Airway Intubation Anatomy
This information is meant to serve as an educational resource. Robert bastian provides an introduction to larynx pharynx and airway anatomy.
Formed by union of facial bones nasal floor towards ear not eye lined with mucous membranes cilia tissues are delicate vascular adenoids.

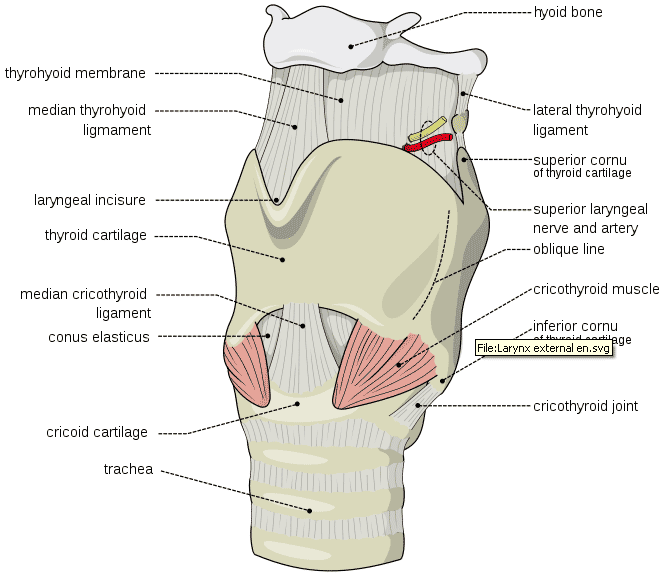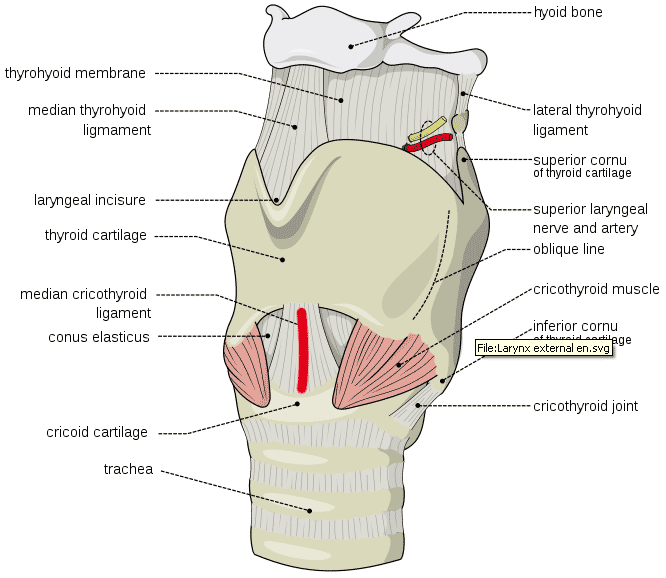
Airway intubation anatomy. A good understanding of airway and intubation is fundamental to managing a sick patient. It includes the mouth the nose the palate the uvula the pharynx and the larynx. Nasotracheal intubation is an alternative approach to orotracheal intubation.
In this presentation dr. Selecting the correct equipment for intubation. Lymph tissue filters bacteria commonly infected.
A keen understanding of airway anatomy can make the process of intubating a patient much easier. This demonstration by anthony lewis from isimulate and todd slesinger provides a brief overview of the basics of the upper airway and laryngoscopy. The upper airway extends from the mouth to the trachea.
And while it does pose some risks it is also safe with the right technique and diligent attention to the patient. Knowledge of the functional anatomy of the airway in these forms the basis of understanding the pathological conditions that may occur. Nasal cavity and nasopharynx.
Navigation best viewed on larger screens. Warm filter and humidify air. Tracheal intubation usually simply referred to as intubation is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs.
The most widely used route is orotracheal in which an en. The two nasal fossae extend from the nostrils to the nasopharynx. Interpreting structures seen on direct laryngoscopy.
Paediatric airway anatomy appropriately positioning children undergoing intubation. It is frequently performed in critically injured ill or anesthetized patients to facilitate ventilation of the lungs including mechanical ventilation and to prevent the possibility of asphyxiation or airway obstruction. Endotracheal intubation is a basic skill that every first responder must master.
Home airway and intubation. The nasal fossae are divided by the midline cartilaginous septum and medial portions of the lateral cartilages fig. Try using search on phones and tablets.
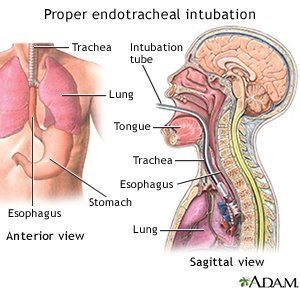 Insertion Of An Endotracheal Tube What You Need To Know
Insertion Of An Endotracheal Tube What You Need To Know
 1 Endotracheal Intubation Extubati On 2 Upper Airway
1 Endotracheal Intubation Extubati On 2 Upper Airway
 Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
 Airway Management Outline Review Of Airway Anatomy Airway
Airway Management Outline Review Of Airway Anatomy Airway
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
 Intubation Step By Step Intubation Technique Explained
Intubation Step By Step Intubation Technique Explained
 A Foundation For Teaching Airway Management Chapter 10
A Foundation For Teaching Airway Management Chapter 10
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
 Chapter 19 Airway Management Morgan Mikhail S Clinical
Chapter 19 Airway Management Morgan Mikhail S Clinical
 Endotracheal Intubation Preparation
Endotracheal Intubation Preparation
 Endotracheal Intubation Crash Airway Intubation For
Endotracheal Intubation Crash Airway Intubation For
 Intubation Step By Step Intubation Technique Explained
Intubation Step By Step Intubation Technique Explained
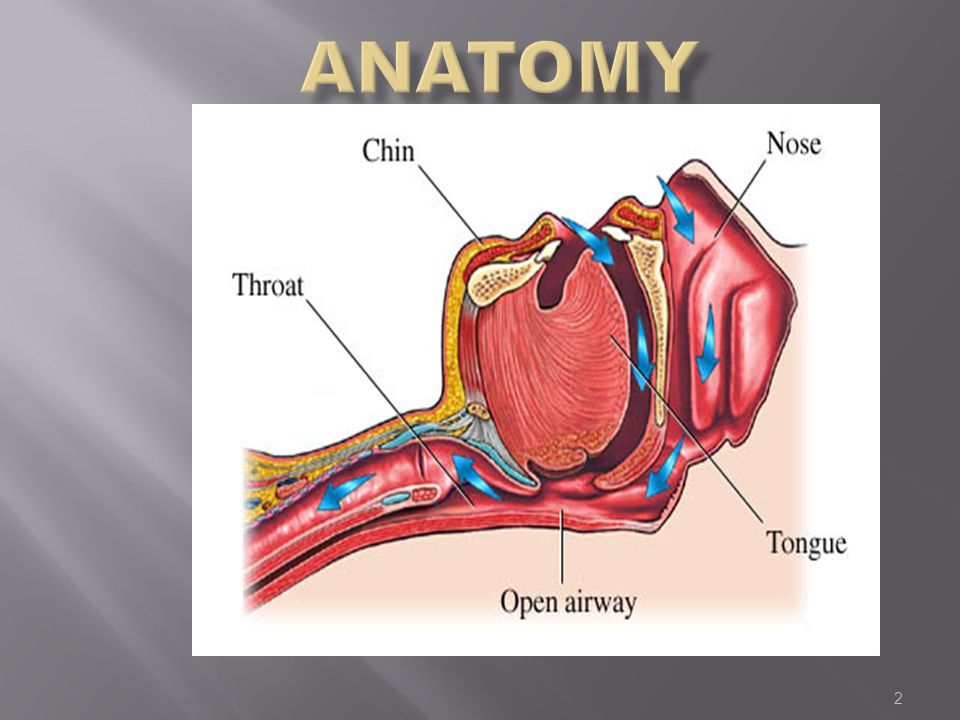 Intubation And Anatomy Of The Airway Ppt Video Online Download
Intubation And Anatomy Of The Airway Ppt Video Online Download
 Chapter 38 Airway Management Principles And Practice Of
Chapter 38 Airway Management Principles And Practice Of
 Demographic Data And Airway Anatomical Measurements Values
Demographic Data And Airway Anatomical Measurements Values
 Tracheal Intubation Critical Care Medicine Merck Manuals
Tracheal Intubation Critical Care Medicine Merck Manuals

 Airway Anatomy And How We Make It Worse The Resus Room U S
Airway Anatomy And How We Make It Worse The Resus Room U S
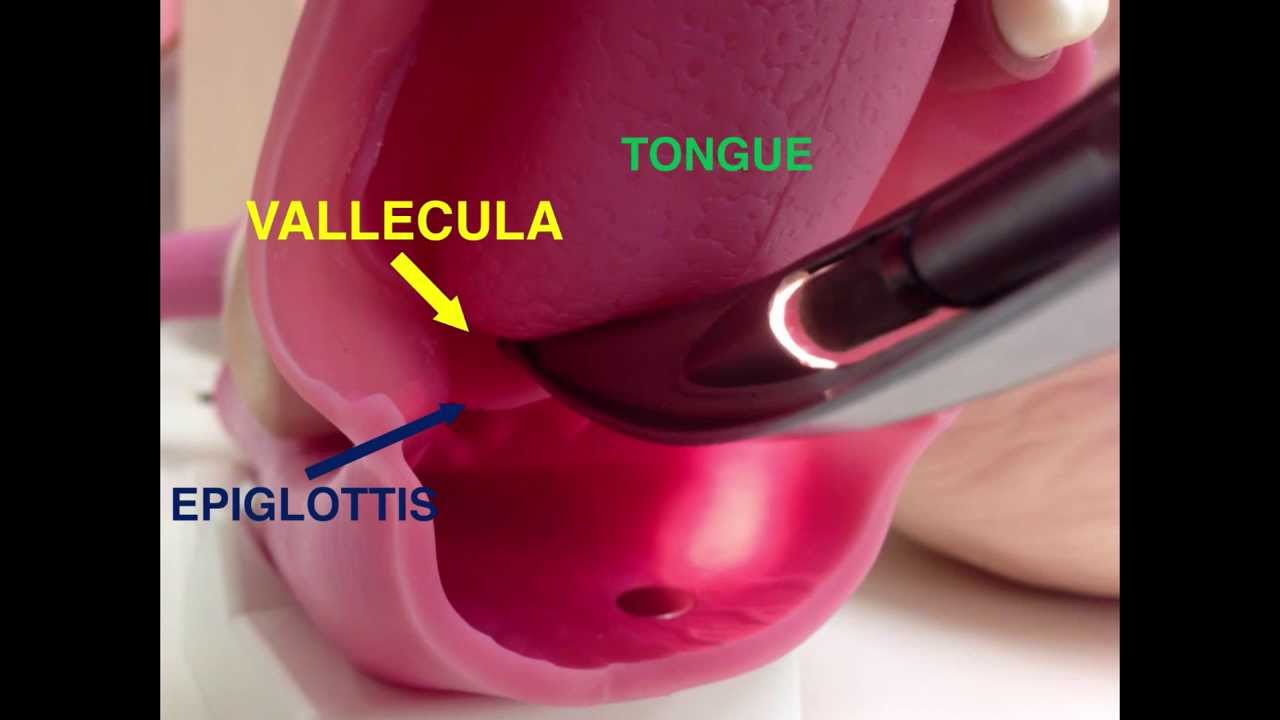 Airway Devices 01 Direct Laryngoscopy
Airway Devices 01 Direct Laryngoscopy


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Airway Intubation Anatomy"
Posting Komentar