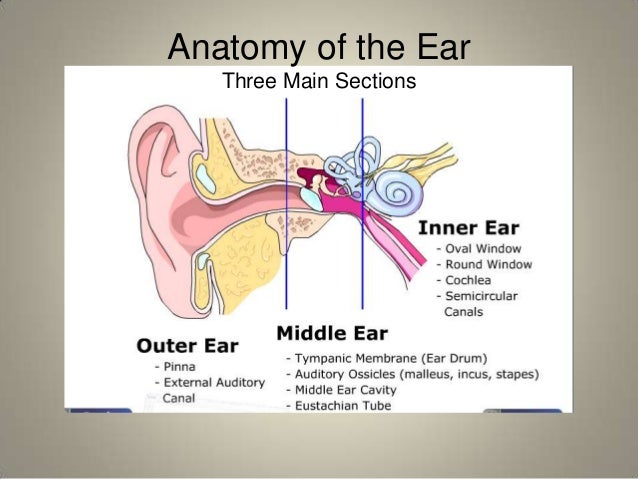
Anatomy Of Ear External
The funnel like curves of auricle collects sound wave and direct them to middle ear. This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear.
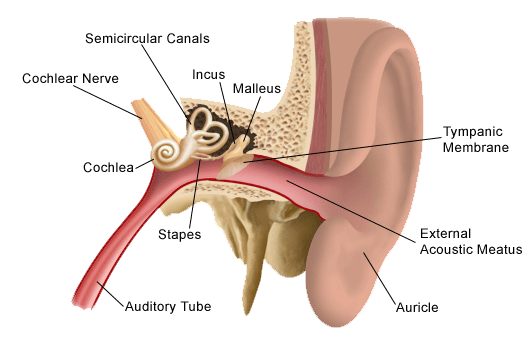
The auricle or pinna and the external acoustic meatus which ends at the tympanic membrane.
Anatomy of ear external. Sound causes the eardrum and its tiny attached bones in the middle portion of the ear to vibrate. Picture of the ear. External or outer ear consisting of.
Acquired entities can further be delineated into intrinsic processes such as cancer and extrinsic processes such as trauma. All three parts of the ear are important for detecting sound by working together to move sound from the outer part through the middle and into the inner part of the ear. Fine hairs directed outward and modified sweat glands that produce earwax or cerumen line the canal and discourage insects from entering it.
External ear is composed of auricle and external auditory canal meatus. The outer middle and inner ear. Its function is to trap sound waves auricle and transmit it to the inner ear by passing down the canal and causing the eardrum to vibrate.
Congenital abnormalities of the ear are common and largely affect the shape of the auricle. Tympanic membrane also called the eardrum. The outer ear is called the pinna and is made of ridged cartilage covered by skin.
The outer ear external ear or auris externa is the external portion of the ear which consists of the auricle also pinna and the ear canal. Variant anatomy of the external ear can be divided into congenital and acquired entities. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum tympanic membrane.
The external ear outer is made up of the auricle ear canal and lateral surface of the tympanic membrane. The medical term for the ear drum is the tympanic membrane. The entire length of the passage 24 mm or almost 1 inch is lined with skin which also covers the outer surface of the tympanic membrane.
External auditory canal or tube. Sound funnels through the pinna into the external auditory canal a short tube that ends at the eardrum tympanic membrane. This is the outside part of the ear.
The external ear can be divided functionally and structurally into two parts. By teachmeseries ltd 2019. The parts of the ear include.
The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. The ear drum is a transparent gray membrane. Auricle pinna auricle is composed of thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by layer of skin.
Ear anatomy outer ear. Attached to the center part of the drum is the middle ear bone the malleus. The ear is made up of three parts.
Ear drum the ear drum is about the size of a dime and is the same size in the new born baby as in the adult. Ears also help to maintain balance.
 Ear Auricle The Human Outer Ear Anatomy Stock Photo
Ear Auricle The Human Outer Ear Anatomy Stock Photo
 Anatomy Of The Ear S External Structures
Anatomy Of The Ear S External Structures
 Anatomy Of The Ear External Ear Auricle Or Pinna
Anatomy Of The Ear External Ear Auricle Or Pinna
Anatomy Of The External Ear American Academy Of Ophthalmology
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear Children S Wisconsin
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear Children S Wisconsin
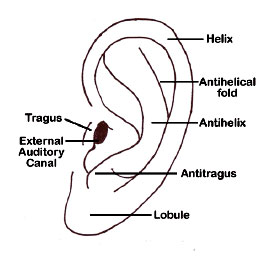 Hearing Outer Ear Development Embryology
Hearing Outer Ear Development Embryology
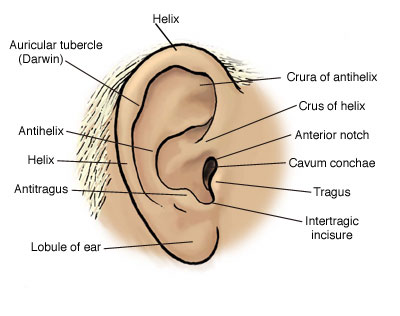 Anatomy Atlases Anatomy Of First Aid A Case Study Approach
Anatomy Atlases Anatomy Of First Aid A Case Study Approach
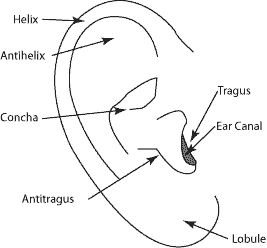 Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Mcgovern Medical School
Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Mcgovern Medical School
 External Ear Anatomy Google Images
External Ear Anatomy Google Images
 Ear Anatomy Cross Section Of The Right External Middle And
Ear Anatomy Cross Section Of The Right External Middle And
 Figure 2 From Anatomy And Physiology Of The Canine Ear
Figure 2 From Anatomy And Physiology Of The Canine Ear
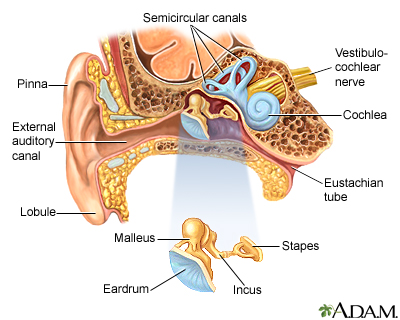 Ear Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Ear Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
 Outer External Part Of Human Ear Structure Picture And Definitions
Outer External Part Of Human Ear Structure Picture And Definitions
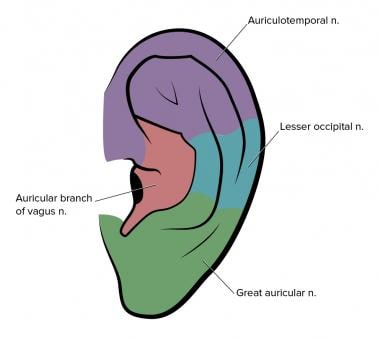 Ear Anesthesia Overview Indications Contraindications
Ear Anesthesia Overview Indications Contraindications
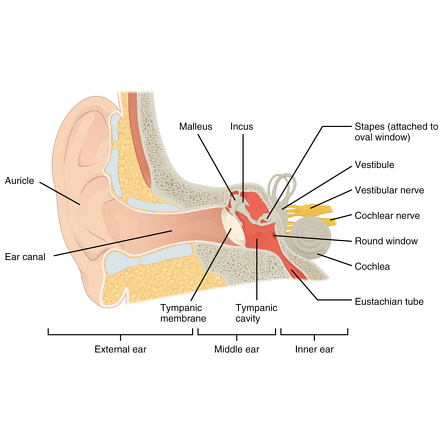 Middle Ear Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Middle Ear Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
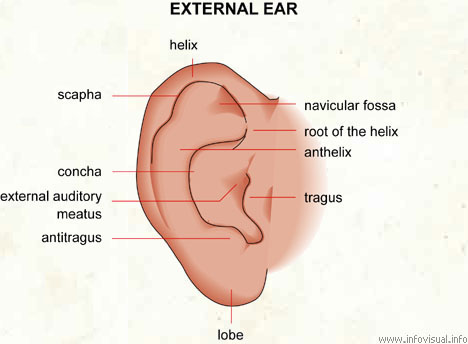 External Ear Visual Dictionary
External Ear Visual Dictionary
 External Ear Malformation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
External Ear Malformation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Healthcare Health Solution External Ear Anatomy And Function
Healthcare Health Solution External Ear Anatomy And Function
 Chapter 19 Ear The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
Chapter 19 Ear The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
Ear Anatomy Causes Of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
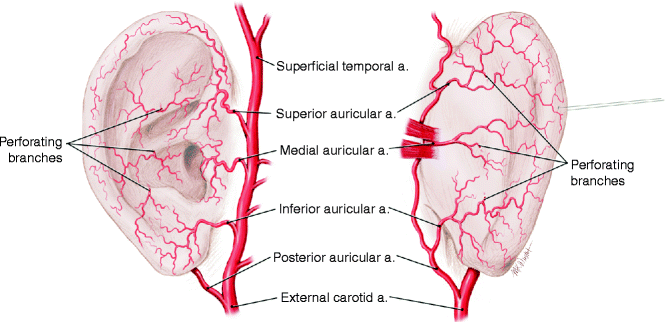 Anatomy Of The External Ear Springerlink
Anatomy Of The External Ear Springerlink


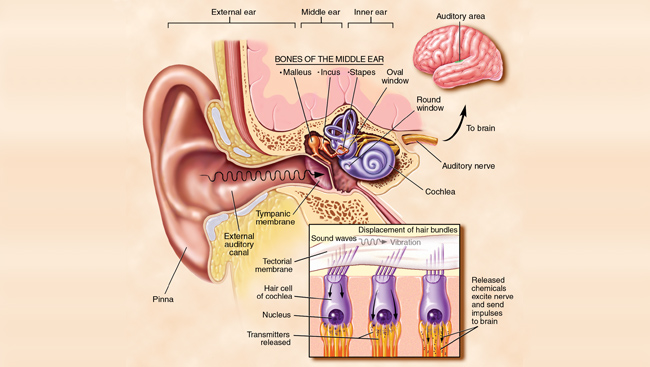
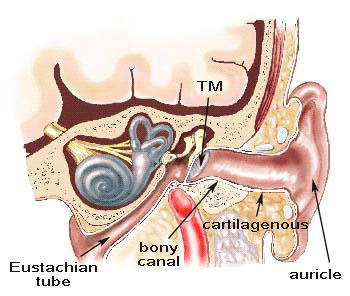


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Ear External"
Posting Komentar