Anatomy Hip Joint
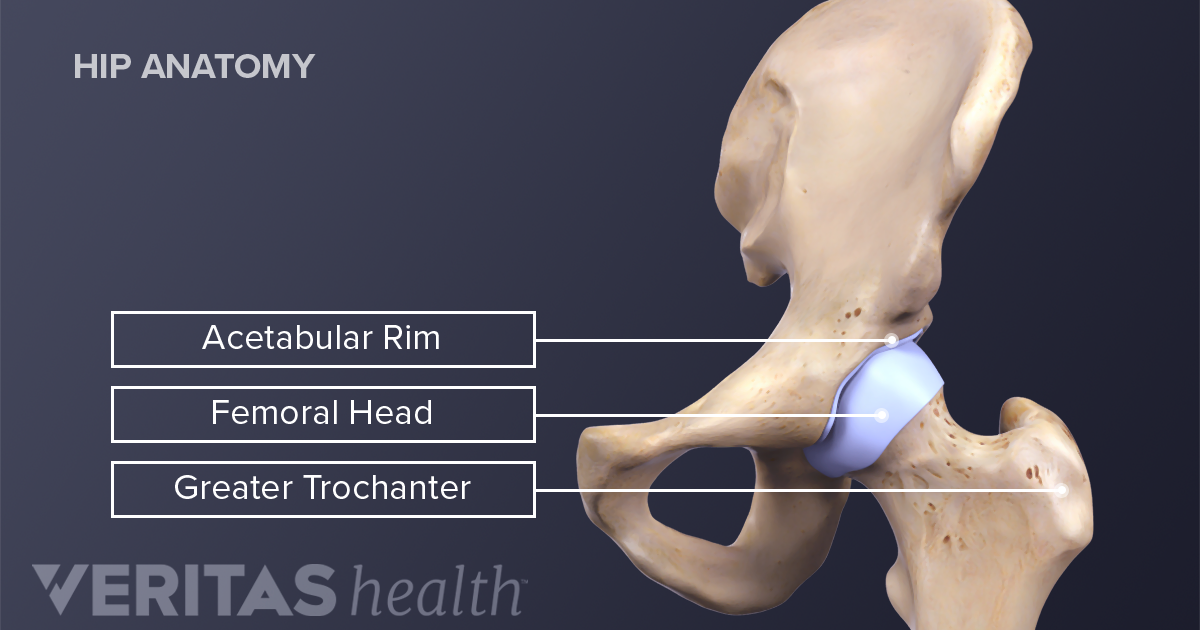
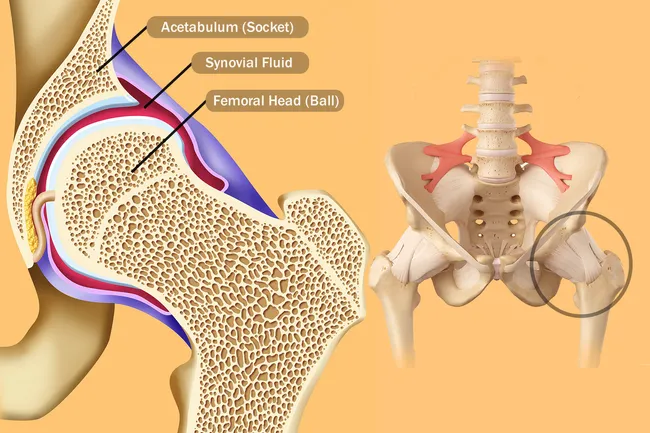
It forms a connection from the lower limb to the pelvic girdle and thus is designed for stability and weight bearing rather than a large range of movement. The hip joint is a ball and socket synovial joint formed by an articulation between the pelvic acetabulum and the head of the femur.
 Yoga For Hip Stability Understanding Hypermobility
Yoga For Hip Stability Understanding Hypermobility
Quadriceps a group of four muscles that comprise the.
Anatomy hip joint. The movements of the hip joint is thus performed by a series of muscles which are here presented in order of importance with the range of motion from the neutral zero degree position indicated. Large ligaments tendons and muscles around the hip joint hold the bones ball and socket in place and keep it from dislocating. The hip joint is a ball and socket type joint and is formed where the thigh bone femur meets the pelvis.
This portion is referred to as the head of the femur or femoral head. The hip joint is the articulation of the pelvis with the femur which connects the axial skeleton with the lower extremity. The adult os coxae or hip bone is formed by the fusion of the ilium the ischium and the pubis which occurs by the end of the teenage years.
Its primary function is to make the legs mobile without weakening the ability to support the weight of human body in both static and dynamic postures. Hip joint is technically known as acetabulofemoral joint occurs between acetabulum and femur. It is a synovial ball and socket joint that occurs between head of femur and acetabulum of hip bone.
Lateral or external rotation 30 with the hip extended 50 with the hip flexed. It is the largest bone in the body. Hip muscles the hip joint is surrounded by several muscles including.
The iliopsoas muscle which extends from the lower back to upper femur. The femur has a ball shaped head on its end that fits into a socket formed in the pelvis called the acetabulum. There are two other protrusions near the top of the femur known as the greater and lesser trochanters.
The hip joint is one of the most important joints in the human body. It allows us to walk run and jump. Bones of the hip joint.
The range of movements of the hip joint are marked in degrees and are categorised by name. It bears our bodys weight and the force of the strong muscles of the hip and leg. At the top of the femur is a rounded protrusion which articulates with the pelvis.
Gluteal muscles located on the back of the hip buttocks. The adductor muscle on the inner thigh. Yet the hip joint is also one of our most flexible joints and allows a greater range of motion than all other joints in the body except for the shoulder.
 Hip Anatomy Yoga Understanding The Hips For Yoga Jason
Hip Anatomy Yoga Understanding The Hips For Yoga Jason
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/hip-joint-3/viwpOeWZpKjfLaqqpsJJw_Hip_Joint_01.png) Hip Joint Ligaments Movements Muscles Kenhub
Hip Joint Ligaments Movements Muscles Kenhub
Ligaments Of The Lumbar Spine And Pelvis
 Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
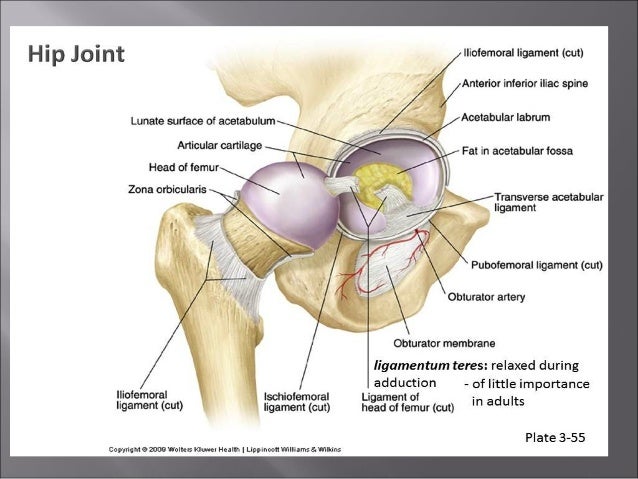 Anatomy Of The Hip Joint Anoop
Anatomy Of The Hip Joint Anoop
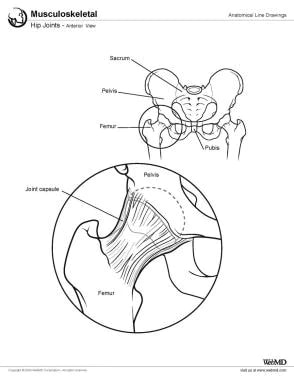 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
 Osteoarthritis Definition Causes Symptoms Treatment
Osteoarthritis Definition Causes Symptoms Treatment
 Total Hip Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
Total Hip Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
 Normal Hip Joint Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Normal Hip Joint Anatomy Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
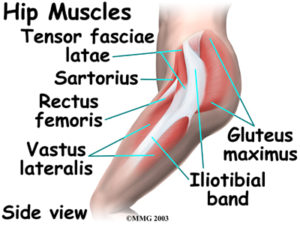 Ligaments Tendons And Muscles Of The Hip Joint Naples
Ligaments Tendons And Muscles Of The Hip Joint Naples
Basics Of Hip Anatomy Mike Scaduto
Osteonecrosis Of The Hip Orthoinfo Aaos
Hip Labral Tear Cleveland Clinic
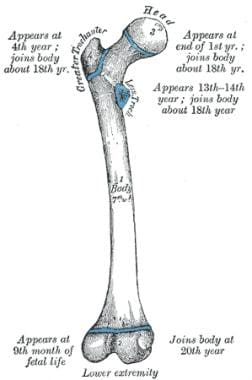 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
 Hip Surgery Illustrations Pelvis Hip Anatomy Medical
Hip Surgery Illustrations Pelvis Hip Anatomy Medical
Hip Joint Treatment Sydney Hip Ligaments Treatment Sydney
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11162/anatomy-hip-joint_english.jpg) Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
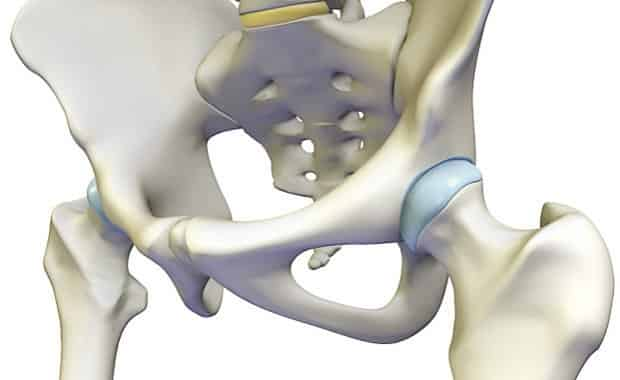 Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles
Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles
 1 Anatomy Of Hip Joint Adapted From 33 Download
1 Anatomy Of Hip Joint Adapted From 33 Download
 Hip Joint Post Thigh Knee Anatomy 5007 With Steven Popoff
Hip Joint Post Thigh Knee Anatomy 5007 With Steven Popoff
 Hip Joint Bones Ligaments Blood Supply And Innervation Anatomy Kenhub
Hip Joint Bones Ligaments Blood Supply And Innervation Anatomy Kenhub
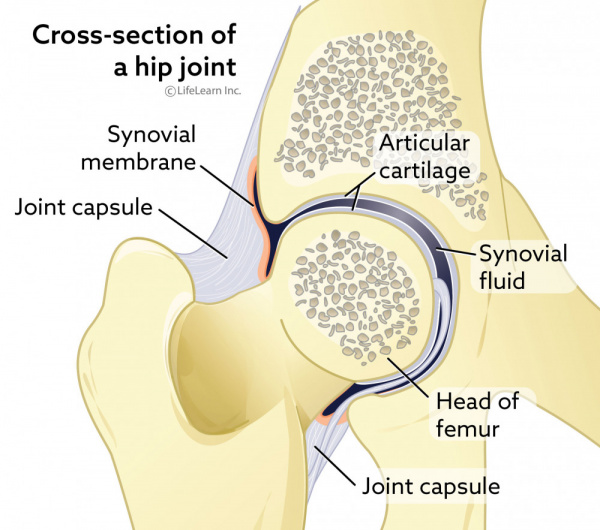 Hip Dislocation And Post Operative Care In Cats Vca Animal
Hip Dislocation And Post Operative Care In Cats Vca Animal
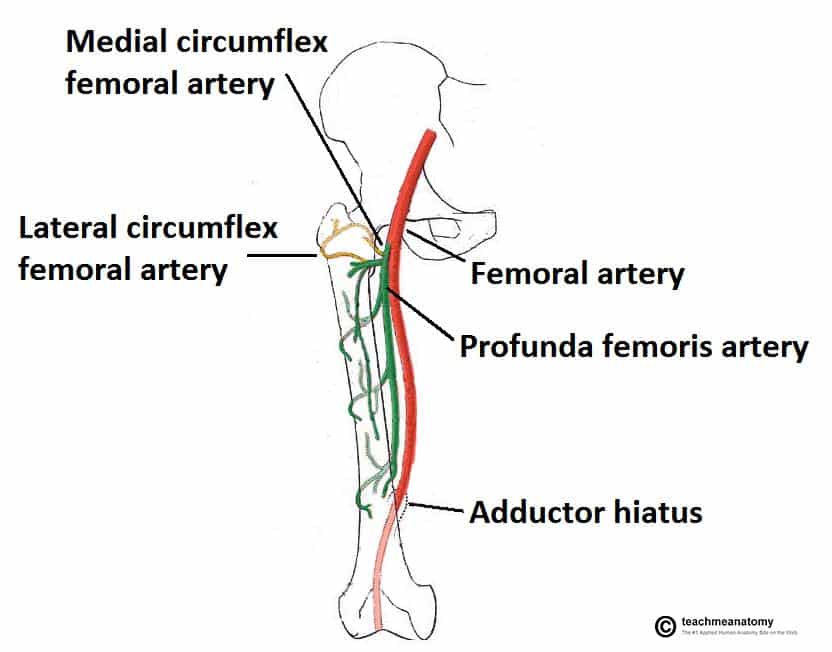 The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Hip Joint"
Posting Komentar