vein Anatomy
 Dentistry And Medicine Blood Supply Venous Drainage
Dentistry And Medicine Blood Supply Venous Drainage
 Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Upper Limb
Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Upper Limb
 Anatomy Of Veins Advanced Vein Care
Anatomy Of Veins Advanced Vein Care
 Chapter 33 Venous And Intraosseous Access In Adults
Chapter 33 Venous And Intraosseous Access In Adults
 Superior Vena Cava And The Azygos System Clinical Anatomy Svc Obstruction Oncology Emergency
Superior Vena Cava And The Azygos System Clinical Anatomy Svc Obstruction Oncology Emergency
 Chapter 54 Peripheral Venous Cutdown Emergency Medicine
Chapter 54 Peripheral Venous Cutdown Emergency Medicine
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Rcemlearning
Deep Vein Thrombosis Rcemlearning
 Catheter Interventions For Hemodialysis Fistulas And Grafts
Catheter Interventions For Hemodialysis Fistulas And Grafts
 Online Cme Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation
Online Cme Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation
 Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
 Anatomy Of Gsv And Ssv With Common Variants Of Ssv Gsv
Anatomy Of Gsv And Ssv With Common Variants Of Ssv Gsv
 Venous Drainage Of The Upper Limb Basilic Cephalic
Venous Drainage Of The Upper Limb Basilic Cephalic

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Arm Venous Anatomy"
Posting Komentar