Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
These in turn become vibrations in the fluid within the cochlea. In order for a sound to be transmitted to the central nervous system the energy of the sound undergoes three transformations.
Afferent And Efferent Pathways Xenopraxis
The ear is the organ of hearing and balance.

Anatomy and physiology of the ear. The parts of the ear include. The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. Human ear is one of the essential part of our head.
The middle ear acts to. The stapes moves in and out of the oval window of the cochlea creating a fluid motion or hydraulic energy. External auditory canal or tube.
Tympanic membrane also called the eardrum. The parts of the ear include. The external and middle portions of the ear are solely used for hearing functions.
External auditory canal or tube. Human ear anatomy and physiology is our todays topics. External or outer ear consisting of.
The physiology of hearing. This is the outside part of the ear. The middle ear ossicles transmit the sound waves to the inner ear cochlea.
The external ear collects sound pressure waves and funnels them toward the tympanic membrane. This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. This is the outside part of the ear.
Anatomy and physiology of the ear what is the ear. First the air vibrations are converted to vibrations of the tympanic membrane and ossicles of the middle ear. The fluid movement causes membranes in the organ of corti to shear against the hair cells.
This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. Anatomy and physiology of the ear the ear can be crudely divided into three parts known as the external ear middle ear and internal ear. The ears are paired sensory organ comprising the auditory system involved in the detection of sound and vestibular system involved with the maintaining of body balance.
54 anatomy and physiology of the ear and hearing figure 21. The pinna and external auditory canal form the outer ear which is separated from the middle ear by the tympanic membrane. The middle ear houses three ossicles the malleus incus and stapes and is connected to the back of the nose by the eustachian tube.
External or outer ear consisting of. The malleus which is attached to the tympanic membrane starts the ossicles into motion. Anatomy physiology of vestibular apparatus macula of utricle saccule h air cells statoconial membrane caco3 crystals in mucopolysaccharide bed static position linear acceleration.
Anatomy and physiology of the ear.
A Beginner S Guide To Ear Anatomy And Physiology
1 18 General Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
 Picture Of The Ear Ear Conditions And Treatments
Picture Of The Ear Ear Conditions And Treatments

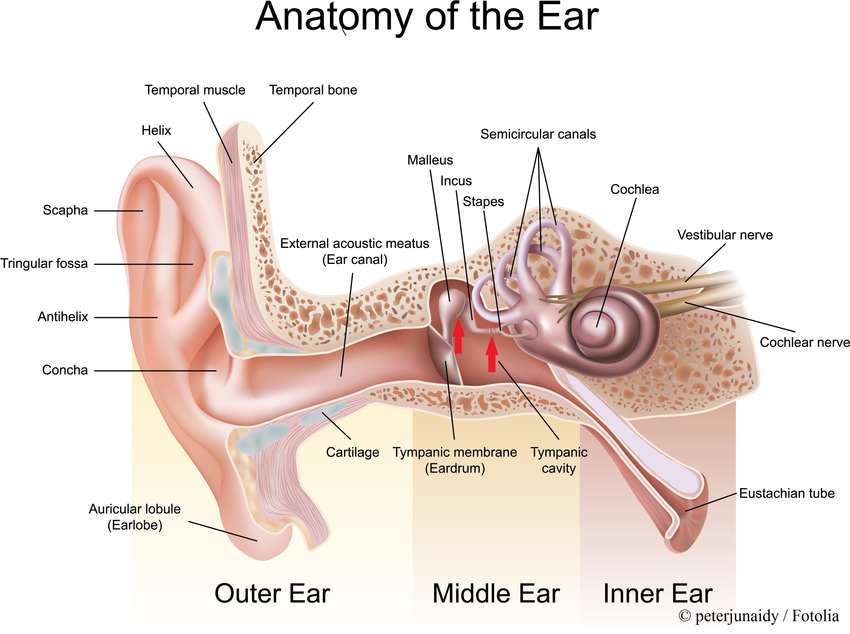 Human Ear Structure And Anatomy Online Biology Notes
Human Ear Structure And Anatomy Online Biology Notes
 Cabs Ear Nose And Throat Anatomy And Physiology Part I
Cabs Ear Nose And Throat Anatomy And Physiology Part I
Sensory Perception Anatomy And Physiology Openstax
 Exam 12 Chap 15 Hearing Anatomy Physiology Kaap309
Exam 12 Chap 15 Hearing Anatomy Physiology Kaap309
 Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Ear Medicine Flashcards
Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Ear Medicine Flashcards
 Anatomy I Exam 5 Ear Anatomy Physiology 120 With
Anatomy I Exam 5 Ear Anatomy Physiology 120 With
 The Ear Anatomy And Physiology
The Ear Anatomy And Physiology
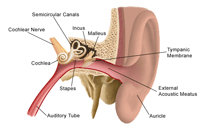 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
 Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Ear Medicine Flashcards
Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Ear Medicine Flashcards
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear Archives Fast French
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear Archives Fast French
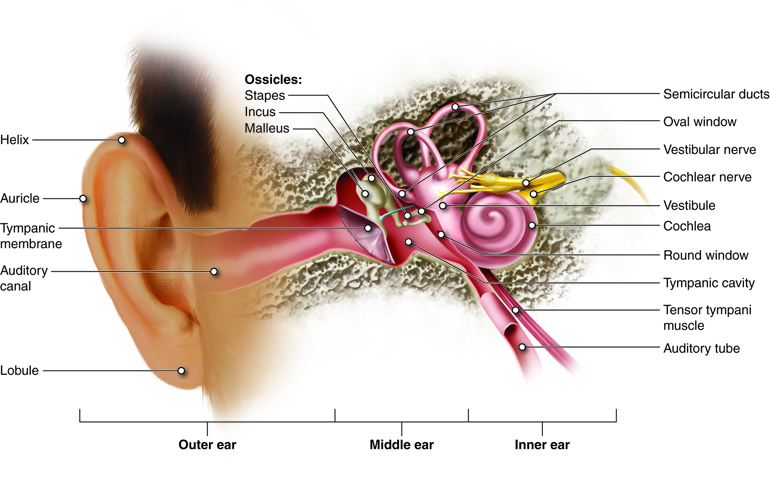 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
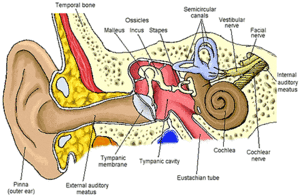 Microbiota Of The Human Ear Microbewiki
Microbiota Of The Human Ear Microbewiki
 Chapter 44 Anatomy Physiology Of The Ear Current
Chapter 44 Anatomy Physiology Of The Ear Current
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear
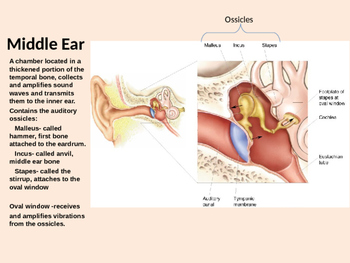 Anatomy Physiology Of The Ear How We Hear
Anatomy Physiology Of The Ear How We Hear
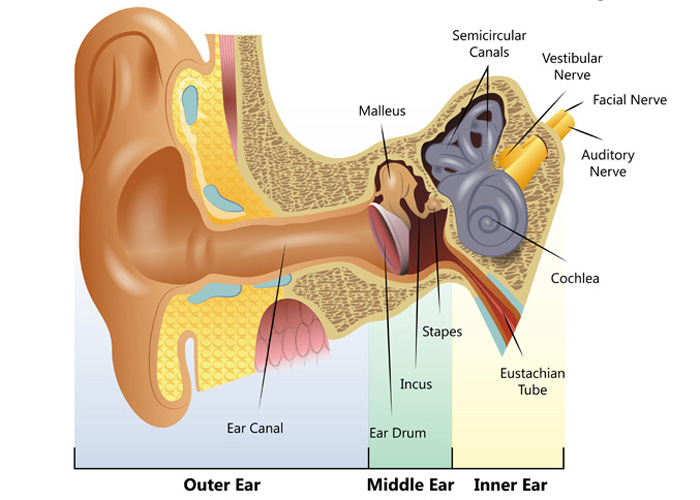 Understanding How The Ear Works Hearing Link
Understanding How The Ear Works Hearing Link
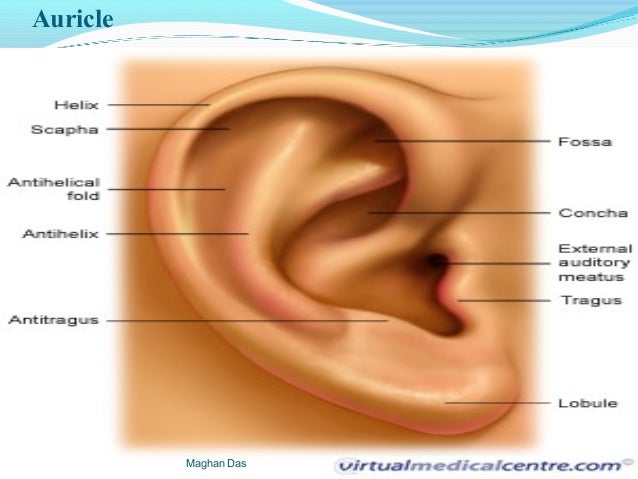 Anatomy And Physiology Of Ear By Maghan Das
Anatomy And Physiology Of Ear By Maghan Das
 Human Ear And Physiology Of Hearing
Human Ear And Physiology Of Hearing
 Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica
Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica
![]() Basic Human Ear Anatomy And Physiology Outer Middle And
Basic Human Ear Anatomy And Physiology Outer Middle And
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear"
Posting Komentar