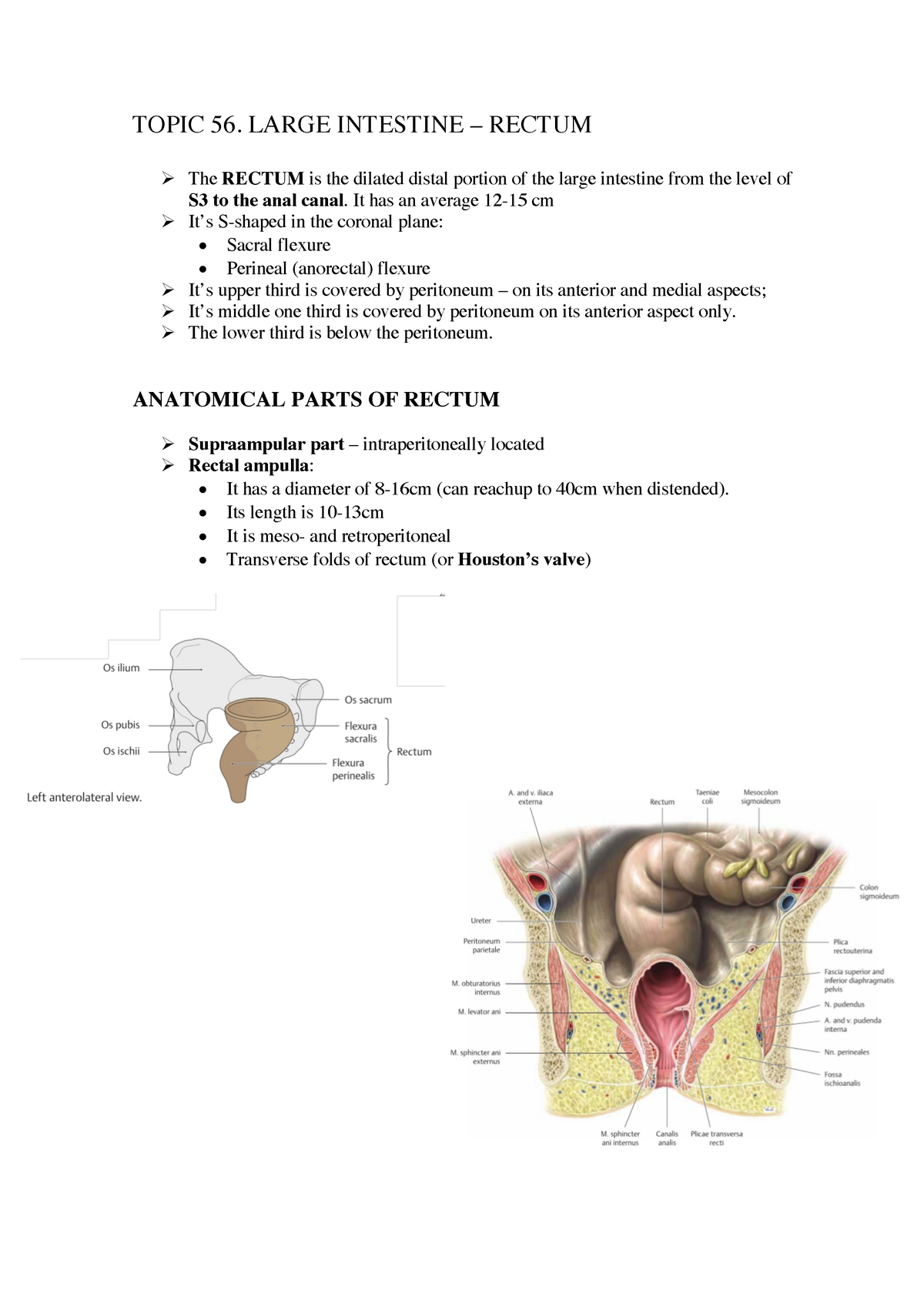
Rectal Anatomy
Certain types of cancers may be diagnosed by performing an endoscopy in the rectum. Veins corresponding to their named arteries form a rectal venous plexus.
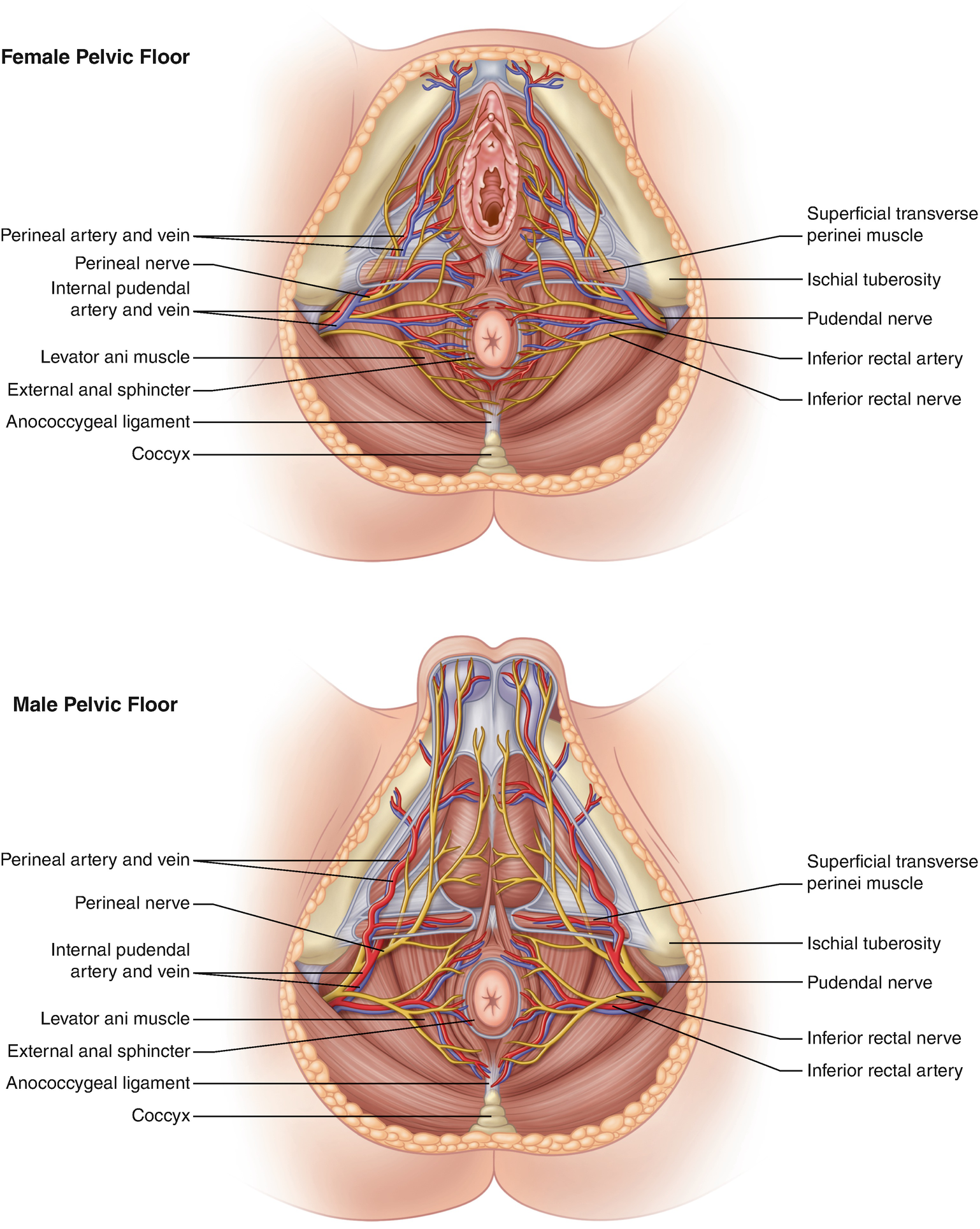
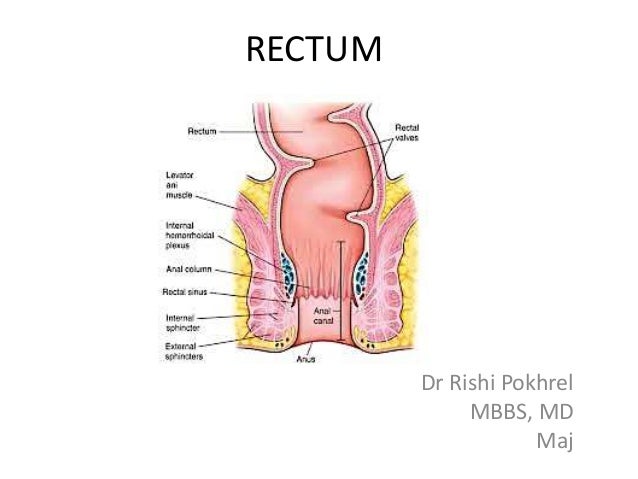
There are two sphincter muscles.
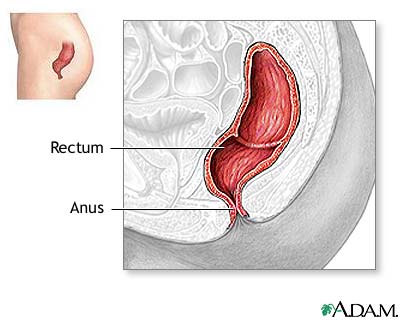
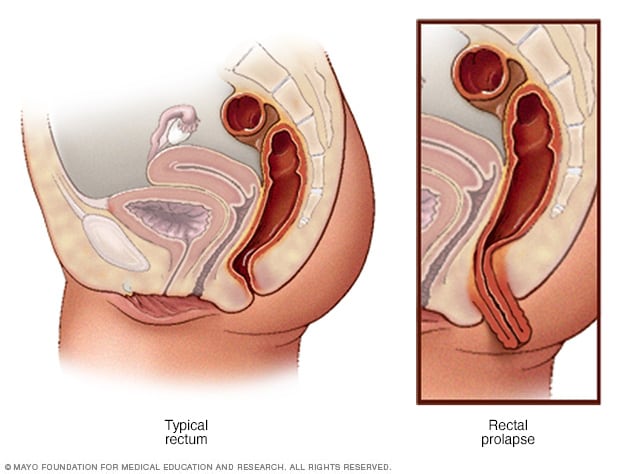
Rectal anatomy. Rectal prolapse referring to the prolapse of the rectum into the anus or external area. An internal sphincter muscle which can be felt as a muscular ring beyond which is the rectum. It extends from the inferior end of the sigmoid colon along the anterior surface of the sacrum and coccyx in the posterior of the pelvic cavity.
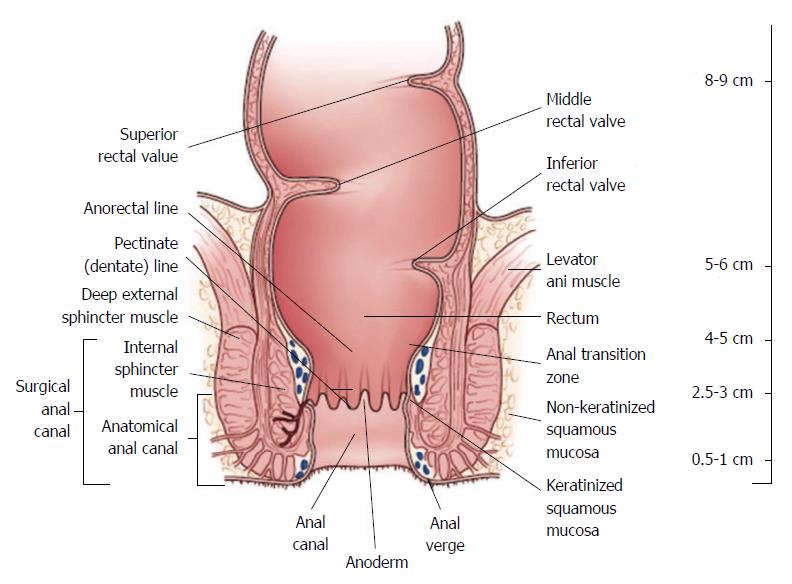
A muscular sheet called the pelvic diaphragm runs perpendicular to the juncture of the rectum and rectum terminal segment of the digestive system in which feces accumulate just prior to discharge. The anorectal line separates the anus from the rectum. Tough tissue called fascia surrounds the anus and attaches it to nearby structures.
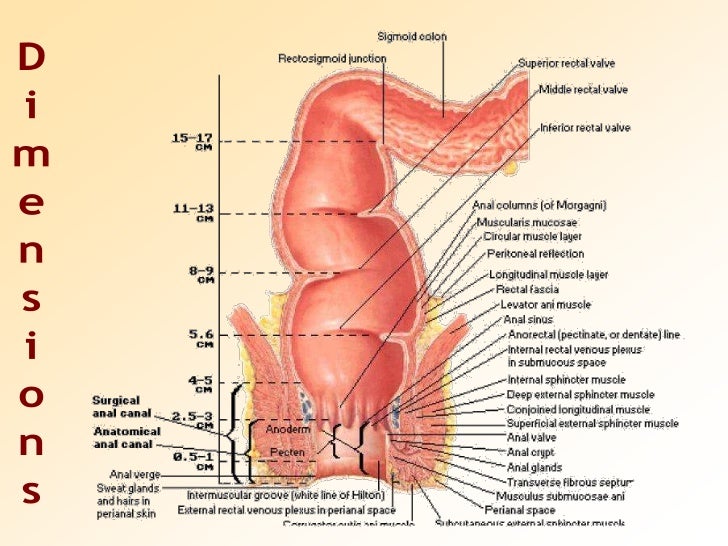
An endoscopy is a procedure where a doctor uses an endoscope a small flexible tube with a camera and light to examine areas inside the body. The rectum is continuous with the sigmoid colon and extends 13 to 15 cm 5 to 6 inches to the anus. The anus is the opening where the gastrointestinal tract ends and exits the body.
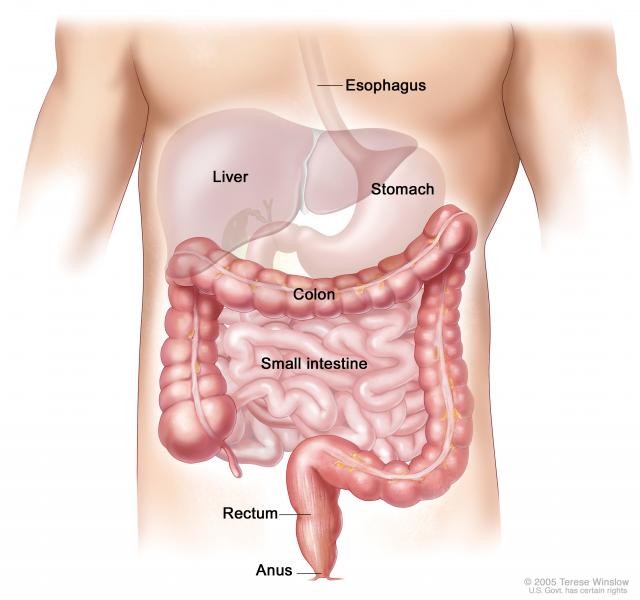
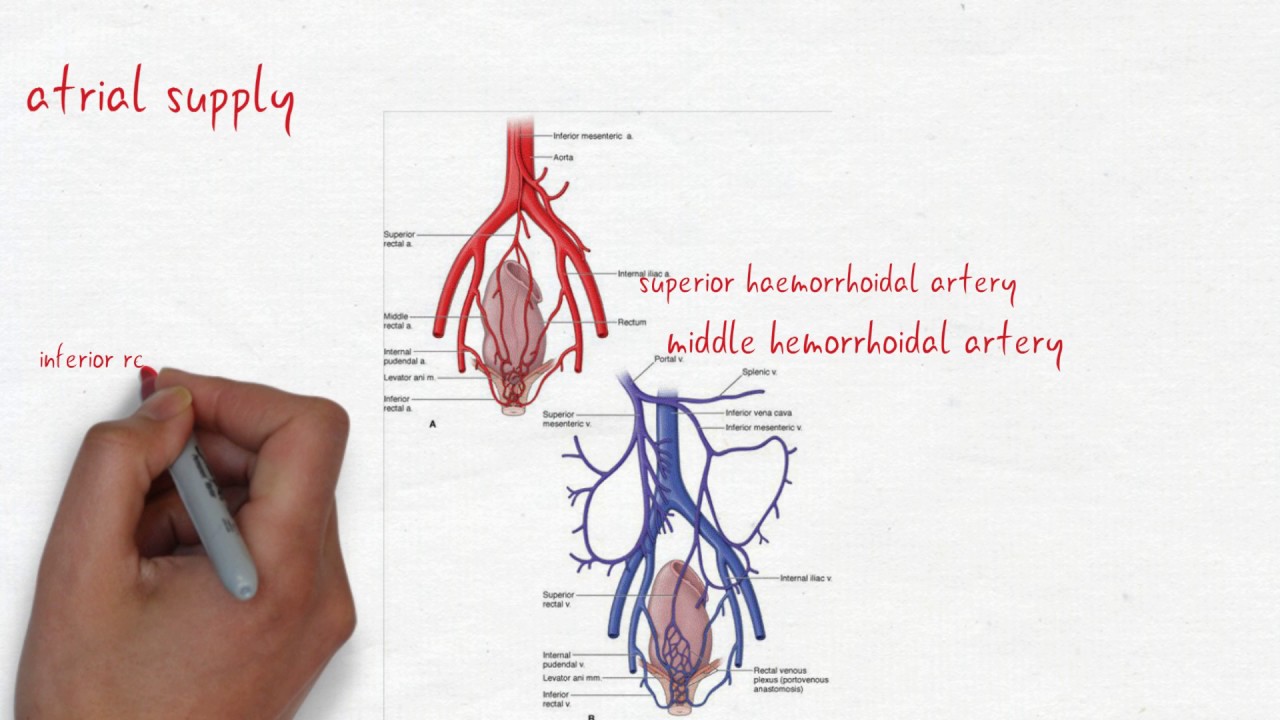
Anatomy the rectum is a hollow muscular tube about 8 inches 20 cm in length and 25 inches in diameter at its widest point. The peritoneum firmly attaches the rectum to the sacrum. Arterial supply to the rectum is formed from an anastomotic submucous plexus.
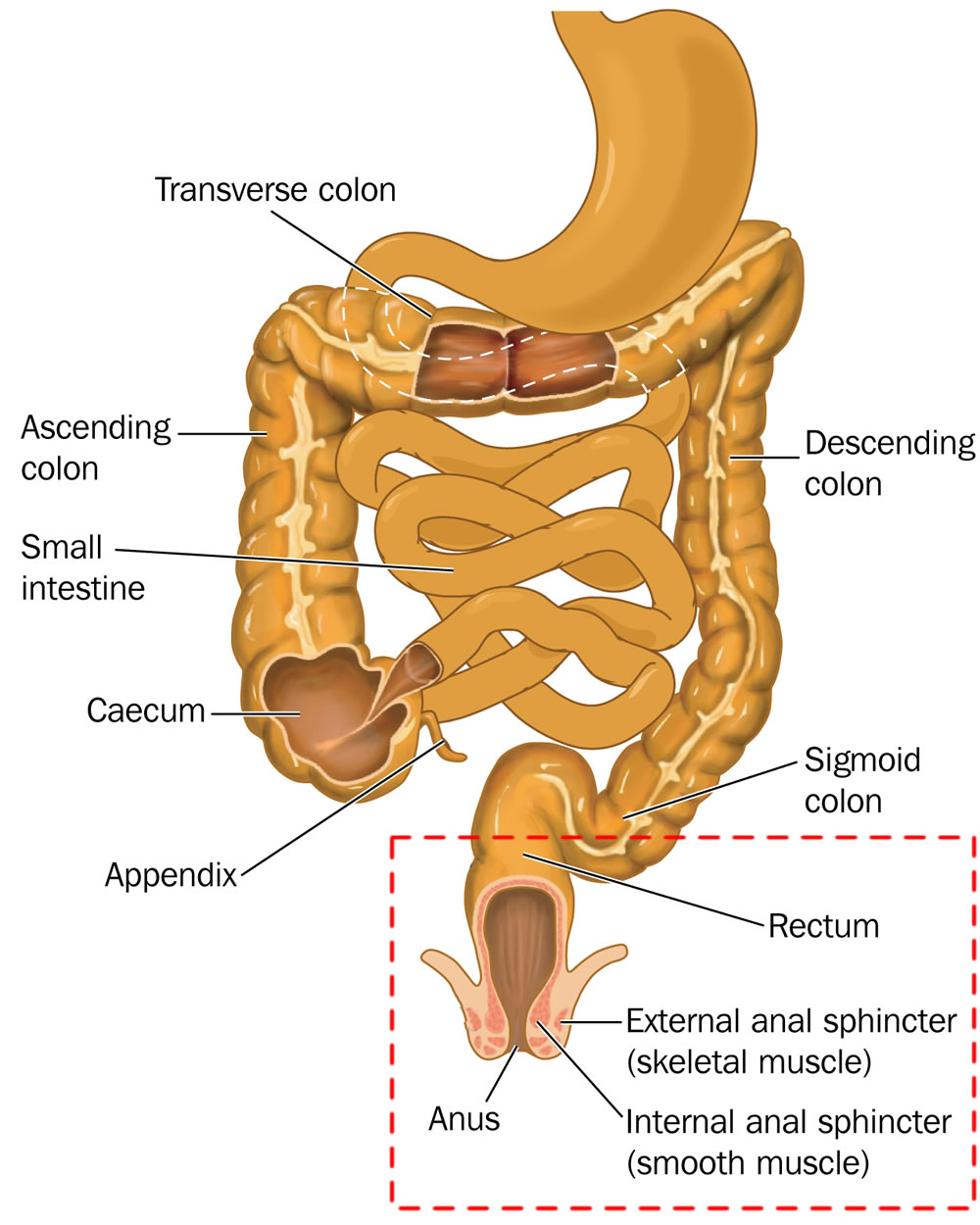
The rectum is the most distal segment of the large intestine and has an important role as a temporary store of faeces. The anus starts at the bottom of the rectum the last portion of the colon large intestine. The anal columns are united below by anal valves which bound anal sinuses.
At the level of the s3 vertebral body the sigmoid colon loses its mesentery. It is continuous proximally with the sigmoid colon and terminates into the anal canal. Several vertical mucosal folds the anal formerly called rectal columns are usually visible in the upper half of the canal fig.
The upper portion of the anus or that part that connects to the rectum is known as the squamocolumnar junction. Body temperature may also be obtained from the rectal area. The rectum is an expandable organ for the temporary storage of feces.
And an external sphincter muscle. In this article we will discuss the anatomy of the rectum its structure anatomical relationships and clinical relevance. Anatomy of the anus.
The columns are vascular and enlargement of their venous plexus results in internal hemorrhoids. This is commonly caused by a weakened pelvic floor after childbirth. The rectum lies next to the sacrum and generally follows its curvature.
 Rectal Cancer An Evidence Based Update For Primary Care
Rectal Cancer An Evidence Based Update For Primary Care
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10928/the-rectum-and-anal-canal_english.jpg) Rectum Anatomy Histology Function Kenhub
Rectum Anatomy Histology Function Kenhub
 Operative Anatomy Of The Colon Rectum And Anus Sciencedirect
Operative Anatomy Of The Colon Rectum And Anus Sciencedirect
 Rectum And Anal Canal Anatomy And Function Preview
Rectum And Anal Canal Anatomy And Function Preview
 Rectal Cancer Treatment Mhealth Org
Rectal Cancer Treatment Mhealth Org
Anal Dysplasia And Anal Cancer Cleveland Clinic
 Git Anatomy The Rectum And The Anal Canal
Git Anatomy The Rectum And The Anal Canal
 Rectal Prolapse Repair Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
Rectal Prolapse Repair Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
 2 Rectal Anatomy Lateral View Download Scientific Diagram
2 Rectal Anatomy Lateral View Download Scientific Diagram
 What Is The Difference Between Anal Cancer And Colon Cancer
What Is The Difference Between Anal Cancer And Colon Cancer
 Department Of Surgery Rectal Cancer
Department Of Surgery Rectal Cancer
 Anatomy And Embryology Of The Colon Rectum And Anus
Anatomy And Embryology Of The Colon Rectum And Anus
 Rectum And Anus Flashcards Quizlet
Rectum And Anus Flashcards Quizlet
 The Radiology Assistant Rectal Cancer Mr Staging 2 0
The Radiology Assistant Rectal Cancer Mr Staging 2 0
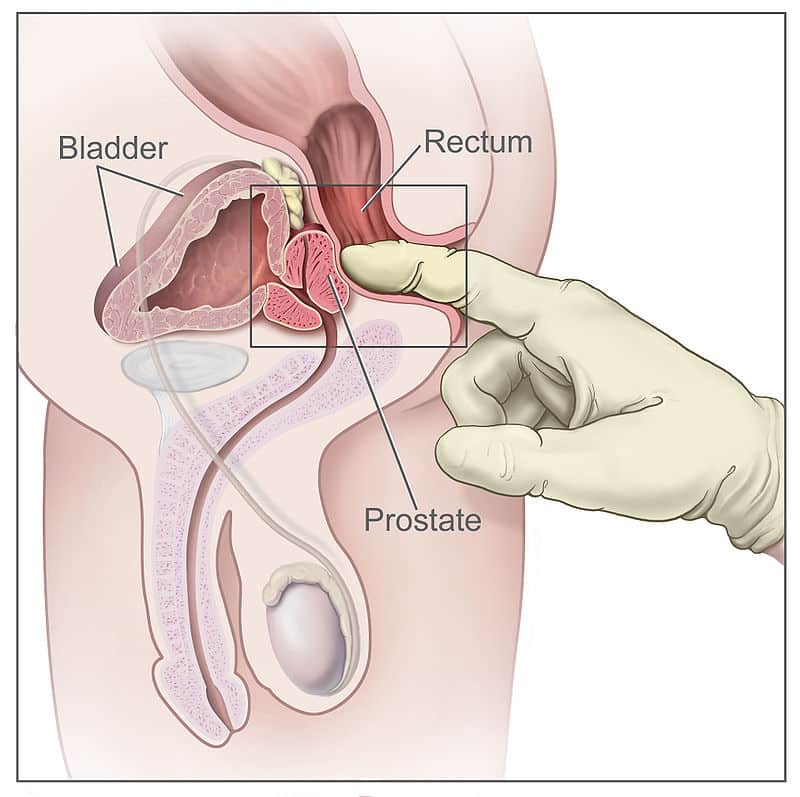 The Rectum Position Neurovascular Supply Teachmeanatomy
The Rectum Position Neurovascular Supply Teachmeanatomy
 Rectal Prolapse Expanded Version Ascrs
Rectal Prolapse Expanded Version Ascrs
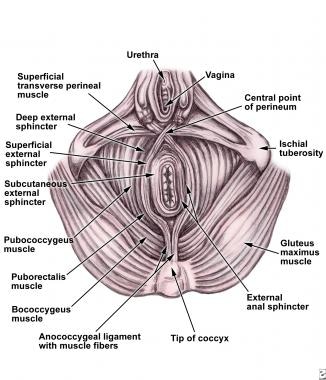 What Is The Anatomy Of The Anal Canal Relevant To Pediatric
What Is The Anatomy Of The Anal Canal Relevant To Pediatric
 The Rectum Anatomy Of The Rectum Physiology Of The
The Rectum Anatomy Of The Rectum Physiology Of The
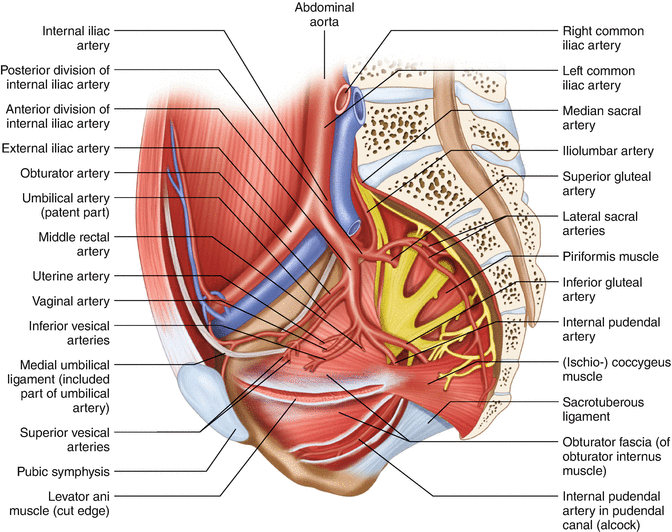 Rectal Anatomy Clinical Perspective Springerlink
Rectal Anatomy Clinical Perspective Springerlink
 Sphincter Saving Rectal Cancer Surgery
Sphincter Saving Rectal Cancer Surgery
 Anal Canal An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Anal Canal An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Topic 56 Large Intestine Rectum Anatomy 06 Studocu
Topic 56 Large Intestine Rectum Anatomy 06 Studocu




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Rectal Anatomy"
Posting Komentar