Fossa In Anatomy
Cerebral fossa any of the depressions on the floor of the cranial cavity. When it is lateral to the humerus it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum as it moves into the forearm anterior to the lateral epicondyle between the brachialis and brachioradialis.
 The Forehead And Temporal Fossa Anatomy And Technique
The Forehead And Temporal Fossa Anatomy And Technique
Fossa a concavity in a surface especially an anatomical depression pit.

Fossa in anatomy. Arm and cubital fossa. Superior border hypothetical line between the epicondyles of the humerus. The popliteal fossa is 25 cm wide and mainly consists of fat tissue.
Fossa ovalis is one of the most important parts of the cardiovascular system of human since the fetal development until the death. Glenoid cavity glenoid fossa the concavity in the head of the scapula that receives the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint. In anatomy a hollow or depressed area.
Closure of the foramen ovale as the baby grows and starts using the lungs the pressure is created in the foramen ovale causing it to close. Amygdaloid fossa the depression in which the tonsil is lodged. The fossa evolved on the catless island of madagascar where it became the ecological equivalent of a cat.
A trench or channel. Plural fossae ˈfsiː or ˈfsa. Teachme anatomy part of the teachme series the medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes.
From the latin fossa ditch or trench is a depression or hollow usually in a bone such as the hypophyseal fossa the depression in the sphenoid bone. The cubital fossa is triangular in shape and thus has three borders. Blood vessels are located deep to the nerves within the fossa and include.
The superomedial aspect of the popliteal fossa is bounded by the semimembranosus and. Condylar fossa condyloid fossa either of two pits on the lateral portion of the occipital bone. Lateral border medial border of the brachioradialis muscle.
Medial border lateral border of the pronator teres muscle. A slender long tailed carnivorous mammal cryptoprocta ferox of the family eupleridae of madagascar that has retractile claws usually reddish brown or sometimes black short thick fur and anal scent glands. In anatomy a fossa ˈfs.
Descends inferolaterally with the deep artery of the arm in the radial groove between the lateral and medial heads of the triceps.
 Figure Cubital Fossa Image Courtesy S Bhimji Md
Figure Cubital Fossa Image Courtesy S Bhimji Md
 Supraclavicular Fossa Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes Anatomy
Supraclavicular Fossa Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes Anatomy
 Anatomy Of The Right Popliteal Fossa The Dashed Line
Anatomy Of The Right Popliteal Fossa The Dashed Line
 Ischio Rectal Ischio Anal Fossa Anatomy Qa
Ischio Rectal Ischio Anal Fossa Anatomy Qa
 What Is The Difference Between Ridge Process Fossa And
What Is The Difference Between Ridge Process Fossa And
 What Is The Difference Between Ridge Process Fossa And
What Is The Difference Between Ridge Process Fossa And
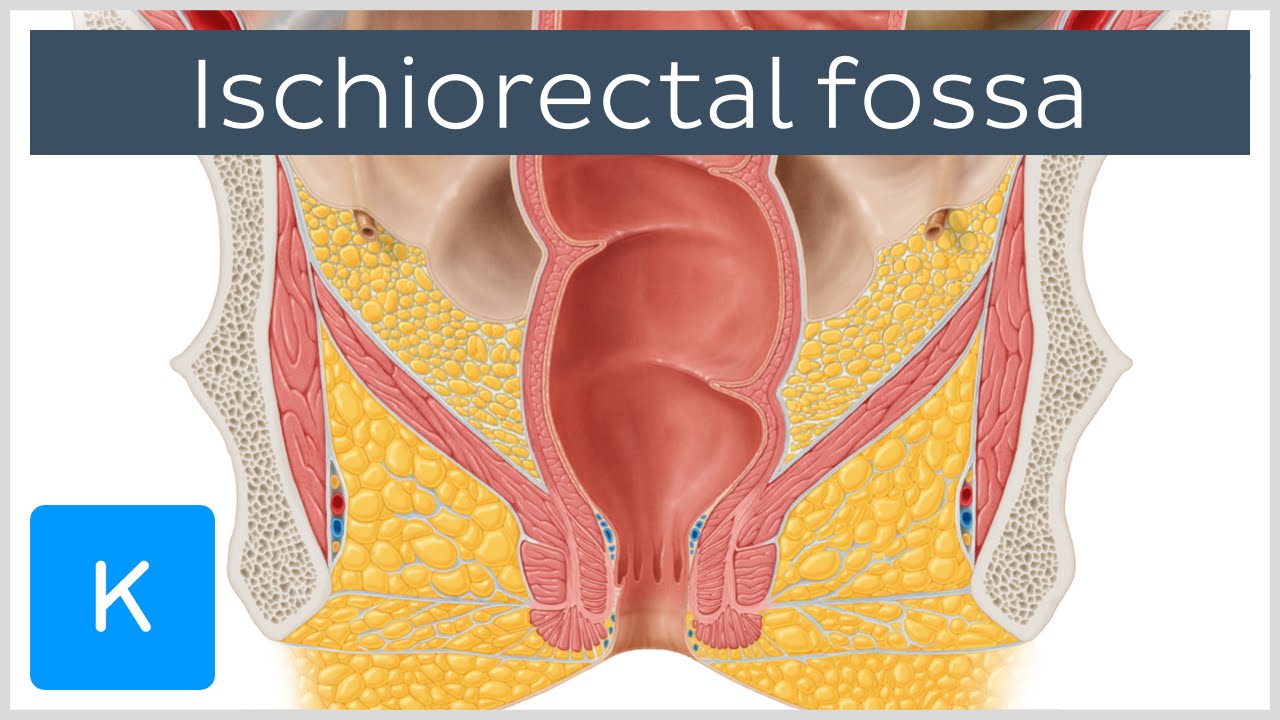 Anatomy Of The Ischiorectal Fossa Human Anatomy Kenhub
Anatomy Of The Ischiorectal Fossa Human Anatomy Kenhub
 Infratemporal Fossa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Infratemporal Fossa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Humerus Bone Anatomy Pictures And Video
Humerus Bone Anatomy Pictures And Video
 Rectum Digestion Gastrointestinal Tract Human Digestive
Rectum Digestion Gastrointestinal Tract Human Digestive
 Ischiorectal Fossa Benign And Malignant Neoplasms Of This
Ischiorectal Fossa Benign And Malignant Neoplasms Of This
 Nasal Fossa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Nasal Fossa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Openings In The Cranial Fossa Skull Anatomy Sphenoid Bone
Openings In The Cranial Fossa Skull Anatomy Sphenoid Bone
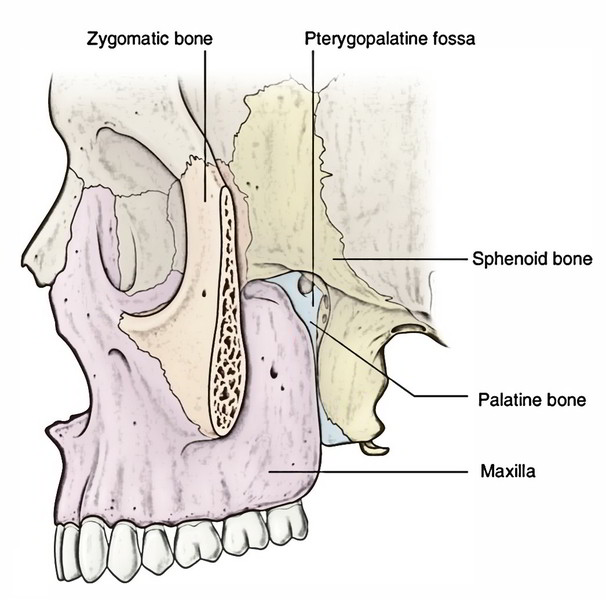 Easy Notes On Pterygopalatine Fossa Learn In Just 3
Easy Notes On Pterygopalatine Fossa Learn In Just 3
 Middle Cranial Fossa Wikipedia
Middle Cranial Fossa Wikipedia
 Popliteal Fossa Anatomy And Posterior View Of The Leg
Popliteal Fossa Anatomy And Posterior View Of The Leg
 Anatomy Of The Posterior Fossa Clinical Gate
Anatomy Of The Posterior Fossa Clinical Gate
 Pterygopalatine Fossa Wikipedia
Pterygopalatine Fossa Wikipedia
 Antecubital Fossa Definition Anatomy
Antecubital Fossa Definition Anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12539/l6iXeJ1PwzYeHdqTrBw_Pterygopalatine_fossa.png) Pterygopalatine Fossa Anatomy Contents And Gateways Kenhub
Pterygopalatine Fossa Anatomy Contents And Gateways Kenhub
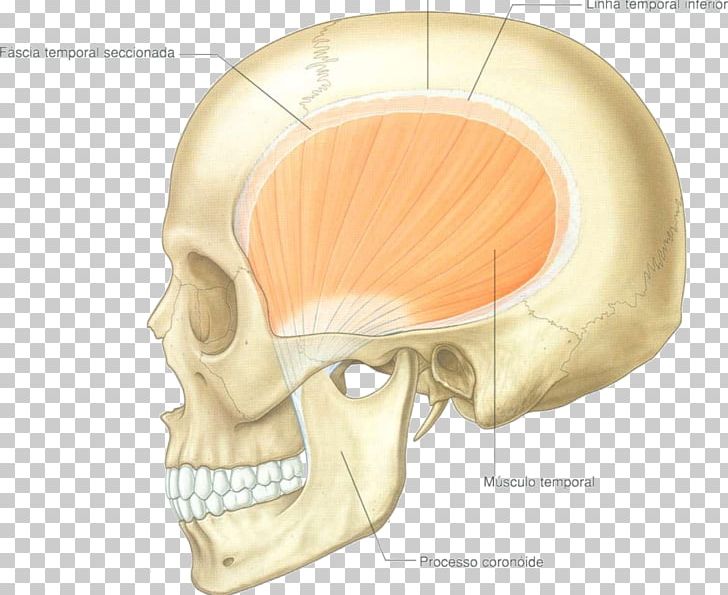 Temporal Muscle Temporal Bone Infratemporal Fossa Anatomy
Temporal Muscle Temporal Bone Infratemporal Fossa Anatomy



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Fossa In Anatomy"
Posting Komentar