Anatomy Of Neuron
Neurons or nerve cells are specialized cells that transmit and receive electrical signals in the body. Neuron also called nerve cell basic cell of the nervous system in vertebrates and most invertebrates from the level of the cnidarians eg corals jellyfish upward.
Human Anatomy Physiology At Free Ed Net
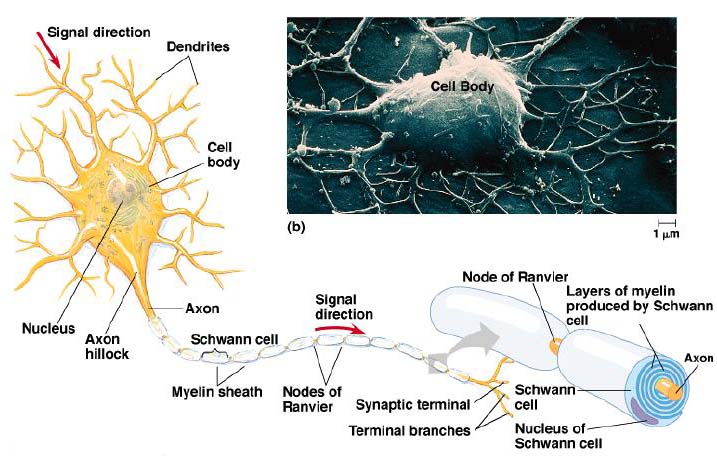
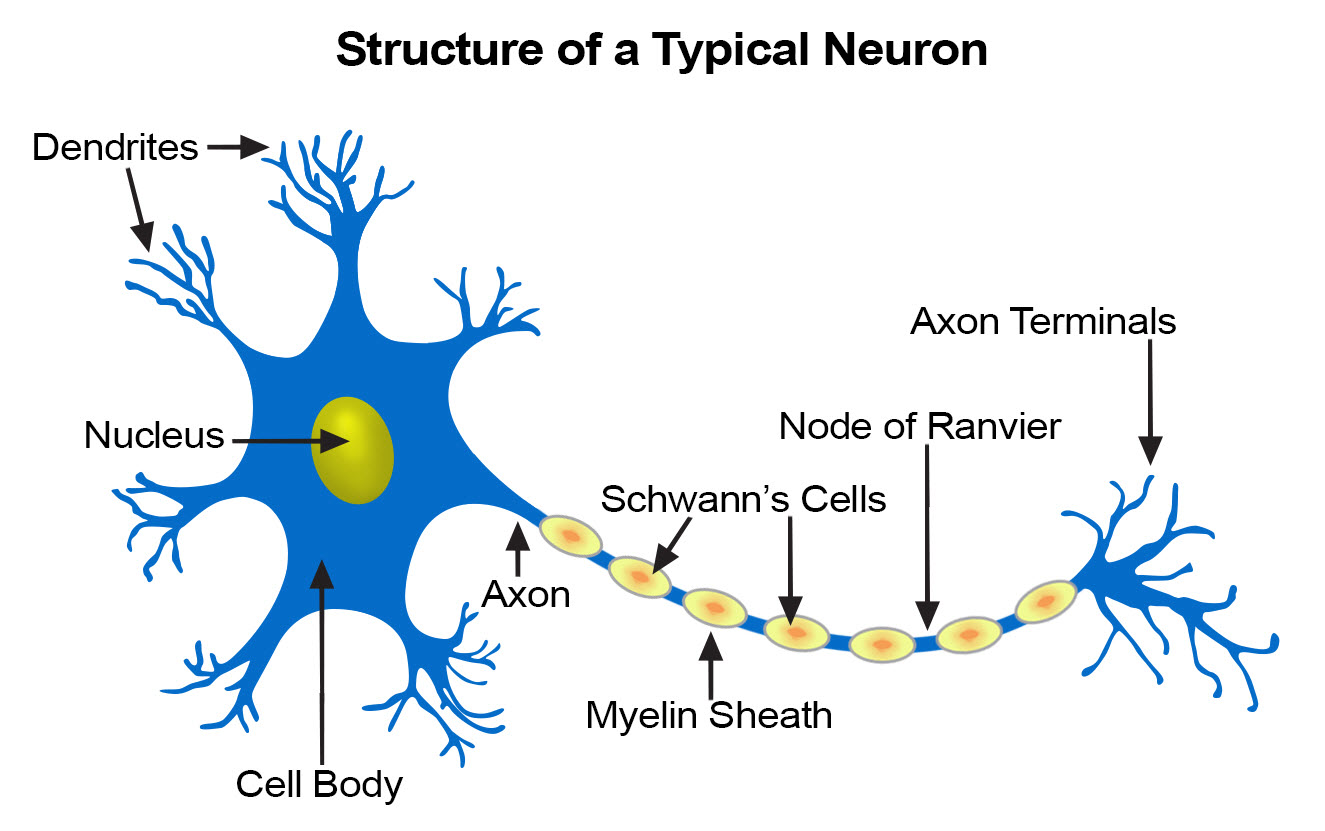
The central cell body is the largest part of a neuron and contains the neurons nucleus associated cytoplasm organelles and other cell structures.

Anatomy of neuron. Lies entirely within the cns. From there the signal travels to the main cell body known as the soma. These inter neurons sum up all the messages from these neurons before they communicate with the motor neurons.
Axon nerve fibre. And at the end it ends at the axon terminal where it can connect to other dendrites or maybe to other types of tissue or muscle if the point of this neuron is to tell a muscle to do something. So the axon will look something like this.
The basic structure of a nerve is that of a cell body soma. Processes information nerves of the body cranial and spinal nerves. Synapse the point where the end button sends the message to the next n the nervous system is the bodys information gatherer storage brain and spinal cord.
Dendrites a cell body and an axon. A neuron also known as a neurone old british spelling or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. So at the end of the axon you have the axon terminal right there.
The nucleus of the neuron is found in the soma. The neurons dendrites are effectively branching extensions of the cell body. Various processes appendages or protrusions extend from the cell body.
A neuron that connects afferent and efferent neurons. Presynaptic neuron first neuron that is sending the message. Myelin sheaths cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep the electrical signal inside the cell which makes it move more quickly.
Neurons like other cells have a cell body called the soma. Soma cell body the soma or cell body is the central part of the neuron and contains. A typical neuron has a cell body containing a nucleus and two or more long fibres.
Anatomy of a neuron. Next the signal leaves the soma and travels down the axon to the synapse. A neuron consists of two major parts.
Can receive input from sensory neurons and also from other inter neurons in the cns. A cell body and nerve processes. Neurons basic nerve structure.
Neurons need to produce a lot of proteins and most neuronal proteins are synthesized in the soma as well. It is the main component of nervous tissue. Neurons are composed of three main parts.
Neurons contain the same cellular components as other body cells.
Nervous System Overview Anatomy And Physiology
 Types Of Neurons By Structure Neuroanatomy Basics Anatomy Tutorial
Types Of Neurons By Structure Neuroanatomy Basics Anatomy Tutorial
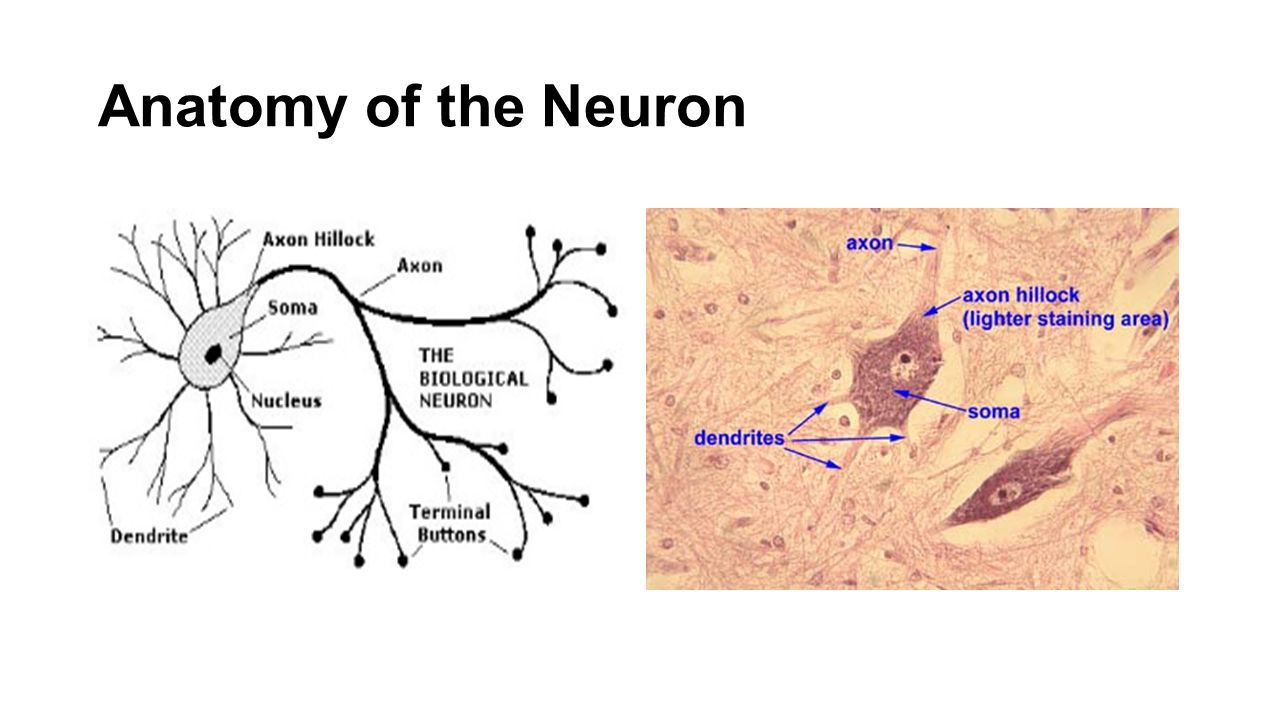 Anatomy Physiology Of The Neuron Ppt Video Online Download
Anatomy Physiology Of The Neuron Ppt Video Online Download
 Neuron Anatomy And Myelin Sheath Art Print Poster
Neuron Anatomy And Myelin Sheath Art Print Poster
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/purkinje_neuron-599da56d396e5a0011a0d344.jpg) Neuron Anatomy Nerve Impulses And Classifications
Neuron Anatomy Nerve Impulses And Classifications
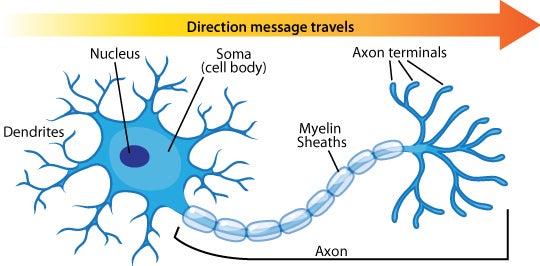 Neuron Diagram Types Ask A Biologist
Neuron Diagram Types Ask A Biologist
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neuron-anatomy-58530ffe3df78ce2c34a7350.jpg) Neuron Anatomy Nerve Impulses And Classifications
Neuron Anatomy Nerve Impulses And Classifications
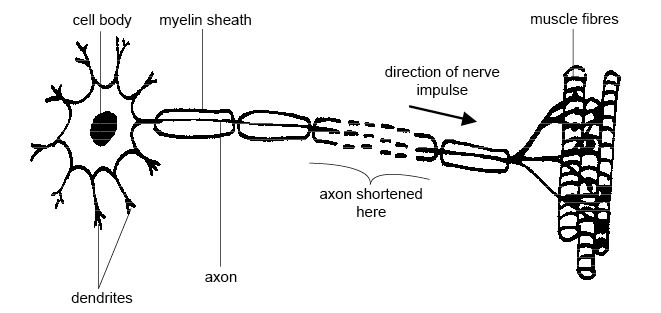 Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Nervous System Wikibooks
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Nervous System Wikibooks
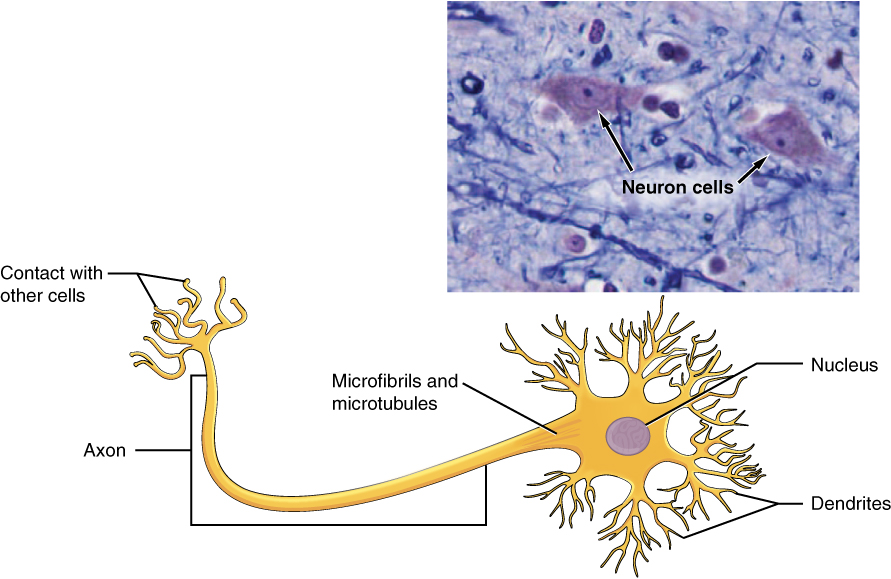 4 5 Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception And Response
4 5 Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception And Response
 Anatomy Of A Typical Human Neuron Axon Synapse Dendrite Mitochondrion
Anatomy Of A Typical Human Neuron Axon Synapse Dendrite Mitochondrion
 Neuron Nerve Cell Anatomy Clipart K47695721 Fotosearch
Neuron Nerve Cell Anatomy Clipart K47695721 Fotosearch
 Aab Neuron Anatomy Activity Pdf Document
Aab Neuron Anatomy Activity Pdf Document
 Neuron Bipolar Anatomy Infographic Stock Vector
Neuron Bipolar Anatomy Infographic Stock Vector
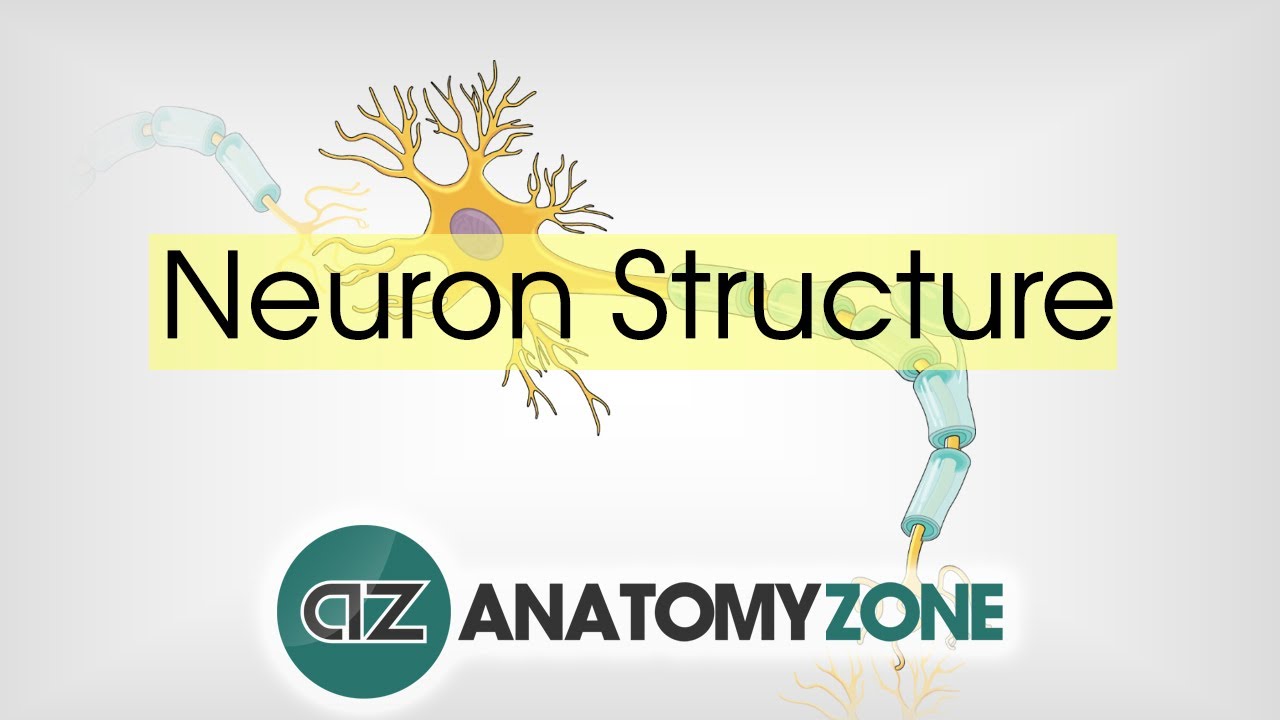 Neuron Structure Neuroanatomy Basics Anatomy Tutorial
Neuron Structure Neuroanatomy Basics Anatomy Tutorial
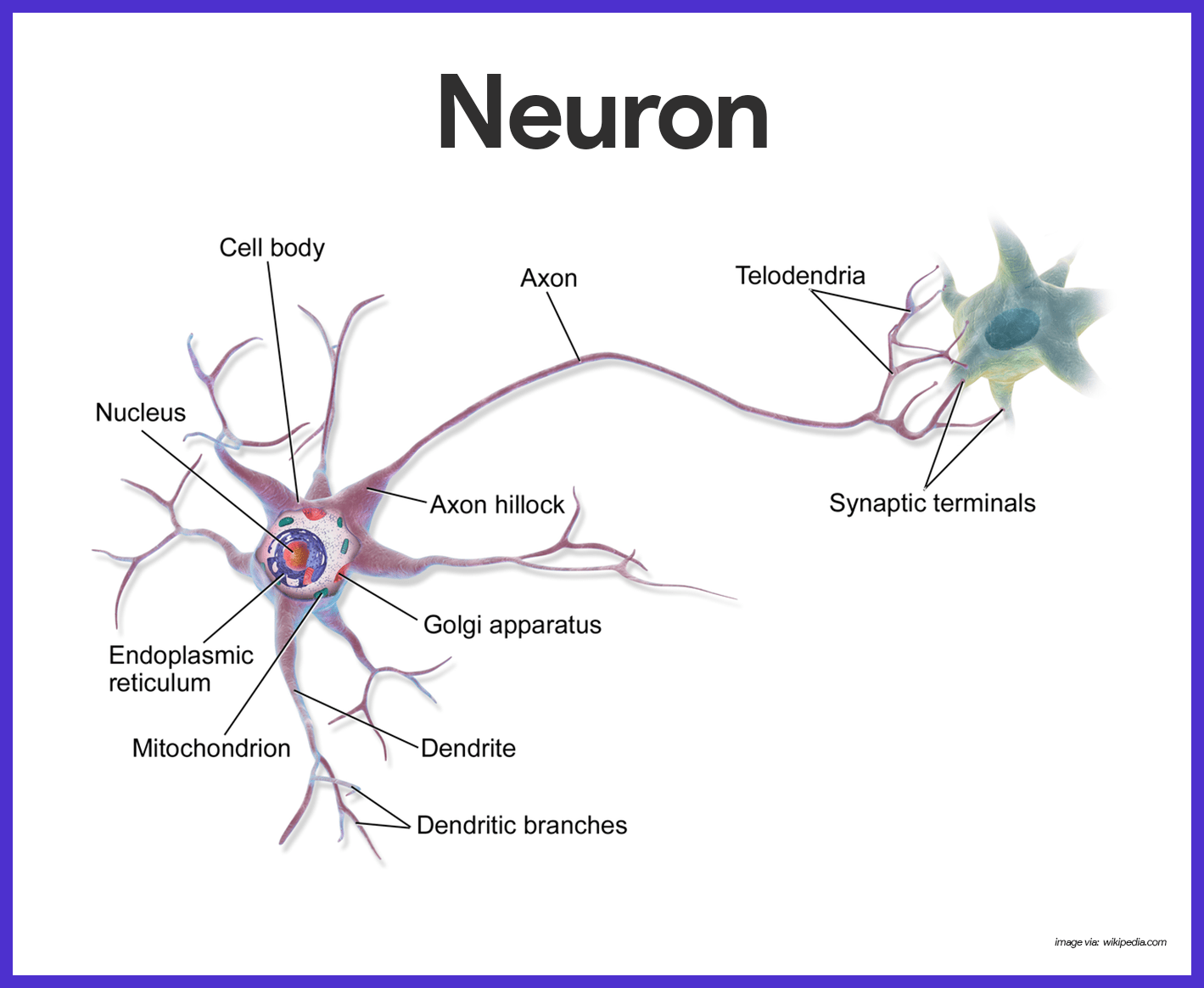 Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Neuron Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Neuron Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Anatomy Of A Typical Human Neuron Art Print
Anatomy Of A Typical Human Neuron Art Print
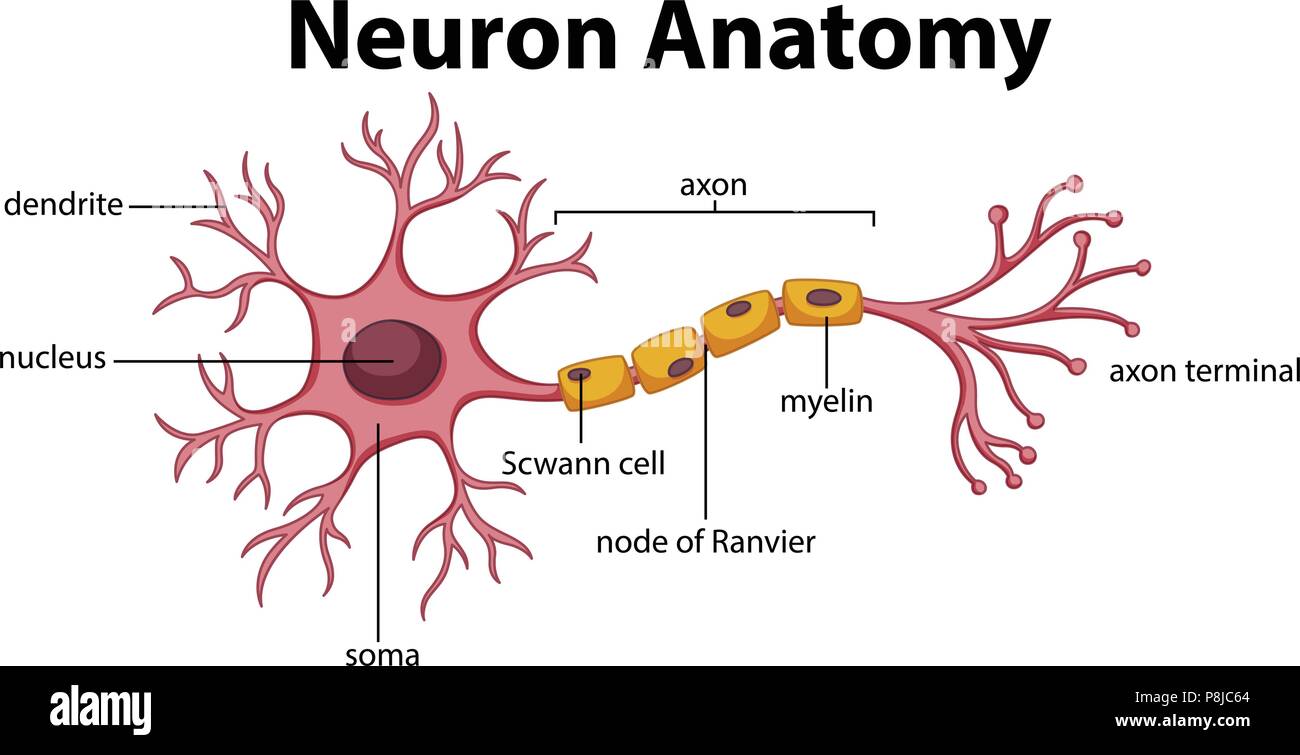 Diagram Of Neuron Anatomy Illustration Stock Vector Art
Diagram Of Neuron Anatomy Illustration Stock Vector Art
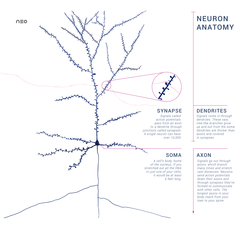
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Neuron"
Posting Komentar