Root Anatomy
Root structure aids in this process. Examples of napiform roots include radishes beets turnips and carrots.
Root anatomy the body.

Root anatomy. Therefore the root is best defined as the non leaf non nodes bearing parts of the plants body. Root anatomy microtomy and microscopy anatomy is the study of the structure of living organisms while morphology is the study of an organisms form and the development of that form. Also called cement this bone like material covers the tooths root.
In vascular plants the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. Its made up of several parts. The root canal is a passageway that contains pulp.
Lesson 2 understanding root anatomy slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance and to provide you with relevant advertising. The root is the part of the tooth that extends into the bone and holds the tooth in place. This section will review the different kinds of root systems an look at some specialized roots as well as describe the anatomy of the roots in monocots and dicots.
Its anatomy is identical to selaginella except for the fact that the central xylem is star shaped. It makes up approximately two thirds of the tooth. Characterized by having one main root the taproot from which smaller branch roots emerge.
The most common type of trichome which greatly increase the surface area of the root and thereby improves the absorption of water and minerals. In a sense they are to plants what veins and arteries are to animals. However important internal structural differences between stems and roots exist.
Furthermore a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either. Anatomy of root or types of tissues in root is discussed here. A type of taproot highly specialized for the storage of starches is called a napiform root.
A root system that is composed of one main primary root and many secondary roots branching off of the primary root. V ascular plants contain two main types of conduction tissue the xylem and phloem. Many dicot plants have taproot systems.
The classic root which is studied in all botany courses is that of ranunculus a dicot. Cross section of ranunculus root. These two tissues extend from the leaves to the roots and are vital conduits for water and nutrient transport.
A root system that is composed of one main primary root and many secondary roots branching off the primary root is called a taproot system. Roots can also be aerial or aerating that is growing up above the ground or especially above water. Locate the concentric circles of tissues.
If you continue browsing the site you agree to the use of cookies on this website. Xylems are composed of tracheids and vessels. The vascular tissue and the pericycle form a tube of conducting cells called stele.
Xvlems are present in the centre of the root. Cellular structure of vascular plants.
Anatomy Of An Orchid Root Botany
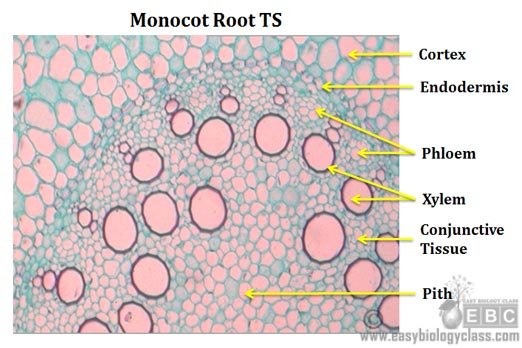 Monocot Root Cross Section Structure With Ppt
Monocot Root Cross Section Structure With Ppt
 Root Anatomy And Root Canal Configuration Of Human Permanent
Root Anatomy And Root Canal Configuration Of Human Permanent
 Pdf Phenotypic Plasticity Of Grass Root Anatomy In Response
Pdf Phenotypic Plasticity Of Grass Root Anatomy In Response
Anatomy Of Root Monocotyledonous And Dicotyledonous Plant
 File Root Tip Anatomy Png Wikimedia Commons
File Root Tip Anatomy Png Wikimedia Commons
Maize The University Of Nottingham
 Anatomical Differences Between Dicot Root And Monocot Root
Anatomical Differences Between Dicot Root And Monocot Root
 Model Of Plant Root Anatomy Structure In Botanical
Model Of Plant Root Anatomy Structure In Botanical
 Plantae Granar A New Computational Tool To Better
Plantae Granar A New Computational Tool To Better
 Root Morphology Anatomy Dental Hygiene Student Dental
Root Morphology Anatomy Dental Hygiene Student Dental
 Anatomy Of The Aortic Root Implications For Aortic Root
Anatomy Of The Aortic Root Implications For Aortic Root
Anatomy Of The Aortic Root Implications For Valve Sparing
 Anatomy Of A Wild American Ginseng Root
Anatomy Of A Wild American Ginseng Root
 Pdf Root Anatomy Morphology And Longevity Among Root
Pdf Root Anatomy Morphology And Longevity Among Root
Roots In Angiospermic Plants Function Modification And Anatomy
Plos One Interrelationships In The Variability Of Root
Anatomical Characteristics Of Dicotyledonous Roots Botany
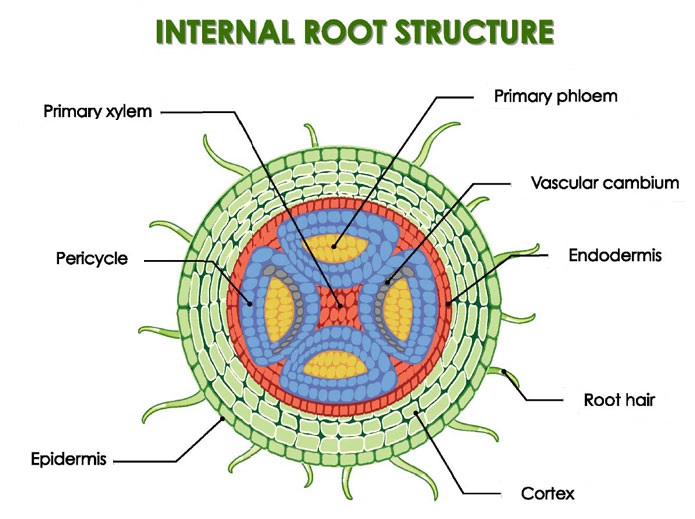 Anatomy Of The Root Of Both Dicot And Monocot Plants
Anatomy Of The Root Of Both Dicot And Monocot Plants
 Clinical Anatomy Of The Aortic Root Heart
Clinical Anatomy Of The Aortic Root Heart


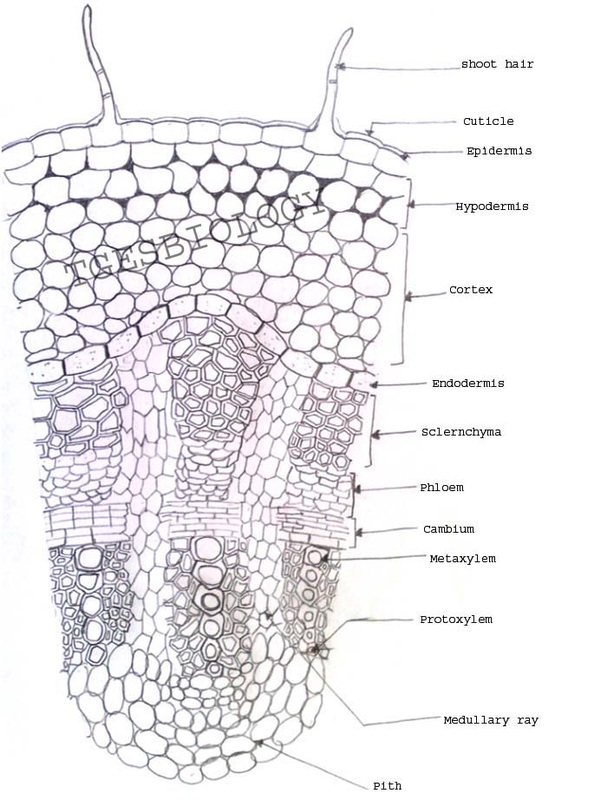
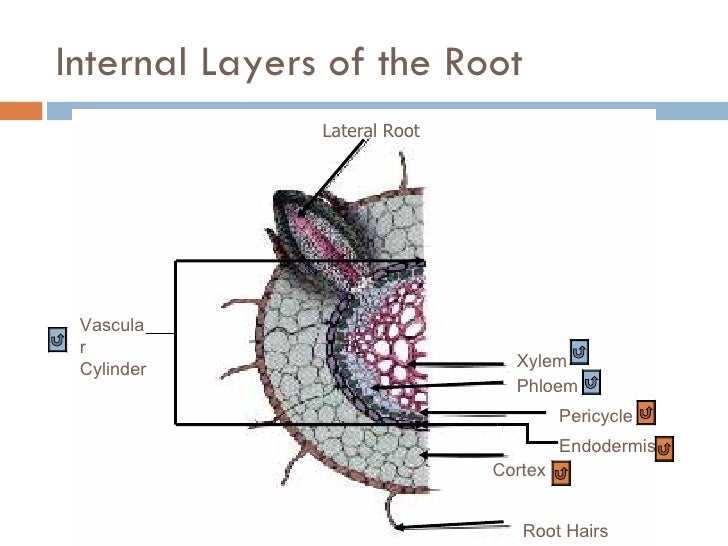


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Root Anatomy"
Posting Komentar