Forehead Anatomy
In men the supraorbital rim is more prominent in its lateral third and there may be a convexity of the upper forehead in association with prominent frontal bossing over the frontal sinus. The skin connective subcutaneous tissue galea aponeurotica loose areolar connective tissue and periosteum.
Factors of sex age familial characteristics.

Forehead anatomy. If we start from the skin layer and reflect this back we will notice that there is a scant amount of subcutaneous fat just below the skin. Cladists classify land vertebrates based on the presence of an upper hole a lower hole both or neither in the cover of dermal bone that formerly covered the temporalis muscle whose origin is the temple and whose insertion is the jaw. It is delineated superiorly by the hairline and inferiorly by the glabella and frontonasal groove centrally and the eyebrows overlying the supraorbital ridges laterally the hairline is not a stable landmark among individuals.
Forehead anatomy introduction surgery in the upper third of the face whether reconstructive or cosmetic can be considered to involve at least 1 of 3 regions. Temple anatomy the bone beneath is the temporal bone as well as part of the sphenoid bone. Abramo ac1 do amaral tp2 lessio bp2 de lima ga2.
Forehead anatomy the bony anatomy is defined primarily by the supraorbital ridges which form the upper boundary of the orbit and separate the mid face from the forehead. Anatomy of forehead glabellar nasal and orbital muscles and their correlation with distinctive patterns of skin lines on the upper third of the face. The anatomy of the forehead for discussion purposes can be compartmentalised but practically it is important to have a complete picture of the anatomy if one wants to perform surgery in that area.
The top of the forehead is marked by the hairline the edge of the area where hair on the scalp grows. The central forehead the hair bearing scalp and the temporal regions. Below this fat layer we have the muscle layer the main muscle being the frontalis.
Being an anatomical continuity of the scalp it consists of the same five distinct layers. In this video we are going to review some of the forehead. The forehead constitutes the upper third of the face.
The observations of the supraorbital nerve are of surgical significance and were included. The forehead could be considered as the hairless frontal elongation of the scalp. In human anatomy the forehead is an area of the head bounded by three features two of the skull and one of the scalp.
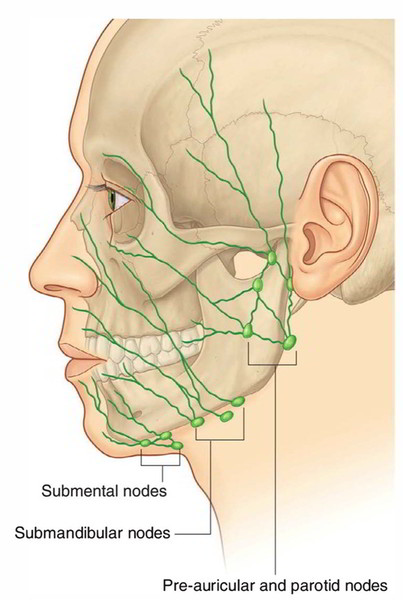 Easy Notes On Lymphatic Drainage Of The Face Learn In
Easy Notes On Lymphatic Drainage Of The Face Learn In
 Head Surface Anatomy 4 Edition
Head Surface Anatomy 4 Edition
 Retained Surgical Gauze In Forehead Medical Illustration
Retained Surgical Gauze In Forehead Medical Illustration
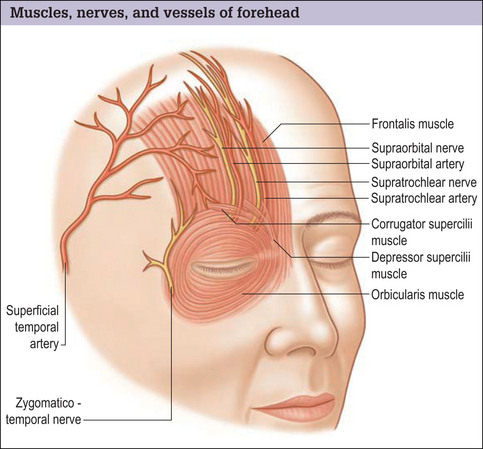 Forehead Rejuvenation Clinical Gate
Forehead Rejuvenation Clinical Gate
 Biology Of The Vertebrates A Comparative Study Of Man And
Biology Of The Vertebrates A Comparative Study Of Man And
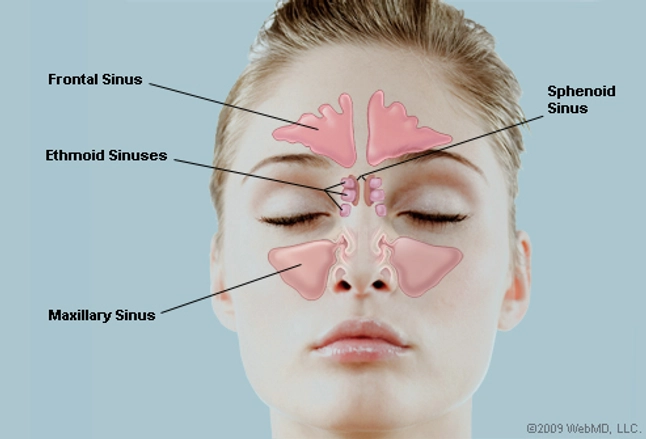 What Are The Sinuses Pictures Of Nasal Cavities
What Are The Sinuses Pictures Of Nasal Cavities
![]() Forehead Png Forehead Kiss Forehead Anatomy
Forehead Png Forehead Kiss Forehead Anatomy
 Facial Landmarks An Overview Of Dental Anatomy
Facial Landmarks An Overview Of Dental Anatomy
 Face Muscle Anatomy Illustration Stock Image C046 1440
Face Muscle Anatomy Illustration Stock Image C046 1440
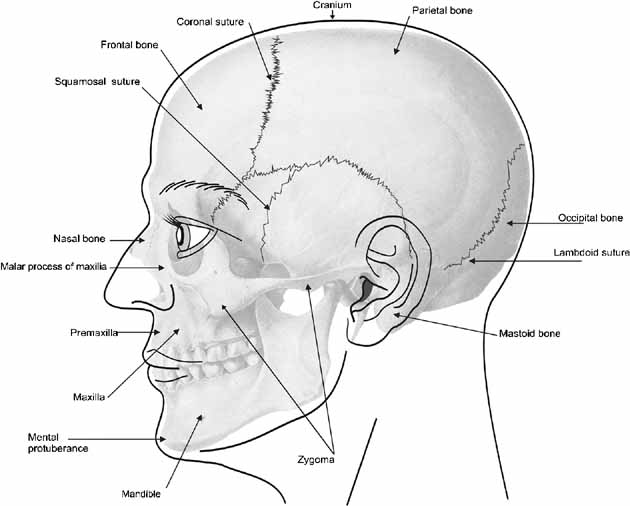 Elements Of Morphology Human Malformation Terminology
Elements Of Morphology Human Malformation Terminology
 Understanding The Functional Anatomy Of The Frontalis And
Understanding The Functional Anatomy Of The Frontalis And
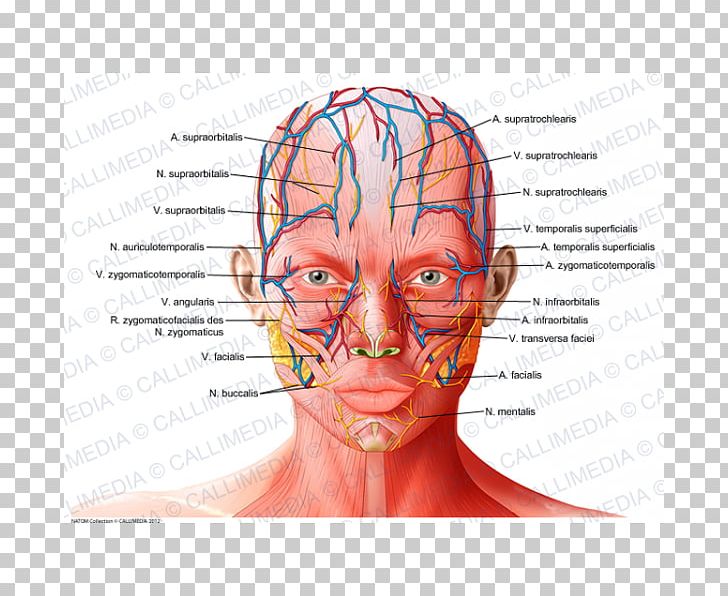 Forehead Anatomy Supratrochlear Artery Supraorbital Artery
Forehead Anatomy Supratrochlear Artery Supraorbital Artery
 Face Anatomy For Makeup Understanding Technical Terms Of
Face Anatomy For Makeup Understanding Technical Terms Of
Video Gallery Plastic And Reconstructive Surgery Global Open
 Soft Anatomy Of The Forehead In The Extant Physeter And
Soft Anatomy Of The Forehead In The Extant Physeter And
Anatomy Of The Face Hill Country Cosmetics
 Cutaneous Surgical Anatomy Fitzpatrick S Dermatology 9e
Cutaneous Surgical Anatomy Fitzpatrick S Dermatology 9e
 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
 What Is The Name Of The Bone In The Forehead Socratic
What Is The Name Of The Bone In The Forehead Socratic
 An Atlas Of Human Anatomy For Students And Physicians
An Atlas Of Human Anatomy For Students And Physicians
 Chapter 20 Superficial Face The Big Picture Gross
Chapter 20 Superficial Face The Big Picture Gross
 Full Text Tailored Botulinum Toxin Type A Injections In
Full Text Tailored Botulinum Toxin Type A Injections In
 Forehead Anatomy Surface Anatomy Bones Of The Forehead
Forehead Anatomy Surface Anatomy Bones Of The Forehead
 Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
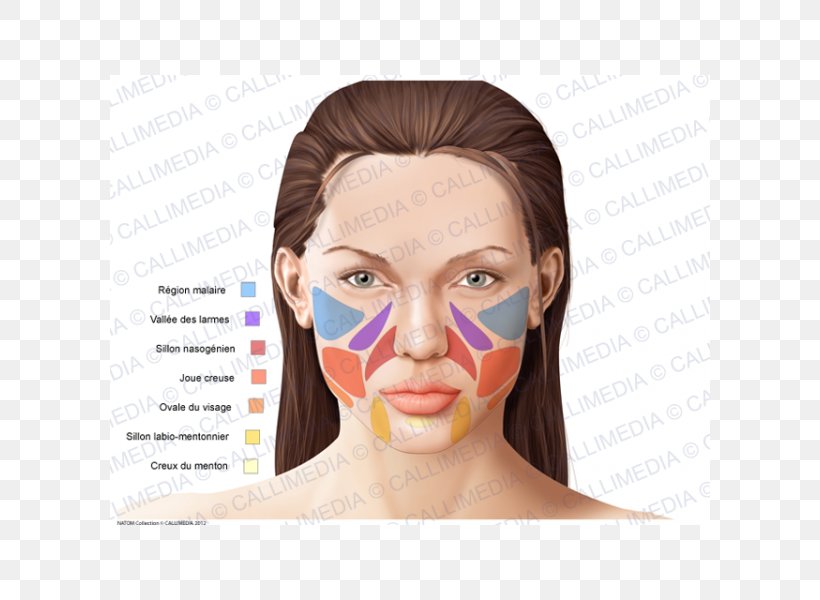 Human Anatomy Nose Chin Zygomatic Bone Png 600x600px
Human Anatomy Nose Chin Zygomatic Bone Png 600x600px
 Facial Muscles And Expressions Classic Human Anatomy In
Facial Muscles And Expressions Classic Human Anatomy In
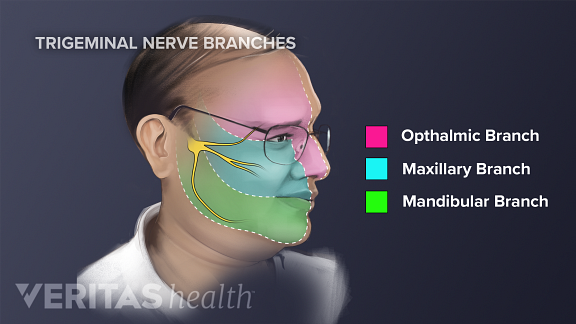
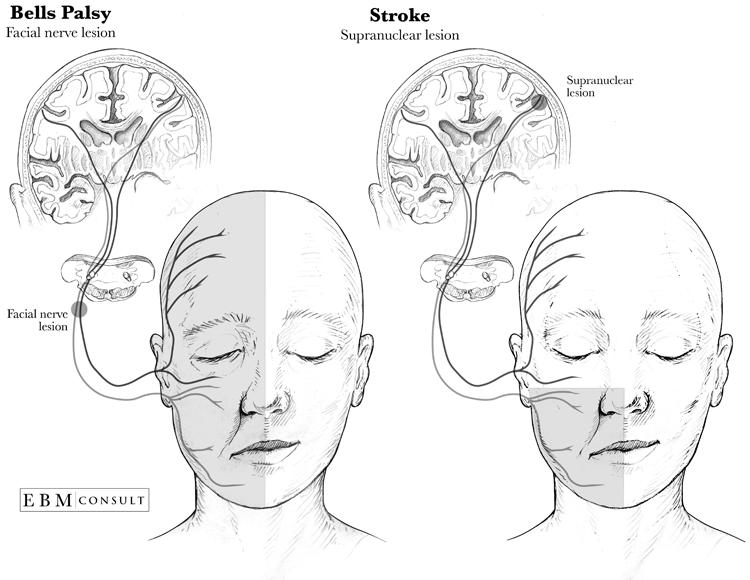


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Forehead Anatomy"
Posting Komentar