Acetabular Anatomy
Anatomy of human skeleton in human skeleton. The labrum forms a gasket around the socket creating a tight seal and helping to provide stability to the joint.
Search Right Acetabular Anatomy
Elsewhere it is attached to the margins of the acetabulum.

Acetabular anatomy. The hip joint or acetabulum is responsible for many movements including walking. It creates a smooth low friction surface that helps the bones glide easily across each other during movement. Bursae in the hip.
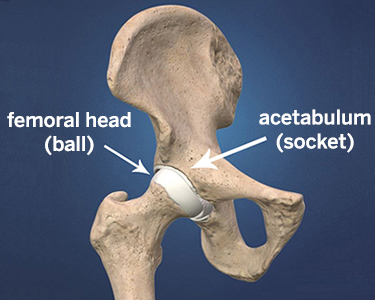
Bursae plural for bursa are flat fluid filled sacs. The acetabulum is the socket of the ball and socket hip joint. The upper leg is called the femur bone and at the very top of that bone there is a ball like structure called the femoral head the closed fist so in short the acetabulum is the cup shaped portion of the hip bone that receives the femoral head of the femur bone and together these two bony structures form the hip joint.
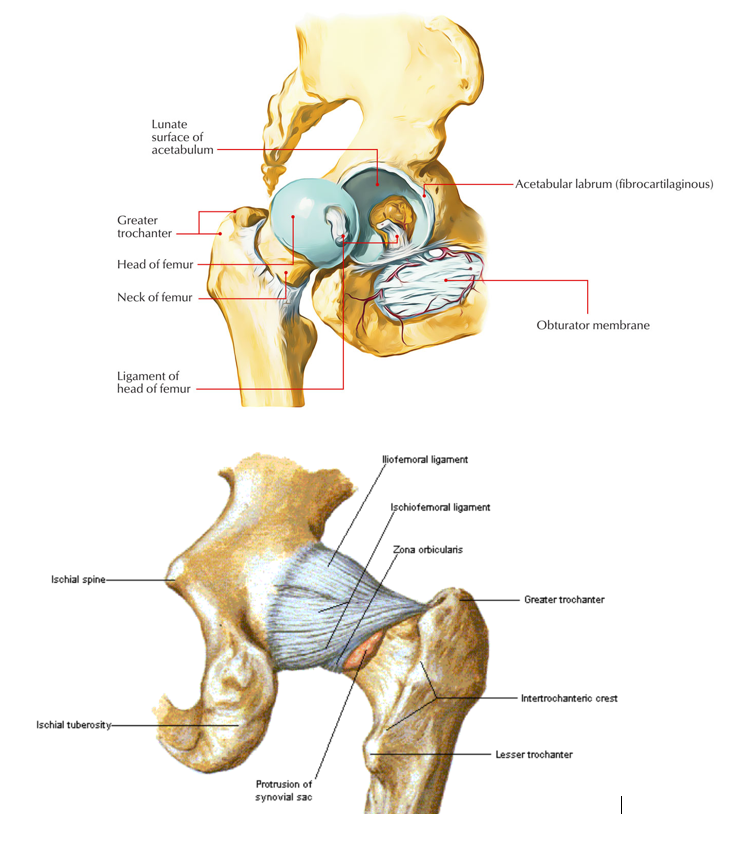
Ligaments of the hip joint. The acetabulum is ringed by strong fibrocartilage called the labrum. Ligaments of the hip are extremely tough and strong.
Although simplicity is suggested in its most basic understanding as a containing device for the femoral head the acetabulum in reality is a complex and elegantly designed structure. Pectoral girdle and pelvic girdle contributes a part of the acetabulum the deep cavity into which the head of the thighbone or femur is fitted. Together with the labrum it is responsible for both the high stability of the hip joint and the mechanics and lubrication of the articular surface.
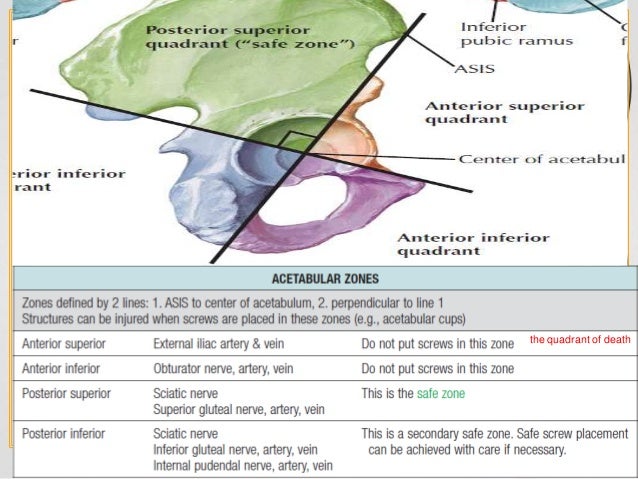
All three bones of the pelvis the ilium ischium and pubis together form the acetabulum. The acetabulum æ s ə ˈ t æ b j ʊ l ə m cotyloid cavity is a concave surface of a pelvis. The largest window trial that bottomed out in the acetabulum was secured with its face parallel to the face of the acetabulum making the anteversion and abduction of the window trial equal to that of the native acetabulum.
Here it is bridged by the transverse ligament thus forming the acetabular foramen beneath it. The three bones are initially separated by a y shaped triradiate cartilage that begins to fuse after puberty. Hip anatomy the acetabular joint the hip joint.
Gross anatomy the acetabular labrum is a c shaped fibrocartilaginous structure with an opening anteroinferiorly at the site of the acetabular notch. The head of the femur meets with the pelvis at the acetabulum forming the hip joint. Anatomy of the acetabulum.
Acetabula is the large cup shaped cavity on the anterolateral aspect of the pelvis that articulates with the femoral head to form the hip joint.
 Femoroacetabular Impingement Physiopedia
Femoroacetabular Impingement Physiopedia
 Elements Of The Comparative Anatomy Elements Of The
Elements Of The Comparative Anatomy Elements Of The
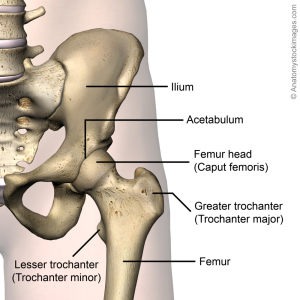
 Hip Anatomy Hip Surgeon Columbia Sc Hip Treatment
Hip Anatomy Hip Surgeon Columbia Sc Hip Treatment
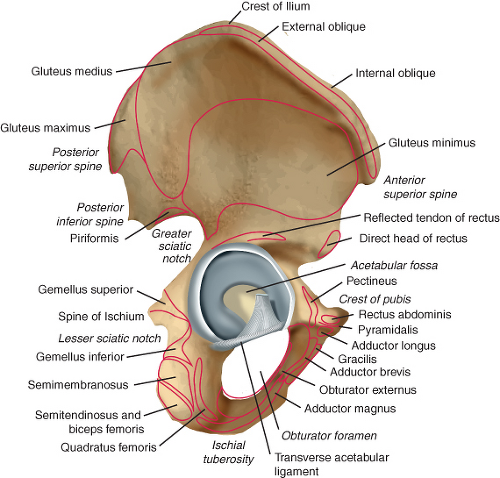 Anatomy Of Acetabulum Musculoskeletal Key
Anatomy Of Acetabulum Musculoskeletal Key
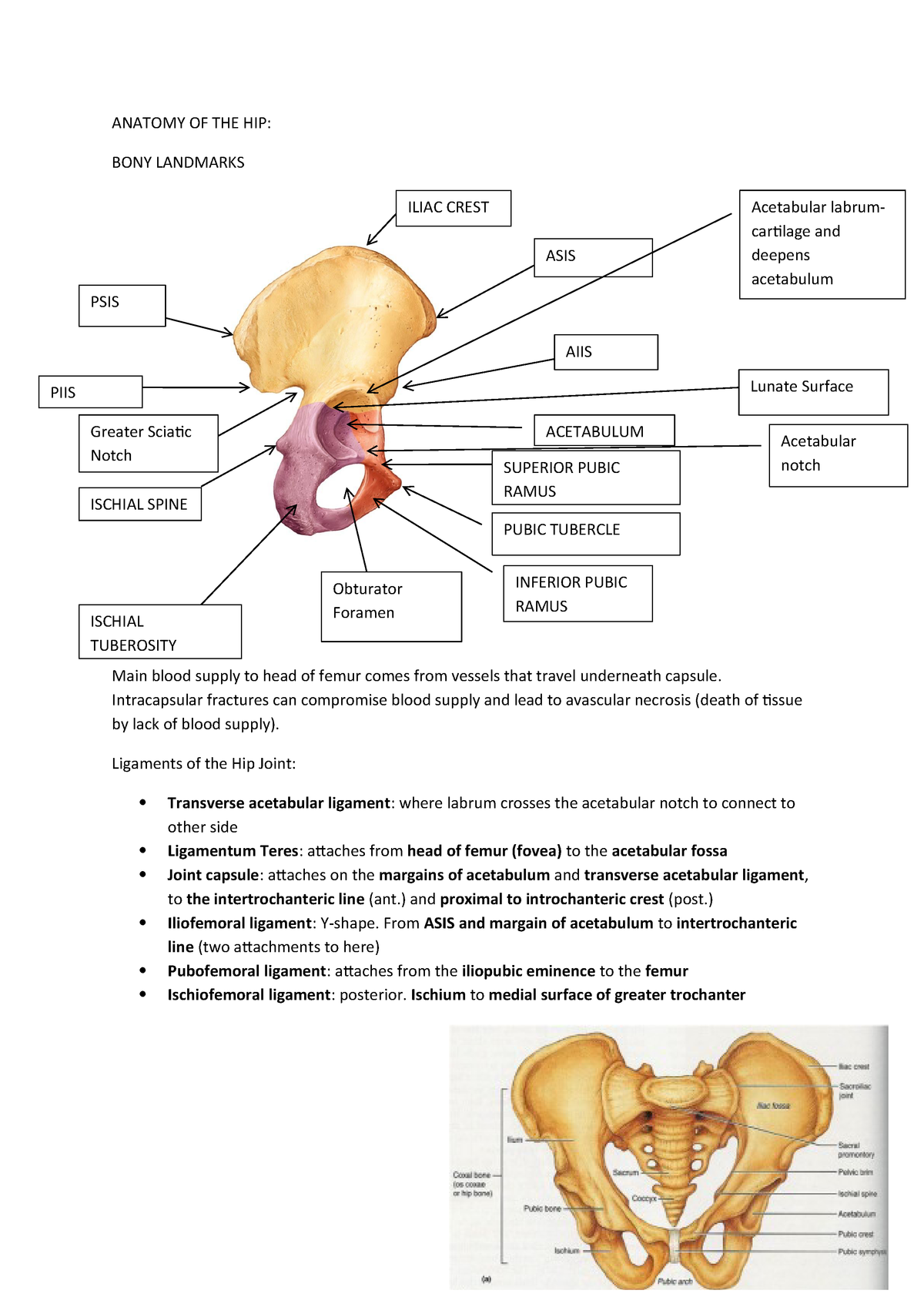 Lecture Notes Anatomy Of The Hip Physiotherapy B106 Studocu
Lecture Notes Anatomy Of The Hip Physiotherapy B106 Studocu
 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Obtubator Xeeve
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy Obtubator Xeeve
 Is Yoga Tearing Labrums Yoga Anatomy
Is Yoga Tearing Labrums Yoga Anatomy
 Acetabular Labrum Tear Physiou
Acetabular Labrum Tear Physiou
 Acetabulum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Acetabulum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Hip Anatomy Hip And Femur Articulation Diagram Quizlet
Hip Anatomy Hip And Femur Articulation Diagram Quizlet
 A The Acetabular Anatomy Is Assessed By Three Measurements
A The Acetabular Anatomy Is Assessed By Three Measurements
 Archive Image From Page 263 Of Cunningham S Text Book Of
Archive Image From Page 263 Of Cunningham S Text Book Of
 Broken Hip Fractures Of The Femur Pelvis And Acetabulum
Broken Hip Fractures Of The Femur Pelvis And Acetabulum
 Commonly Repeated Questions Anatomy 1 Medi Civils
Commonly Repeated Questions Anatomy 1 Medi Civils
 Figure 12 From The Exeter Method Acetabular Impaction
Figure 12 From The Exeter Method Acetabular Impaction
 Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
 Anatomy The Hip Is One Of The Body S Largest Joints It Is A
Anatomy The Hip Is One Of The Body S Largest Joints It Is A
 Exam I Hip Anatomy And Arthrokinematics At University Of
Exam I Hip Anatomy And Arthrokinematics At University Of
 Acetabulum Approach Extended Iliofemoral Approach
Acetabulum Approach Extended Iliofemoral Approach
 Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
 Acetabulum Authors Added Material Ao Surgery Reference
Acetabulum Authors Added Material Ao Surgery Reference
 Anatomy Of The Hip Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
Anatomy Of The Hip Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
 Transverse Acetabular Ligament Wikipedia
Transverse Acetabular Ligament Wikipedia

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Acetabular Anatomy"
Posting Komentar