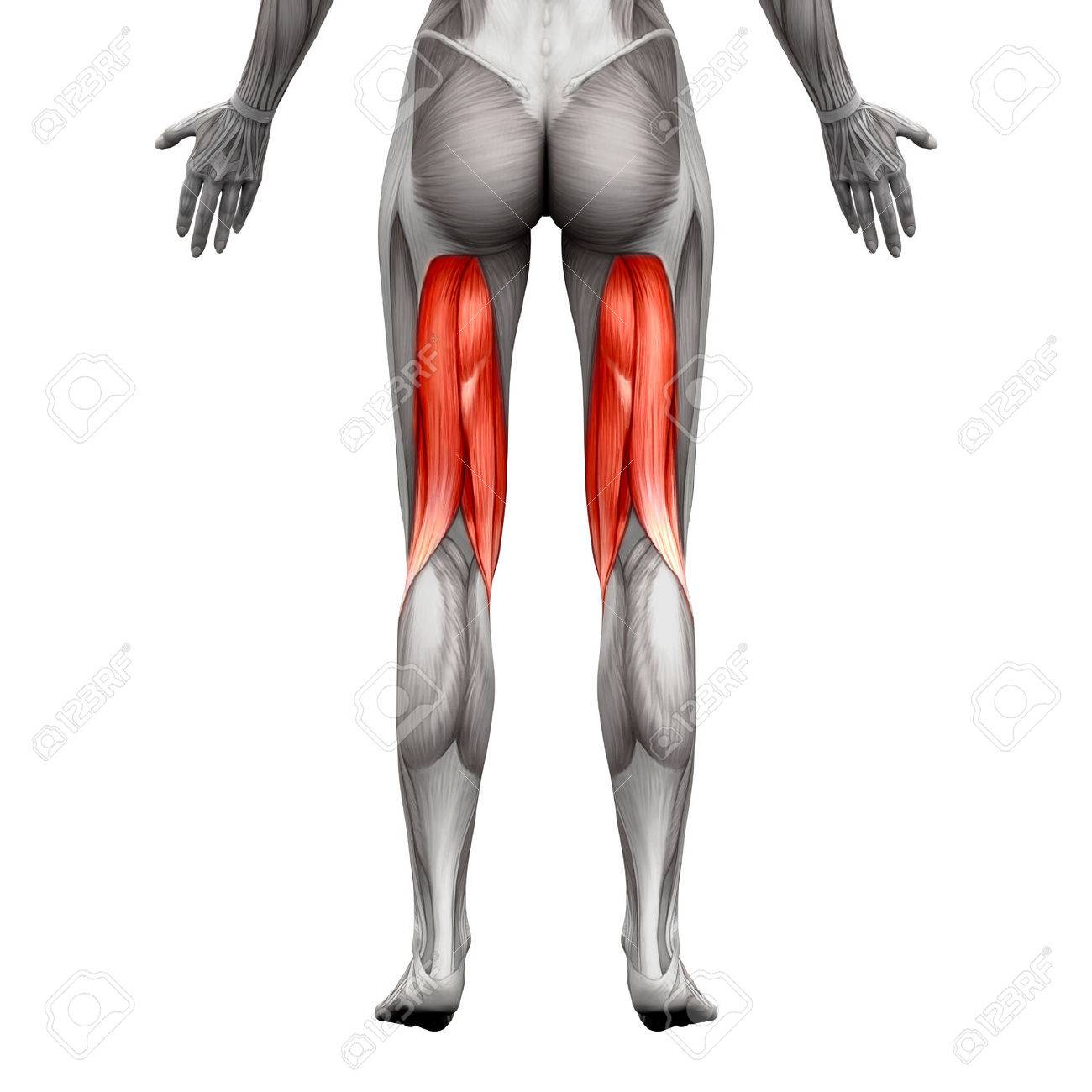
Hamstring Muscles Anatomy
Because these muscles have a common site of origin on the ischial tuberosity and have similar positions in the posterior thigh. The hamstring tendons flank the space behind the knee.
 Hamstring Muscles Functional Anatomy Guide Bodybuilding
Hamstring Muscles Functional Anatomy Guide Bodybuilding
Muscles should be inserted over the knee joint in the tibia or in the fibula.
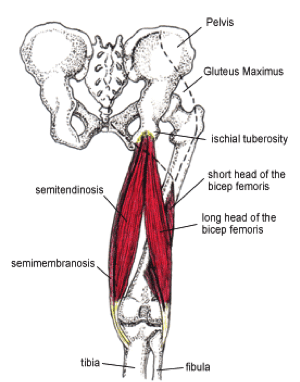
Hamstring muscles anatomy. As group these muscles act to extend at the hip and flex at the knee. Muscle will participate in flexion of the knee. The common criteria of any hamstring muscles are.
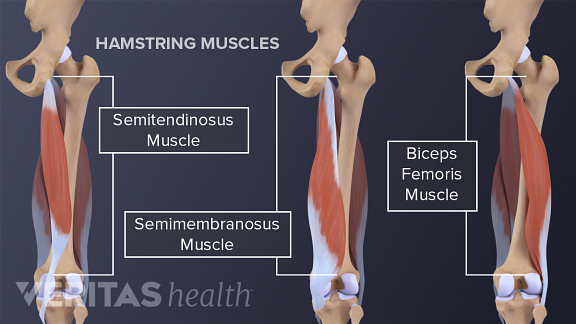
The hamstrings are comprised of three separate muscles. Severe grade 3 strains may include avulsion where some part of the muscle actually detaches from its connection to bone. Anatomy of the hamstring muscles.
These muscles start at the bottom of your pelvis extending down the back of your thigh and along either side of your knee to your lower leg bones. The most medial muscle the semimembranosus. The hamstring muscles have their origin where their tendons attach to bone at the ischial tuberosity of the hip often called the sitting bones and the linea aspera of the femur.
On the other hand hamstring strengthening poses are typically practiced less often so were missing out on their ability to build endurance in the actual muscle fibers. There are three grades of hamstring strain. The biceps femoris is the only two headed hamstring muscle.
They consist of the biceps femoris semitendinosus and semimembranosus which form prominent tendons medially and laterally at the back of the knee. The largest muscle of the hamstrings is the biceps femoris. Working the muscle also creates strength and toughness in the tendons that attach the muscle to the bone making them less likely to strain and tear.
The biceps femoris semitendinosus and semimembranosus. It starts at the bottom of the pelvic bone. The muscles in the posterior compartment of the thigh are collectively known as the hamstrings.
The hamstrings refer to 3 long posterior leg muscles the biceps femoris semitendinosus and semimembranosus. The hamstring muscles the hamstring muscles cross two joints the hip and the knee and can act as extensors of the thigh and flexors of the leg. Muscles should originate from ischial tuberosity.
Anatomy of the hamstring muscles. Grade 1 strains include milder strains that can be treated at home. These muscles originate just underneath the gluteus maximus on the pelvic bone and attach on the tibia.
Like the biceps in your upper arm the largest of the hamstring muscles biceps femoris has two heads long and short. Grade 2 strains are more severe and include more loss of range of motion. The long head is the one toward the outside of the thigh.
Muscles will be innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve.
 Hamstring Tendonitis Or Hamstring Syndrome Zion Physical
Hamstring Tendonitis Or Hamstring Syndrome Zion Physical
 5 Reasons You Have Tight Hamstrings Tight Hamstrings
5 Reasons You Have Tight Hamstrings Tight Hamstrings
How Many Insertions Does The Hamstring Muscle Have Quora
 Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy Fix Your Buttock Pain
Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy Fix Your Buttock Pain
 Hamstring Muscle Injuries Orthoinfo Aaos
Hamstring Muscle Injuries Orthoinfo Aaos
 Muscles Of The Lower Limb Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Muscles Of The Lower Limb Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Muscles Of The Hips And Thighs Human Anatomy And
Muscles Of The Hips And Thighs Human Anatomy And
 Intramuscular Hamstring Tendon Injury Prognosis Surgical
Intramuscular Hamstring Tendon Injury Prognosis Surgical
 Pin By Lindsay Gallagher On A Life Time Of Sports Injuries
Pin By Lindsay Gallagher On A Life Time Of Sports Injuries
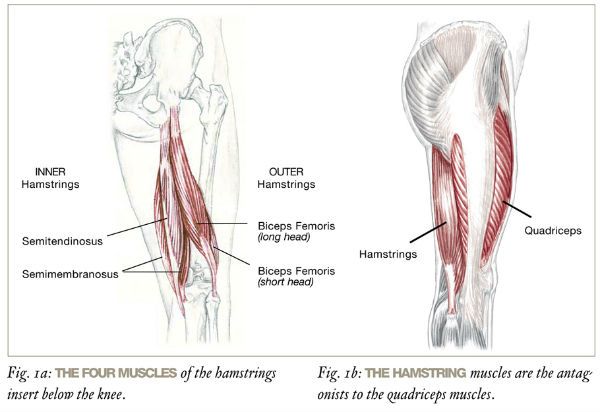 Relief For Tight Hamstrings Yogo For You Bismark North
Relief For Tight Hamstrings Yogo For You Bismark North
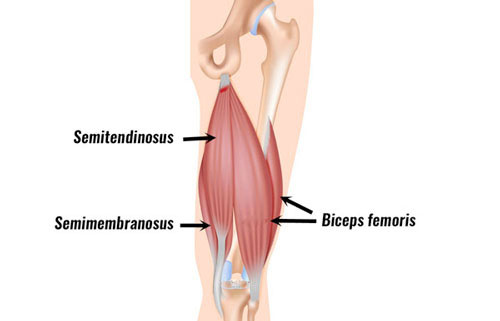 Hamstring Tendon Strain Symptoms Causes Treatment
Hamstring Tendon Strain Symptoms Causes Treatment
 Proximal Lesion A Schematic Representation Of The
Proximal Lesion A Schematic Representation Of The
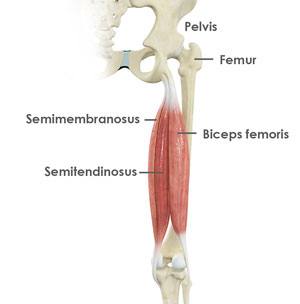 Hamstring Tendon Repair Cork Ir Hamstring Injury
Hamstring Tendon Repair Cork Ir Hamstring Injury
 How To Draw Hamstrings Leg Anatomy For Artists
How To Draw Hamstrings Leg Anatomy For Artists
 Hamstring Muscle Injuries Orthoinfo Aaos
Hamstring Muscle Injuries Orthoinfo Aaos
 Pdf Hamstrings Muscle Anatomy And Function And
Pdf Hamstrings Muscle Anatomy And Function And
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-87308179-56a05f563df78cafdaa14cd4.jpg) Anatomy Of The Hamstring Muscles
Anatomy Of The Hamstring Muscles
 A New Option For The Reconstruction Of Primary Or Recurrent
A New Option For The Reconstruction Of Primary Or Recurrent
 Hamstring Injuries Victorian Wolves Supporters Club
Hamstring Injuries Victorian Wolves Supporters Club
Anatomy Lesson Twenty Nine The Hamstring Muscles Anatomy
 Trigger Point Release For Horses Hamstring Muscles Horse
Trigger Point Release For Horses Hamstring Muscles Horse
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Depositphotos_19871399_original-56a05f523df78cafdaa14cd1.jpg)

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Hamstring Muscles Anatomy"
Posting Komentar