Fascia Anatomy
If we could. There are three main types of fascia.
 Fascia Definition Anatomy Overview Topics Pretty Investing
Fascia Definition Anatomy Overview Topics Pretty Investing
Collagen collagen fibers are the longest molecules ever found.

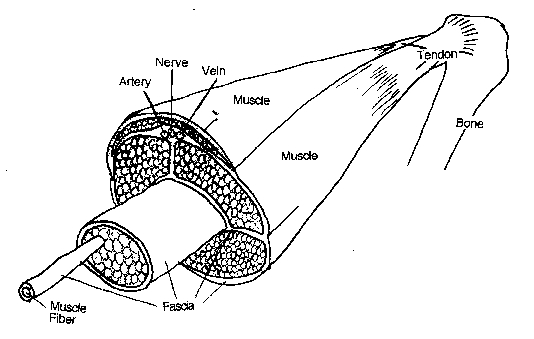
Fascia anatomy. They are all related and they work in concert with one another. Connective tissue is the most pervasive and has three basic ingredients. Fascia is a layer of fibrous tissue that surrounds muscles vessels and nerves.
Fascia has many designations for different areas topologies. The answer lies in fascia. The fascias location and design membranes or other dissectible connective tissue compositions including bindings to internal organs.
Lots of connective tissue large enough to see with the naked eye it has been noted that the fibers. Fascia is internal connective tissue that wraps around organs providing support and holding parts together. All forms of connective tissue are made up of the same elements.
They include collagen elastic fibers and ground fluid. Fibrous collagen tissue that is part of the bodys power. Muscle nervous epithelial and connective tissue.
Your body actually has a system like this in place only its on the inside where we cant see. Beyond the extra cellular matrix. Anatomy atlases and kinesiology texts tend to reduce us.
These 4 types of tissue make up every structure in our body. Superficial fascia which is mostly associated with the skin. Anatomy of fascia there are 4 types of tissue.
It has the appearance of a very thin spider web connecting layers of muscle and surrounding all internal body tissues. Each variety of connective tissue is merely a slightly different chemical makeup from the next form. Deep fascia which is mostly associated with the muscles bones nerves and blood vessels.
Visceral or subserous fascia which is mostly associated with the internal organs. Fascia as a system. These are collagen elastin and ground substance.
Fascia is a web of connective tissue formed in bands that wraps around all the internal parts of the body from head to toe and fuses it all together. In the neck there are several layers of fascia which act to support and compartmentalise the structures of the neck. In fact fascia could be the answer to a lot of questions about structure movement stability pain and healing.
Fascia is one network embryologically and anatomically.
 The Top 5 Ways Fascia Matters To Athletes Breaking Muscle
The Top 5 Ways Fascia Matters To Athletes Breaking Muscle
 Superficial Fascia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Superficial Fascia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Fascia Iliaca Block Nysora Regional Anesthesia App
Fascia Iliaca Block Nysora Regional Anesthesia App
 Fascia The Facts Complete Anatomy
Fascia The Facts Complete Anatomy
 Fascia Anatomy And Properties Atlasbalans
Fascia Anatomy And Properties Atlasbalans
 What Is Fascia In Anatomy Definition Tears Video
What Is Fascia In Anatomy Definition Tears Video
What Is Fascia Pierce Performance
 Fascia Friday Part 2 Superficial Front Line Phe
Fascia Friday Part 2 Superficial Front Line Phe
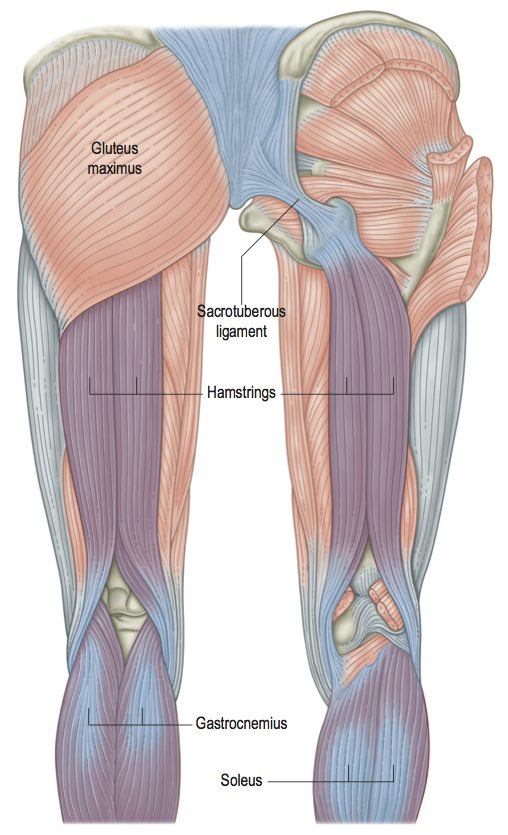 Pure Fascial Release Vs Myofascial Release Anatomy Trains Blog
Pure Fascial Release Vs Myofascial Release Anatomy Trains Blog
 Deep Fascia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Deep Fascia An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
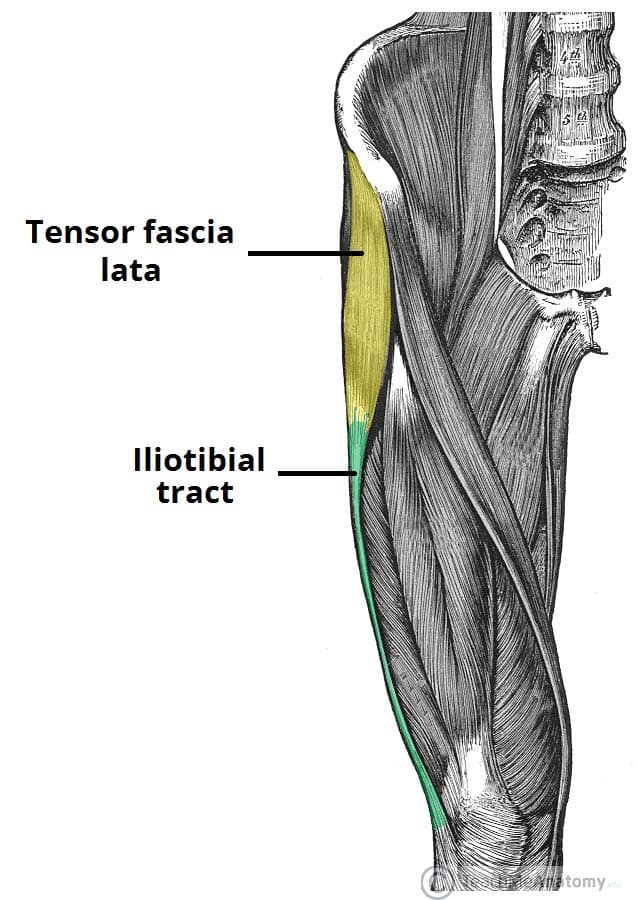 The Fascia Lata Structure Iliotibial Tract Teachmeanatomy
The Fascia Lata Structure Iliotibial Tract Teachmeanatomy
 Eight Fascinating Facts About Fascia Fit N Pilates
Eight Fascinating Facts About Fascia Fit N Pilates
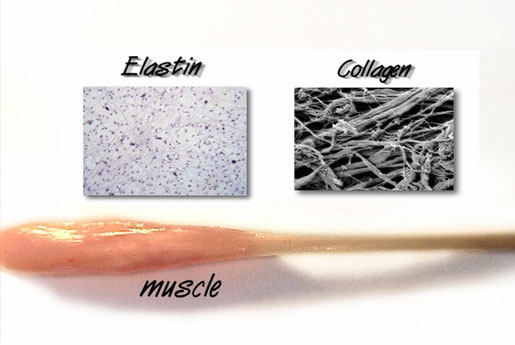 Lesson 1 Anatomy Of Fascia Real Bodywork
Lesson 1 Anatomy Of Fascia Real Bodywork
Notes On Anatomy And Physiology Function Of The
 Thoracolumbar Fascia Wikipedia
Thoracolumbar Fascia Wikipedia
 Plantar Fascia Anatomy Plantar Aponeurosis Anatomy
Plantar Fascia Anatomy Plantar Aponeurosis Anatomy
 Understanding Fascia The Tissues That Hold You Together
Understanding Fascia The Tissues That Hold You Together
 Fascia Movement Assessments Course Canfitpro
Fascia Movement Assessments Course Canfitpro
 Notes On Anatomy And Physiology The Thoracolumbar Fascia
Notes On Anatomy And Physiology The Thoracolumbar Fascia
 Anatomy Fascia Stock Illustrations 153 Anatomy Fascia
Anatomy Fascia Stock Illustrations 153 Anatomy Fascia
 Aponeurosis Definition Function
Aponeurosis Definition Function
 Anatomy Trains Archives Learn Muscles
Anatomy Trains Archives Learn Muscles
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/iStock-512120924-587fdd2b3df78c2ccdefff99.jpg) The Fascia And Muscle Movement
The Fascia And Muscle Movement
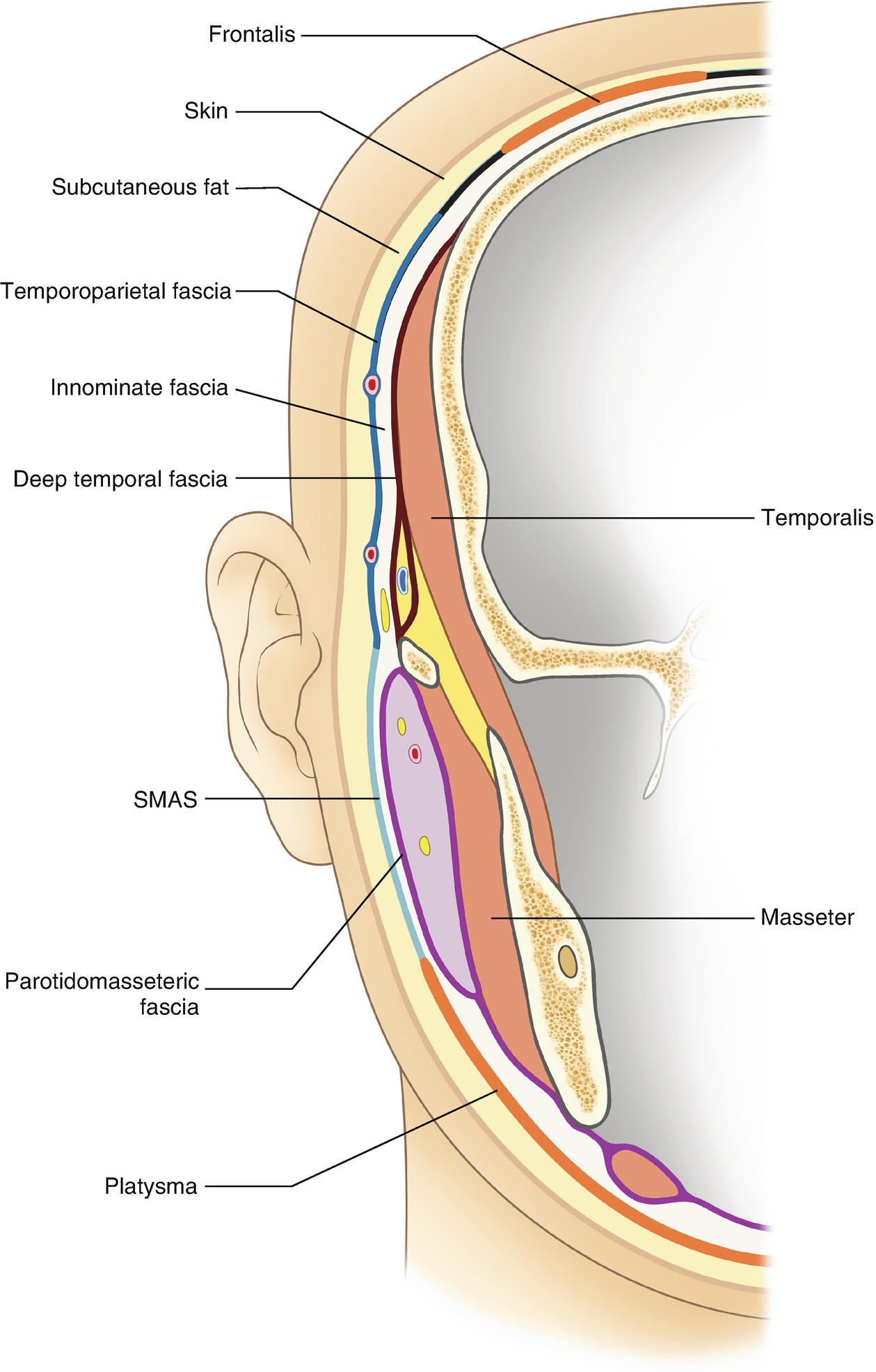 Anatomy For Absorbable Thread Lifting Springerlink
Anatomy For Absorbable Thread Lifting Springerlink
 Notes On Anatomy And Physiology Function Of The
Notes On Anatomy And Physiology Function Of The
 Ultrasound Guided Transversus Abdominis Plane And Quadratus
Ultrasound Guided Transversus Abdominis Plane And Quadratus


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Fascia Anatomy"
Posting Komentar