Orbital Definition Anatomy
Ta the mostly sharp edge of the orbital opening that is the peripheral border of the base of the pyramidal orbit. The inferior half is the infraorbital margin.
 Bony Orbit Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Bony Orbit Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Medially it is thin and becoming separated from the medial palpebral ligament.
Orbital definition anatomy. Sympathetic root comes from ica plexus and enters through superior orbital fissure. Protects the body keeps harmful material out regulates body temperature senses and responds to the environment and creates important chemicals. Orbital cavity the bony cavity in the skull containing the eyeball.
The medial orbital rim is less defined than the other rims. Cranial orbit eye socket orbit. A wave function describing the state of a single electron in an atom atomic orbital or in a molecule molecular orbital.
When the eyes are closed the whole orbital opening is covered by the septum and tarsi. Orbita ta orbital cavity. A long sensory root from the nasociliary branch of v1 10 12 mm with fibers from cornea iris and ciliary body.
The electron in that state. Dictionary thesaurus legal encyclopedia. The bony cavity containing the eyeball and its adnexa.
In the upper eyelid the orbital septum blends with the tendon of the levator palpebrae superioris and in the lower eyelid with the tarsal plate. Bodily cavity cavum cavity anatomy a natural hollow or sinus within the body. Short motor root from inferior division of cn iii supplying the inferior oblique postganglionic fibers supply the iris sphincter.
The entire wall is thin from the base to the apex but it is strengthened by the perpendicular septa of the ethmoid sinus. Anatomy and physiology chapter 1. The medial orbital walls are parallel to the sagittal plane and have the greatest degree of superioinferior curvature.
Orbit anatomy in anatomy the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. Orbit can refer to the bony socket or it can also be used to imply the contents. 101 us fl oz.
Lacrimal bone small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts. In the adult human the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres 106 imp fl oz. It is formed of parts of the frontal maxillary sphenoid lacrimal zygomatic ethmoid and palatine bones.
In anatomy pertaining to the orbit the bony cavity that contains the eyeball. The superior half of the orbital rim is the supraorbital margin.
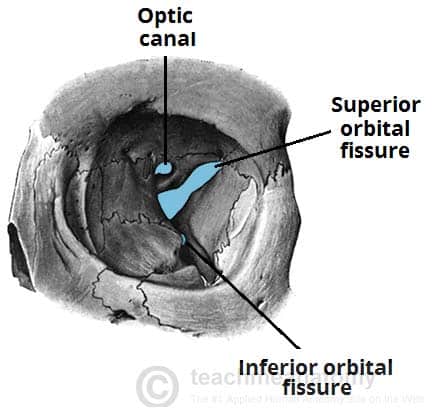 The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures Teachmeanatomy
The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures Teachmeanatomy
Orbit In Cross Section Anatomy The Eyes Have It
 Orbital Chemistry And Physics Britannica
Orbital Chemistry And Physics Britannica
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/processus-zygomaticus-maxilla/cVBMQiB37vcMHqoZ5dlOQ_Zygomatic_process_-_Maxilla_01.png) Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
 Human Eye Definition Structure Function Britannica
Human Eye Definition Structure Function Britannica
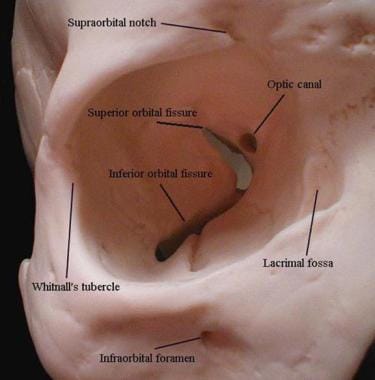 Orbit Anatomy Osteology Lacrimal System Connective Tissue
Orbit Anatomy Osteology Lacrimal System Connective Tissue
Retaining Ligaments Of The Face Review Of Anatomy And
 Orbital Roof Ophthalmology Review
Orbital Roof Ophthalmology Review
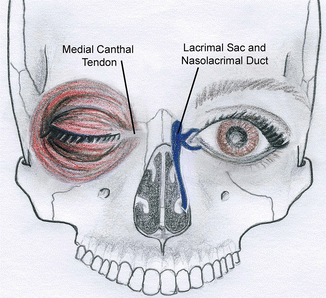 Naso Orbital Ethmoid Fractures Springerlink
Naso Orbital Ethmoid Fractures Springerlink
 What Does Dorso Ventro And Orbital Mean In Prefrontal
What Does Dorso Ventro And Orbital Mean In Prefrontal
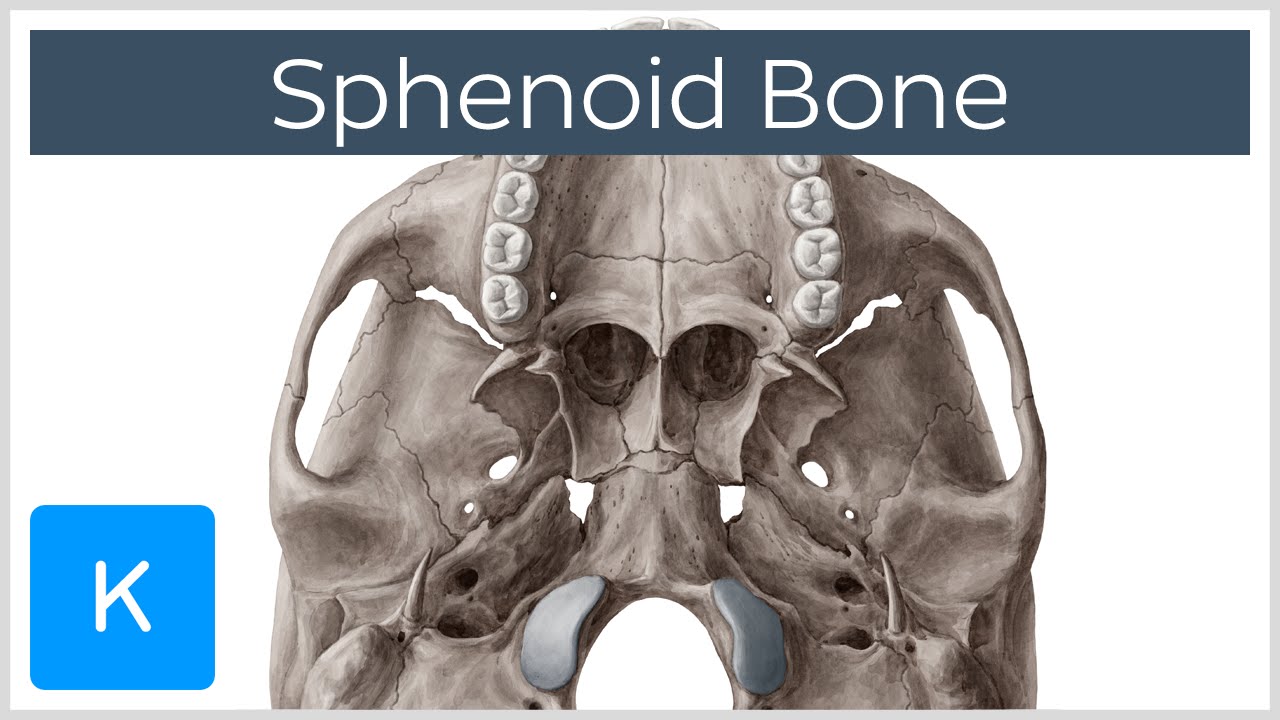 Sphenoid Bone Definition Location Function Human Anatomy Kenhub
Sphenoid Bone Definition Location Function Human Anatomy Kenhub
 Superior Orbital Fissure Wikipedia
Superior Orbital Fissure Wikipedia
 Periorbita An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Periorbita An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Skull Bones Of The Orbit Human Anatomy Kenhub
Skull Bones Of The Orbit Human Anatomy Kenhub
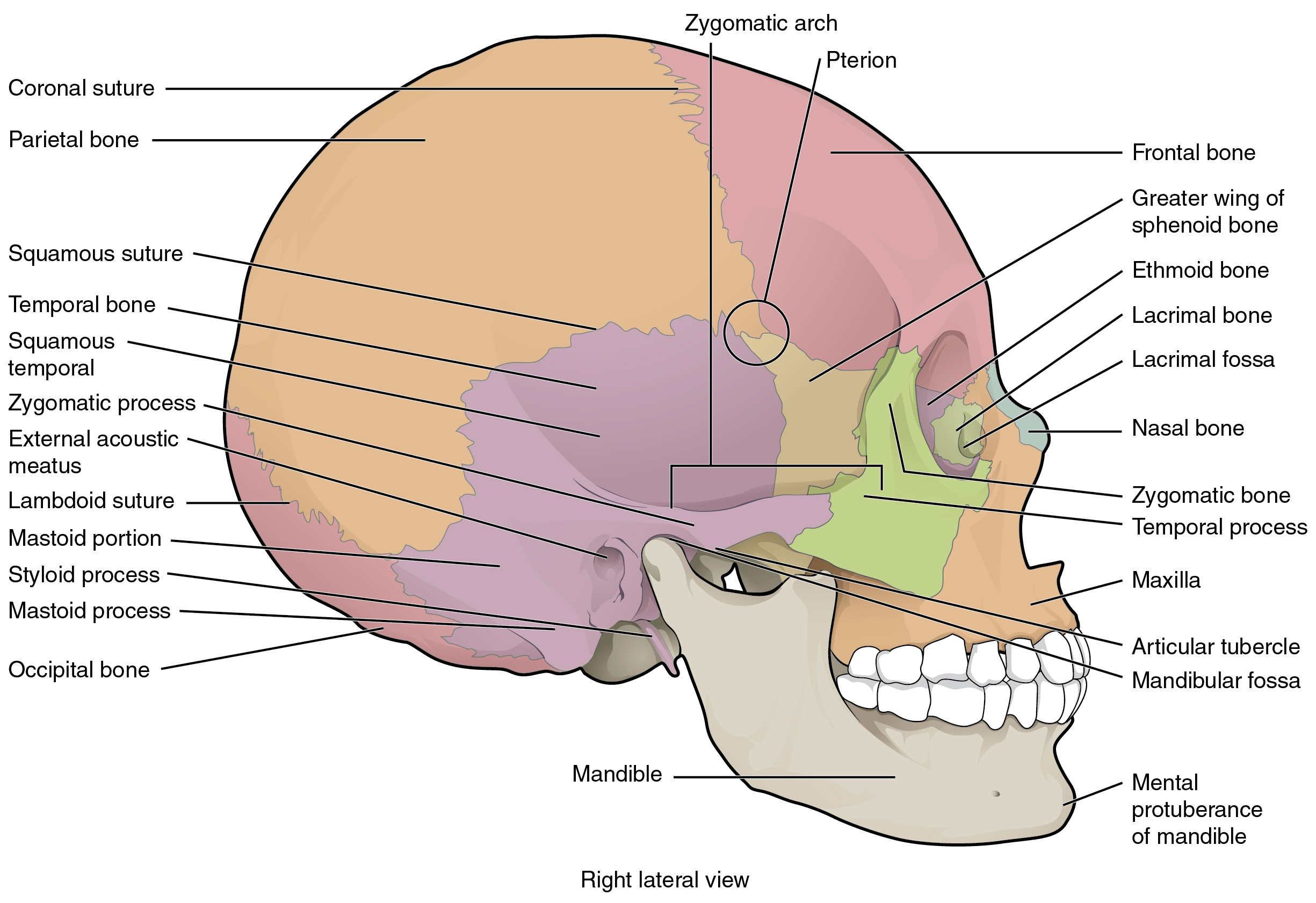 7 2 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
7 2 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
 Anatomy Of The Skull Base And Related Structures Elements
Anatomy Of The Skull Base And Related Structures Elements
 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I
The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I
 Anatomy Lab 2 Optometry 112 With Fitzgerald At Southern
Anatomy Lab 2 Optometry 112 With Fitzgerald At Southern
Orbital Compartment Syndrome Curriculum

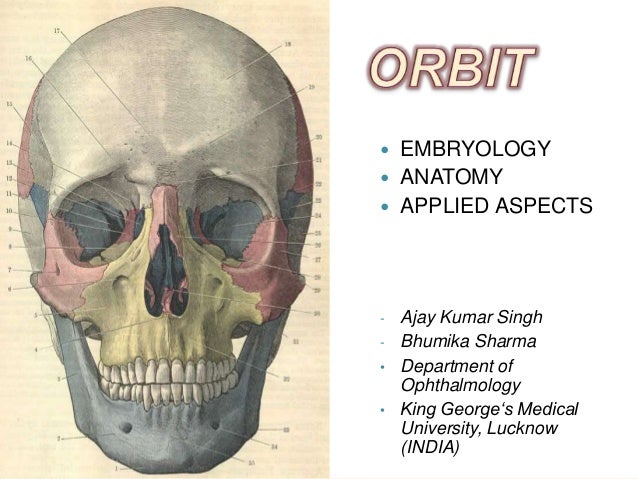

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Orbital Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar