Pelvic Anatomy Muscles
Deep urogenital diaphragm layer. They form a large sheet of skeletal muscle that is thicker in some areas than in others.
The pelvic girdle is formed by a single hip bone.
Pelvic anatomy muscles. They support the pelvic organs especially during increases in intra abdominal pressure and also aid in urinary and faecal continence. Innervated by sacral nerve roots s3 s5. Anterior pubic bodies of the pelvic bones.
This muscle is responsible for holding in urine and feces. They form a large sheet of skeletal muscle that is thicker in some areas than in others. The muscles of the pelvis form its floor.
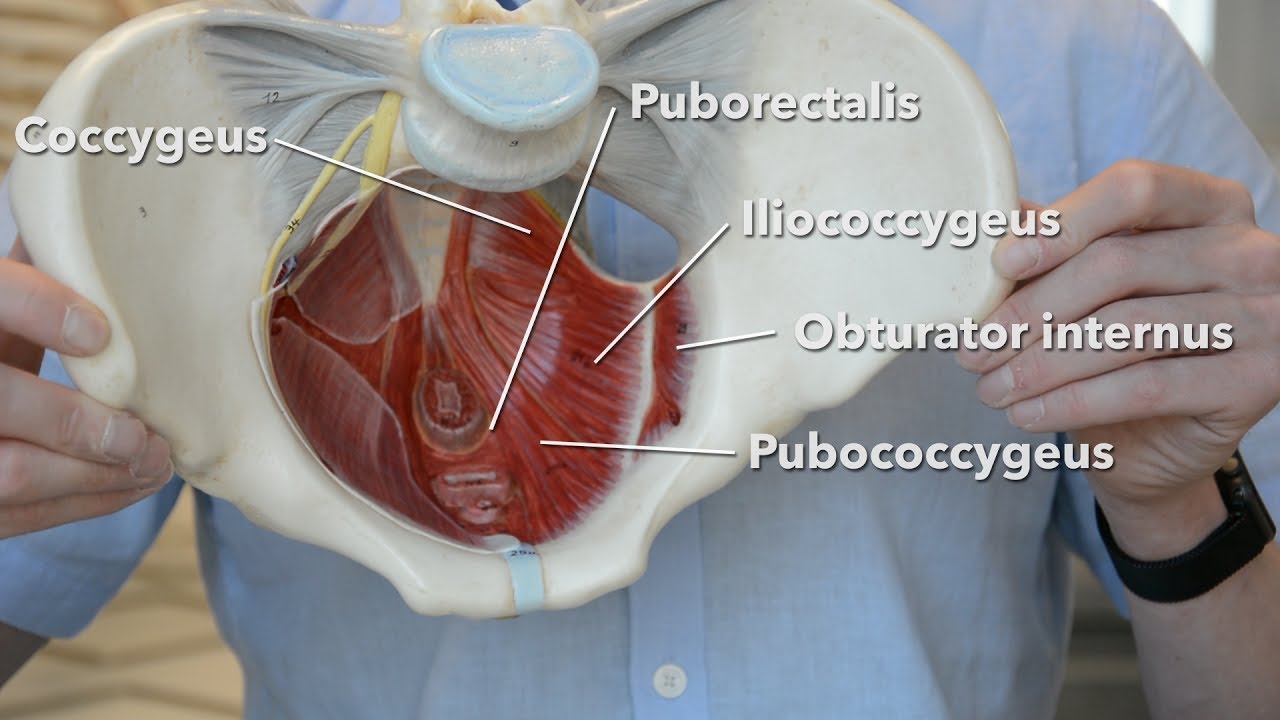
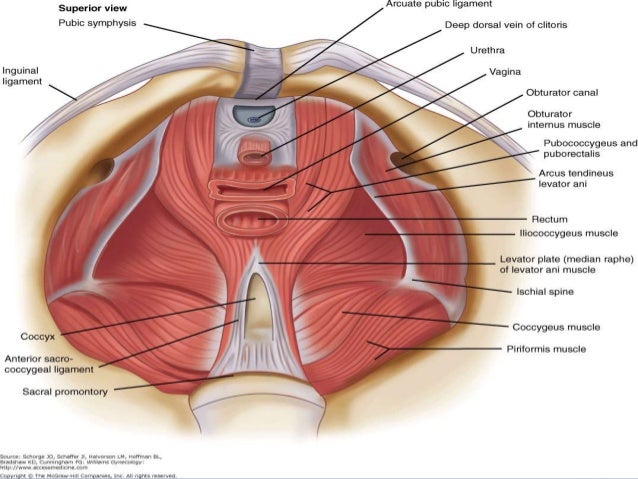
It is enervated by the nerve to the obturator internus. The iliococcygeus has thinner fibers and serves to lift the pelvic floor as well as. Innervated by the pudendal nerve.
The right and left hip bones plus the sacrum and the coccyx together form the pelvis. Lying exposed between the protective bones of the superiorly located ribs and the inferiorly located pelvic girdle the muscles of this region play a critical role in protecting the delicate vital organs within the abdominal cavity. There are many muscles that form the pelvic floor including puborectalis pubococcygeus iliococcygeus and coccygeus.
The hip bone attaches the lower limb to the axial skeleton through its articulation with the sacrum. It originates from the ilium and ischium. Posteriorly ischial spines of the pevlic bones.
This muscle makes up most of the levator ani muscles. The pelvic floor consists of three muscle layers. There are many organs that sit in the pelvis including much of the urinary system and lots of the male or female reproductive systems.
Innervated by pudendal nerve. Laterally thickened fascia of the obturator internus muscle known as the tendinous arch. The skin tissues and organs in the pelvis are supplied by the vasculature of the pelvis and innervated by many nerves of the pelvis including the pudendal nerve.
The floor of the pelvis is made up of the muscles of the pelvis which support its contents and maintain urinary and faecal continence. Female pelvis muscles puborectalis. The muscles of the pelvic floor are collectively referred to as the levator ani and coccygeus muscles.
These muscles have attachments to the pelvis as follows. This muscle forms most of the lateral wall of the pelvis and traverses through the lesser sciatic foramen attaching to the greater trochanter of the femur. The muscles of the abdomen lower back and pelvis are separated from those of the chest by the muscular wall of the diaphragm the critical breathing muscle.
 Appendicular Muscles Of The Pelvic Girdle And Lower Limbs
Appendicular Muscles Of The Pelvic Girdle And Lower Limbs
 The Ultimate Pelvic Anatomy Resource Pelvic Guru Featured
The Ultimate Pelvic Anatomy Resource Pelvic Guru Featured
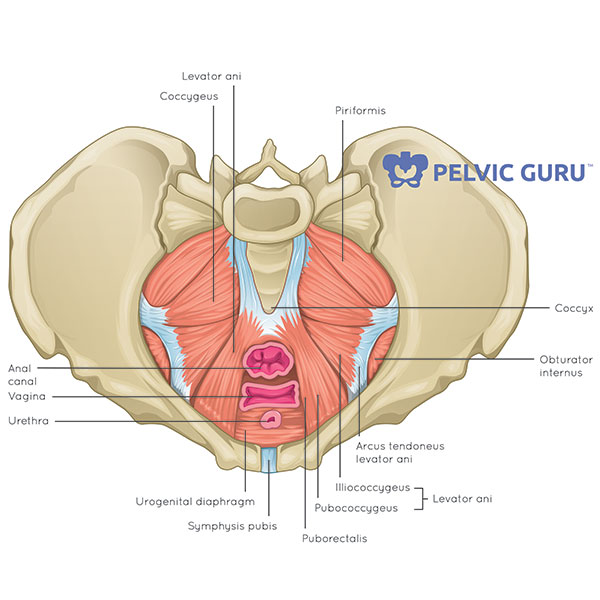 What Is The Pelvic Floor Your Pace Yoga
What Is The Pelvic Floor Your Pace Yoga
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Cleveland Clinic
 Anatomical Model Showing The Human Pelvis Muscles Stock
Anatomical Model Showing The Human Pelvis Muscles Stock
 Pelvic Rehab Therapy Help For Uncomfortable Postpartum
Pelvic Rehab Therapy Help For Uncomfortable Postpartum
 Anatomy Lesson 1 What Is Your Pelvic Floor Wisconsin
Anatomy Lesson 1 What Is Your Pelvic Floor Wisconsin
 About Your Bladder The Facts Continence Foundation Of
About Your Bladder The Facts Continence Foundation Of
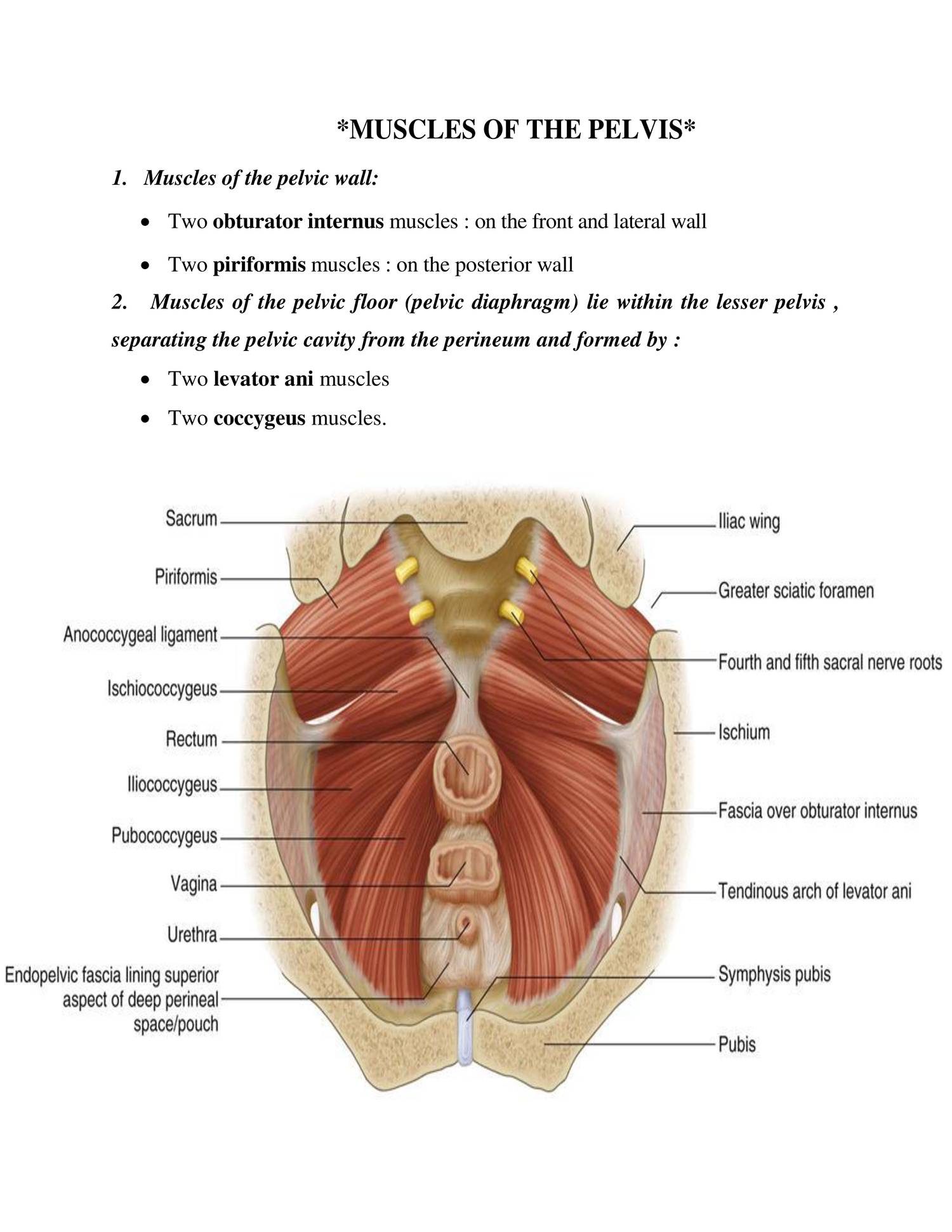 Anatomy Muscles Of Pelvis Doc Docdroid
Anatomy Muscles Of Pelvis Doc Docdroid
 Pelvic Floor Muscles The Base For All Movement Anatomy
Pelvic Floor Muscles The Base For All Movement Anatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/447/cKqKyPqIrfdkM7JgFJ6LkQ_pelvic-floor-muscles_english.jpg) Diagram Pictures Muscles Of The Pelvic Floor Anatomy
Diagram Pictures Muscles Of The Pelvic Floor Anatomy
 Understand Hip Anatomy Muscles For Yoga Jason Crandell Yoga
Understand Hip Anatomy Muscles For Yoga Jason Crandell Yoga
 Amazon Com Anatomy Muscle Pelvis Anus Print Sra3 12x18
Amazon Com Anatomy Muscle Pelvis Anus Print Sra3 12x18
When Getting Hard Is Hard How Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy
Pelvic Cavity Anatomy Www Urology Textbook Com
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/250/Q8w9Sngwp39p33kteitWSQ_female-pelvic-viscera-and-perineum_english.jpg) Muscles Of The Pelvic Floor Anatomy And Function Kenhub
Muscles Of The Pelvic Floor Anatomy And Function Kenhub
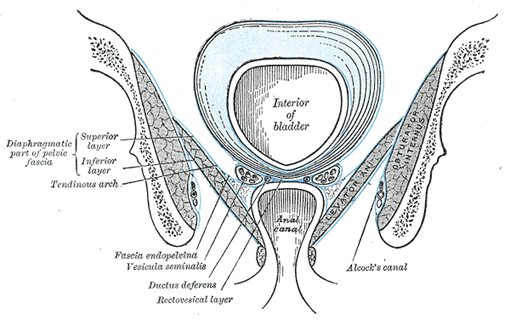 The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Pelvis Human Anatomy
The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Pelvis Human Anatomy
 Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
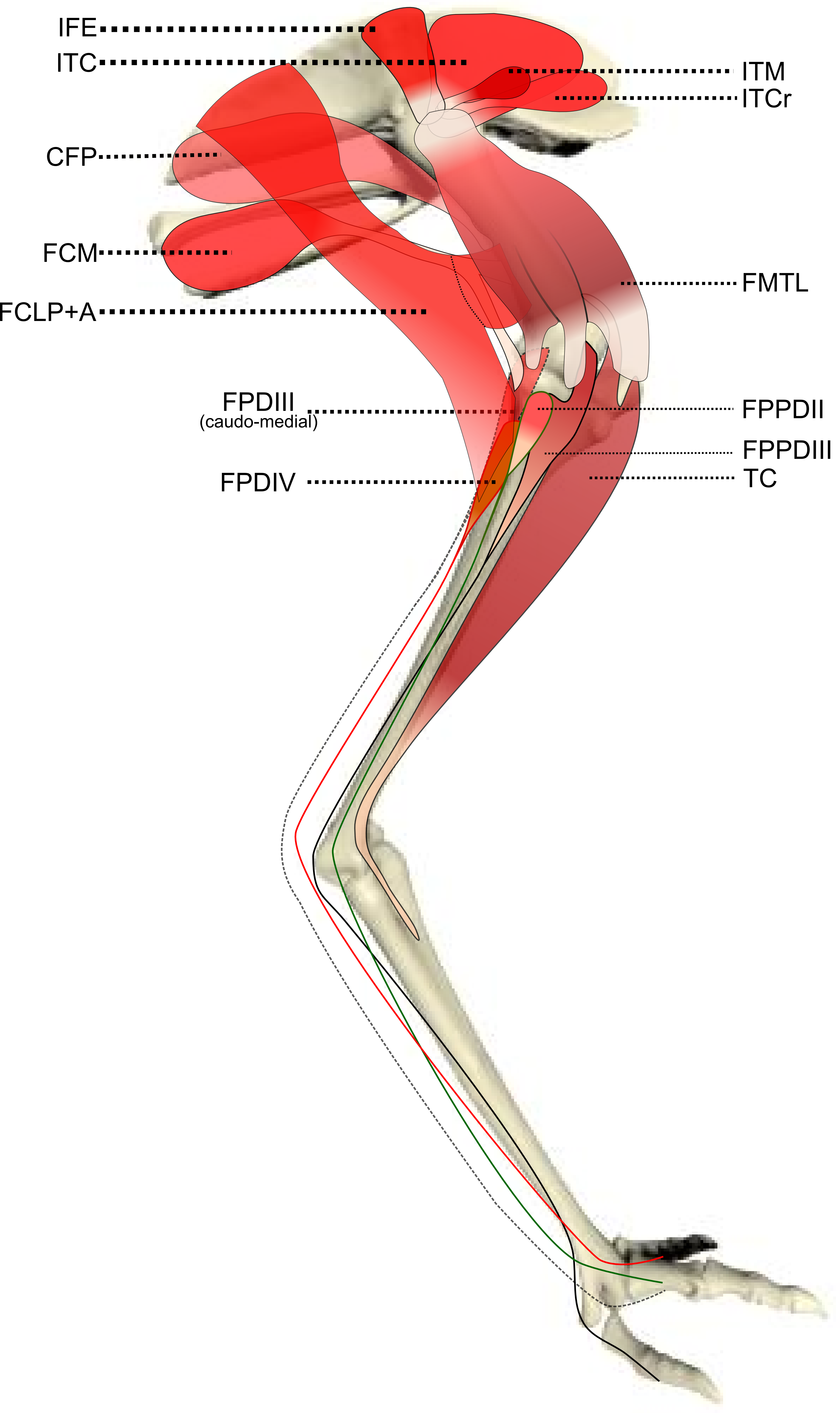 Ontogenetic Scaling Patterns And Functional Anatomy Of The
Ontogenetic Scaling Patterns And Functional Anatomy Of The
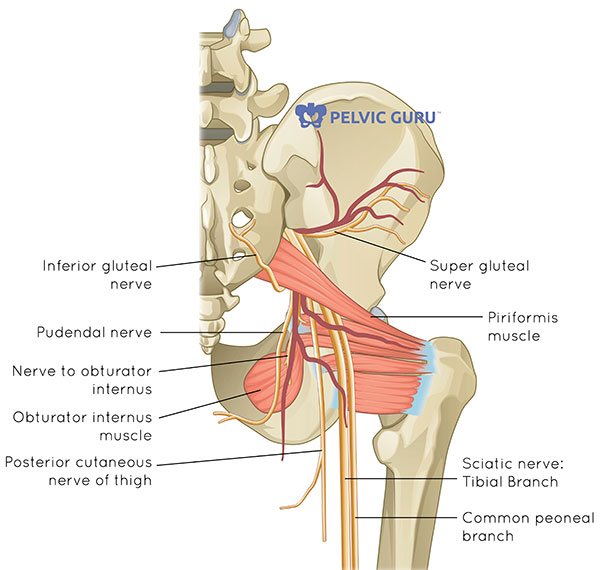 What Is The Pelvic Floor Your Pace Yoga
What Is The Pelvic Floor Your Pace Yoga
 Pelvic Floor Muscles The Facts Continence Foundation Of
Pelvic Floor Muscles The Facts Continence Foundation Of
 Female Pelvis With Detachable Pelvic Floor Muscles 12 Part
Female Pelvis With Detachable Pelvic Floor Muscles 12 Part
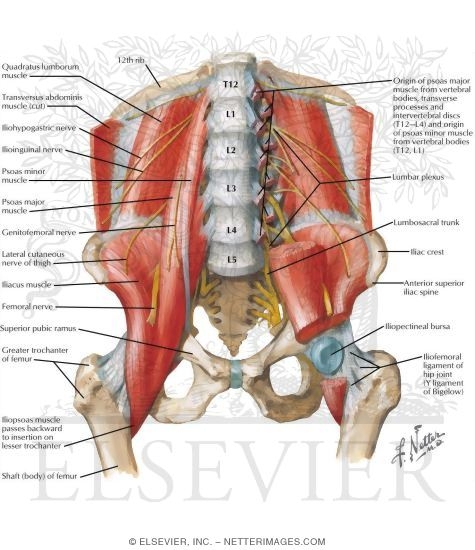 Anterior Muscles Of The Pelvis
Anterior Muscles Of The Pelvis

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Pelvic Anatomy Muscles"
Posting Komentar