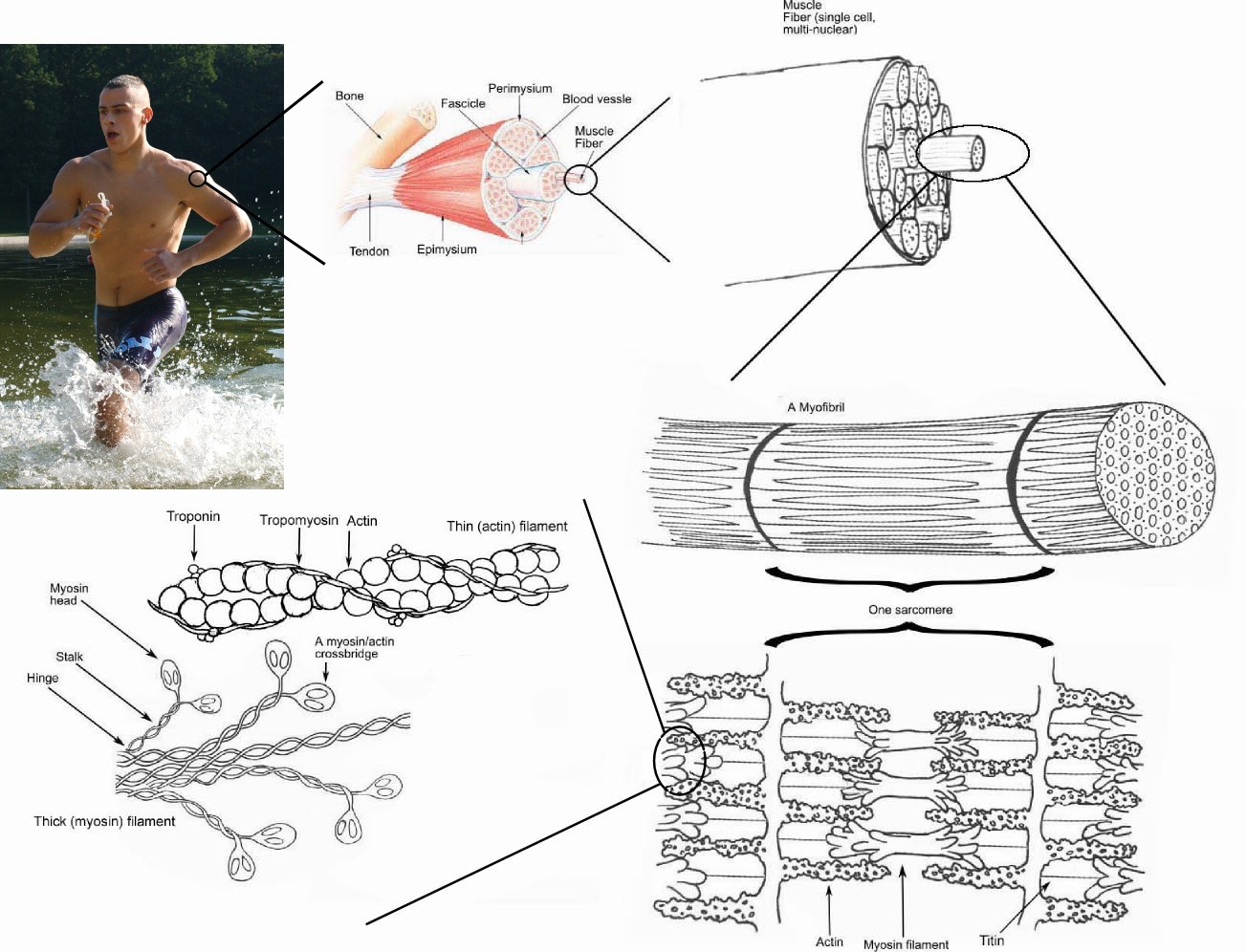
Cross Bridge Anatomy
The period when cross bridges are active and the myogram tracing rises to a peak. The globular head of a myosin molecule that projects from a myosin filament in muscle and in the sliding filament hypothesis of muscle contraction is held to attach temporarily to an adjacent actin filament and draw it into the a band of a sarcomere between the myosin filaments.
As long as ca ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin and as long as atp is available the muscle fiber will continue to shorten.
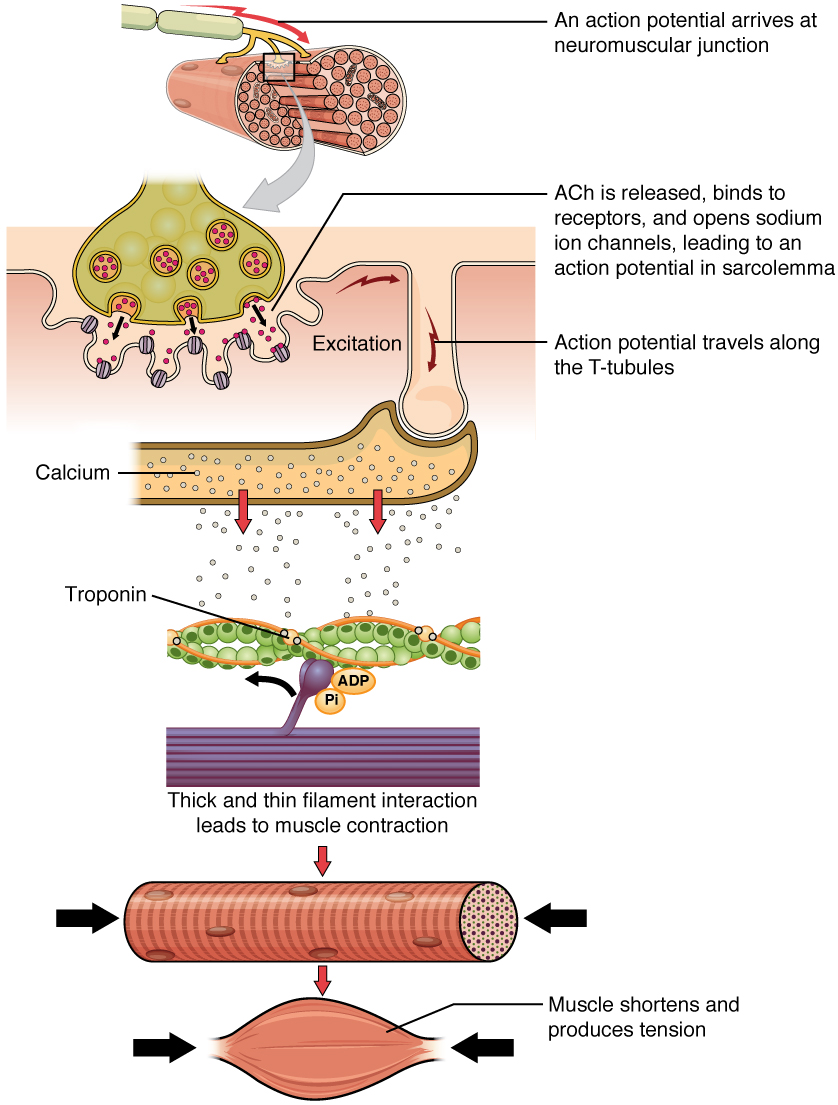
Cross bridge anatomy. All muscle types whether were talking about skeletal cardiac or smooth contract by cross bridge cycling that is repeated attachment of actin and myosin within the cell. What if he falls. What role does troponin play in the cross bridge cycle.
What is the role of calcium in the cross bridge cycle. The importance of this process is illustrated by the muscular contracture called rigor mortis that occurs due to lack of atp when the muscle dies. A cross bridge forms between actin and the myosin heads triggering contraction.
During contraction what prevents actin myofilaments from sliding backward when a myosin head releases. Calcium binds to troponin altering its shape. The globular head of a myosin molecule that projects from a myosin filament in muscle and in the sliding filament hypothesis of muscle contraction is held to attach temporarily to an adjacent actin filament and draw it into the a band of a sarcomere between the myosin filaments.
The muscle is extended in the upper diagram and contracted in the lower one. Contraction of a muscle fiber. Medical definition of crossbridge.
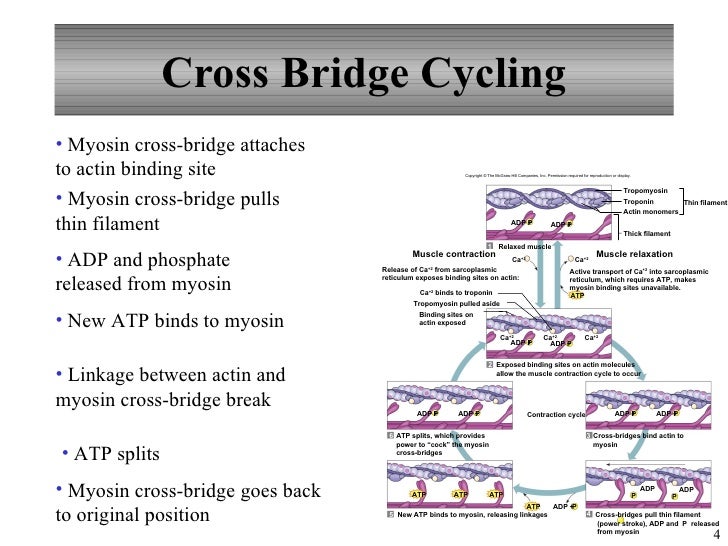
The detachment of a cross bridge from actin at the end of a power stroke requires that a new atp molecule bind to the myosin atpase. Cross bridge formation myosin head attaches to actin forming a cross bridge step 2 the power stroke begins adp and p are released and the myosin head pivots and bends which pulls the actin towards the m line. The new york times recommended for you.
Medical definition of crossbridge. What is a cross bridge in anatomy. In the context of muscular contraction a cross bridge refers to the attachment of myosin with actin within the muscle cell.
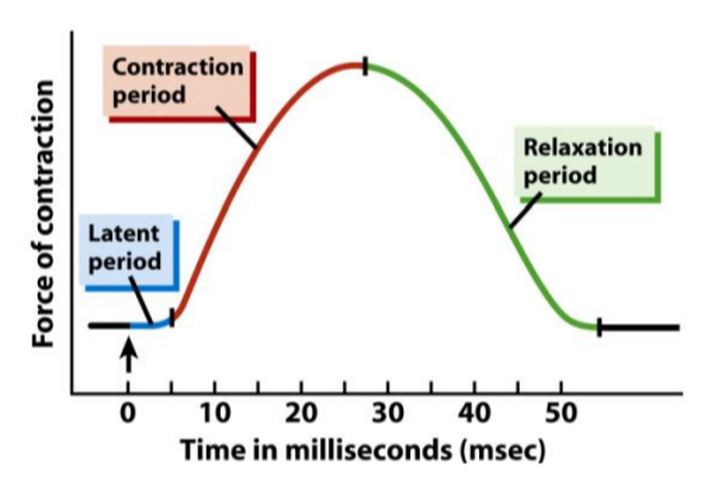
The terrifying reality behind filming free solo op docs duration. Stage of the muscle twitch. The thick filaments are 16 micrometres 00016 millimetre long in vertebrate striated muscle but up to six micrometres long in some arthropods.
Exposes the active sites of actin allowing a cross bridge to form.
 Elements Of Morphology Human Malformation Terminology
Elements Of Morphology Human Malformation Terminology
 The Contraction Cycle And Cross Bridge Detachment Anatomy
The Contraction Cycle And Cross Bridge Detachment Anatomy
 Study Guide Exam 2 Docx Anatomy And Physiology Study Guide
Study Guide Exam 2 Docx Anatomy And Physiology Study Guide
 Lecture 9 3 Cross Bridge Formation And Power Stroke
Lecture 9 3 Cross Bridge Formation And Power Stroke
 Solved Chapter 10 Problem 11sq Solution Principles Of
Solved Chapter 10 Problem 11sq Solution Principles Of
 Biom 3200 Lecture Notes Fall 2017 Lecture 9 Skeletal
Biom 3200 Lecture Notes Fall 2017 Lecture 9 Skeletal
 Pdf Effect Of Cross Bridge Kinetics On Apparent Ca2
Pdf Effect Of Cross Bridge Kinetics On Apparent Ca2
 The Ins And Outs Of Muscle Contractions Aurora Scientific
The Ins And Outs Of Muscle Contractions Aurora Scientific
 10 3 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
10 3 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
 Anatomy Exam 4 Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy Exam 4 Flashcards Quizlet
 Biol 336 Lecture Notes 2017 Lecture 8 Neuromuscular
Biol 336 Lecture Notes 2017 Lecture 8 Neuromuscular
 Anatomy Mechanisms Of Smooth Muscle Contraction
Anatomy Mechanisms Of Smooth Muscle Contraction
 Muscular Contraction Cross Bridge Formation Video
Muscular Contraction Cross Bridge Formation Video
 Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction
Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction
 Muscle Physiology Scientist Cindy
Muscle Physiology Scientist Cindy
 Usmle Prep Kaplan Usmle Step 1 Lecture Notes 2016
Usmle Prep Kaplan Usmle Step 1 Lecture Notes 2016
 General Physiology Skeletal Muscles
General Physiology Skeletal Muscles
Microscopic Anatomy And Contraction Of Skeletal Muscle
The Skeletal Muscle Contraction Cycle Course Hero

 Cross Bridge Cycling In Smooth Muscle A Short Review
Cross Bridge Cycling In Smooth Muscle A Short Review
 Actin And Myosin Human Muscle Anatomy Muscle Anatomy
Actin And Myosin Human Muscle Anatomy Muscle Anatomy
 Cross Bridges Human Physiology 78 Steps Health Journal
Cross Bridges Human Physiology 78 Steps Health Journal
 Ch 09 Sliding Filament Mechanism
Ch 09 Sliding Filament Mechanism
 Muscles 1 Structure Neuromuscular Junction E C Cross
Muscles 1 Structure Neuromuscular Junction E C Cross
 Muscle Soreness Why Do Muscles Get Sore
Muscle Soreness Why Do Muscles Get Sore
 It S Exciting It S Excitation Contraction Coupling
It S Exciting It S Excitation Contraction Coupling



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Cross Bridge Anatomy"
Posting Komentar