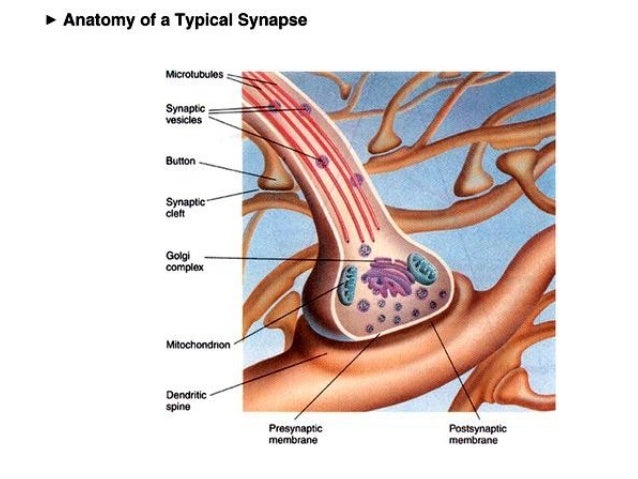
The Anatomy Of A Synapse
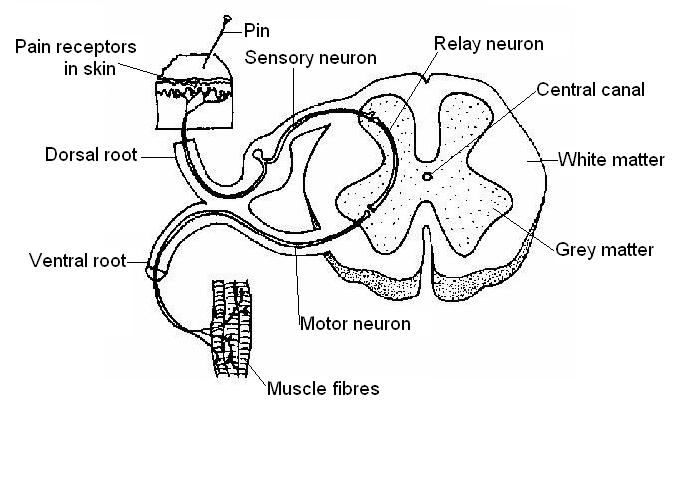
The nerve impulse runs down the axon across the synapse and i transfers electrical impulse from the cell body to the synapse. Synapse the site of transmission of electric nerve impulses between two nerve cells neurons or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell effector.
In the central nervous system a synapse is a small gap at the end of a neuron that allows a signal to pass from one neuron to the next.

The anatomy of a synapse. Synapses are found where nerve cells connect with other nerve cells. Both the sender and receiver cells have elaborate biochemical machinery to create transmit detect and react to signals that cross the synapse. Another type of synapse is found in the bodys immunological system and involves white blood cells rather than neurons.
Synapses are key to the brains function especially when it comes to memory. The anatomy of a synapse includes images for students to color and a description of the action potential. Anatomy physiology of a synapses structure.
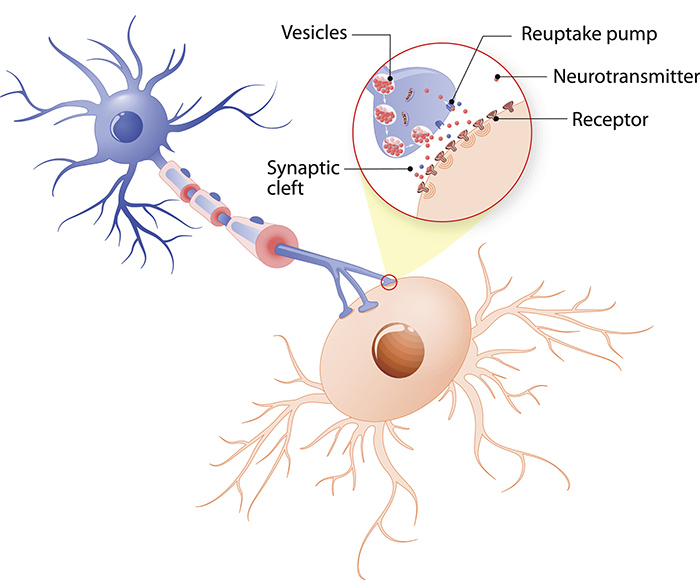
In a chemical synapse a synaptic gap or cleft separates the pre and the postsynaptic cells. Synapse at dendrite axondendritic synapse chemical that an axon end secretes to stimulate a muscle fiber or a neuron to fire an action potential stored in a synaptic vesicle. Functional anatomy of synapses.
Chemical synapses comprise most of the synapses in your body. An action potential propagated to the axon terminal results in the secretion of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters from the axon terminals. When an action potential in the presynaptic neuron reaches the end of the axon and depolarizes the axon terminal voltage gated calcium channels in the membrane open and calcium diffuses from the extracellular fluid into the axon terminal near the docked vesicles.
Chemicals that are the signals from one neuron to the next by direction of nerve impulse the nerve impulse runs down the axon across the synapse. Finally students investigate how ssris work to treat mood disorders. A synaptic connection between a neuron and a muscle cell is called a neuromuscular junction.
Membranous bags that hold the neurotransmitters. The anatomy of a synapse worksheet answers axons from some other neurons arrive in close contact with dendrites of any given neuron and produce an axonal dendritic skip to content home.
 Anatomy Of A Synapse Worksheets Teaching Resources Tpt
Anatomy Of A Synapse Worksheets Teaching Resources Tpt
 Synapse Detailed Anatomy Canvas Print
Synapse Detailed Anatomy Canvas Print
 Biology 12 The Importance Of Neurotransmitters
Biology 12 The Importance Of Neurotransmitters
 Opening Assignment 1 What Are 2 Functions Of The Nervous
Opening Assignment 1 What Are 2 Functions Of The Nervous
 Acetylcholine Definition Function Facts Britannica
Acetylcholine Definition Function Facts Britannica

 The Neuromuscular Junction Function Structure Physiology
The Neuromuscular Junction Function Structure Physiology
 Ch 8 1 Anatomy Of A Neuron And Synapse Diagram Quizlet
Ch 8 1 Anatomy Of A Neuron And Synapse Diagram Quizlet
 How Do Neurons Attach To One Another Quora
How Do Neurons Attach To One Another Quora
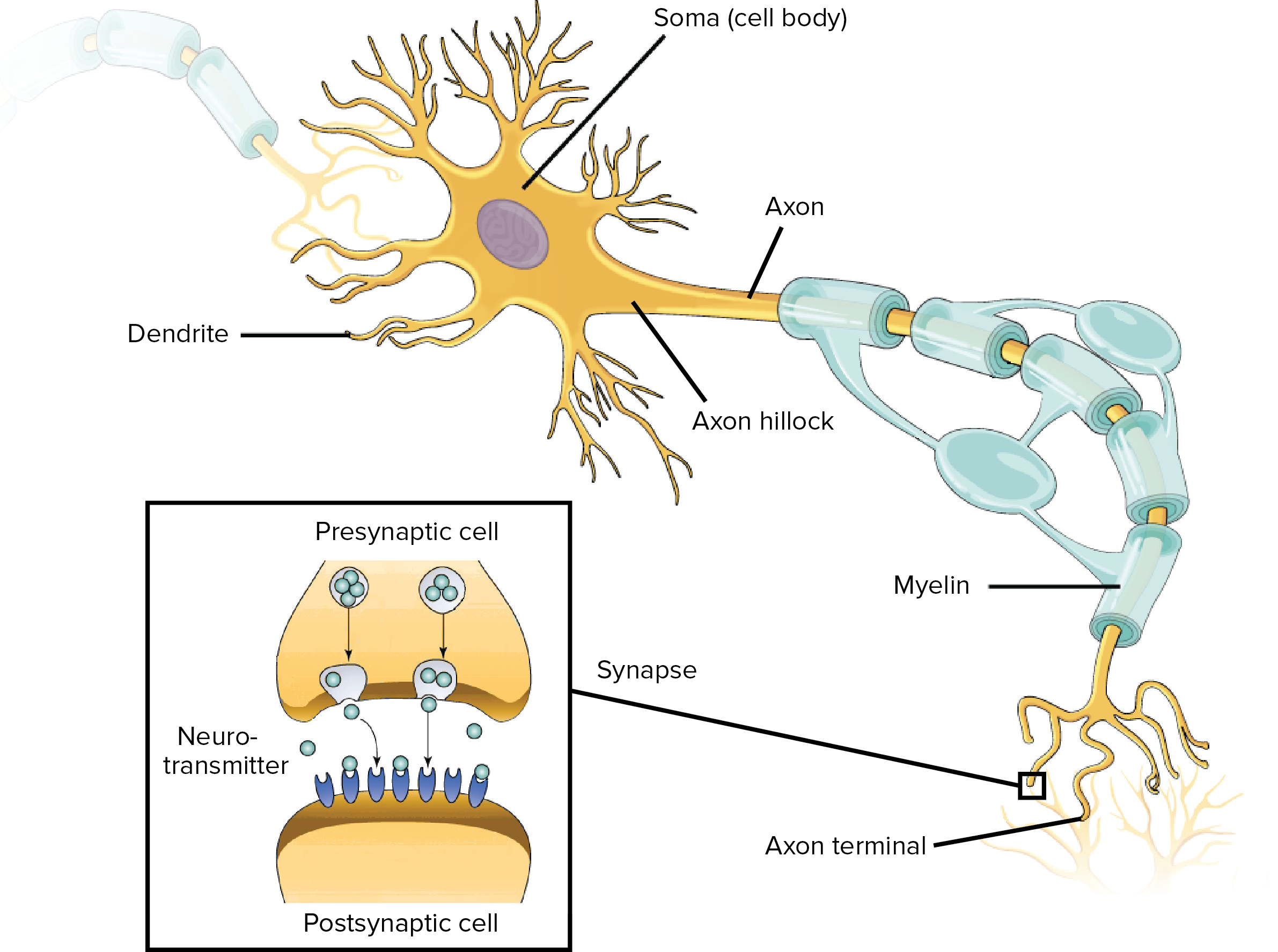 Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan
 Amazon Com Dayanzai Brain Neuron Watercolor Print Brain
Amazon Com Dayanzai Brain Neuron Watercolor Print Brain
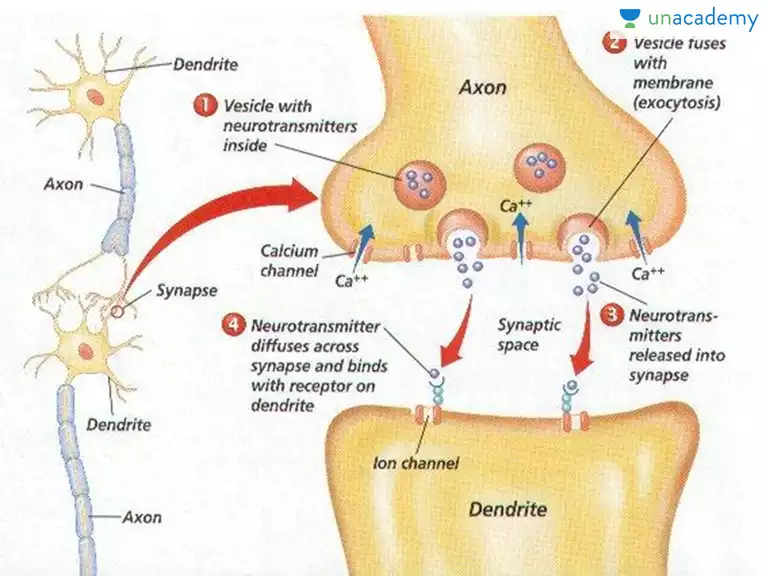 Nervous System Synaptic Transmission Cns Brain
Nervous System Synaptic Transmission Cns Brain
 Storing Memories In Your Synapses
Storing Memories In Your Synapses
 Action Potential Analogy For Anatomy With Key Synapse Epsp Ipsp Nerves
Action Potential Analogy For Anatomy With Key Synapse Epsp Ipsp Nerves
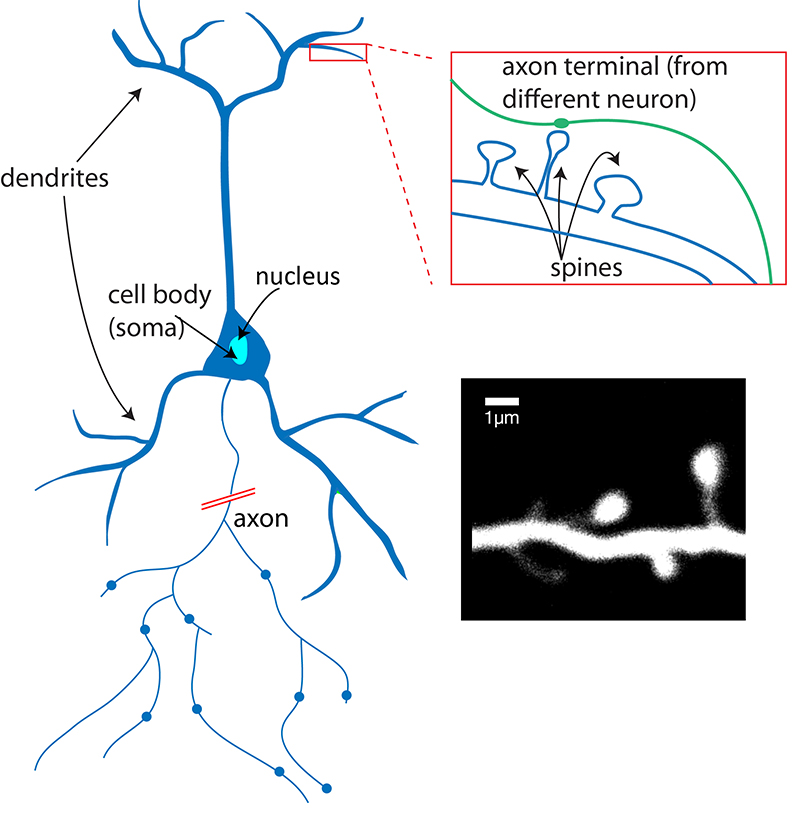 What Is A Neuron Queensland Brain Institute University
What Is A Neuron Queensland Brain Institute University
 Molecular Anatomy Of The Hair Cell S Ribbon Synapse
Molecular Anatomy Of The Hair Cell S Ribbon Synapse
 1 The Anatomy Of A Neuron Bioelectric Signals In The Form
1 The Anatomy Of A Neuron Bioelectric Signals In The Form
 Vector Art Neurons And Closeup Of Synapse Detailed Anatomy
Vector Art Neurons And Closeup Of Synapse Detailed Anatomy
 Synaptic Cleft Anatomy Structure Diseases Functions
Synaptic Cleft Anatomy Structure Diseases Functions
 Nervous System General Principles Ppt Video Online Download
Nervous System General Principles Ppt Video Online Download
 Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Nervous System Wikibooks
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Nervous System Wikibooks
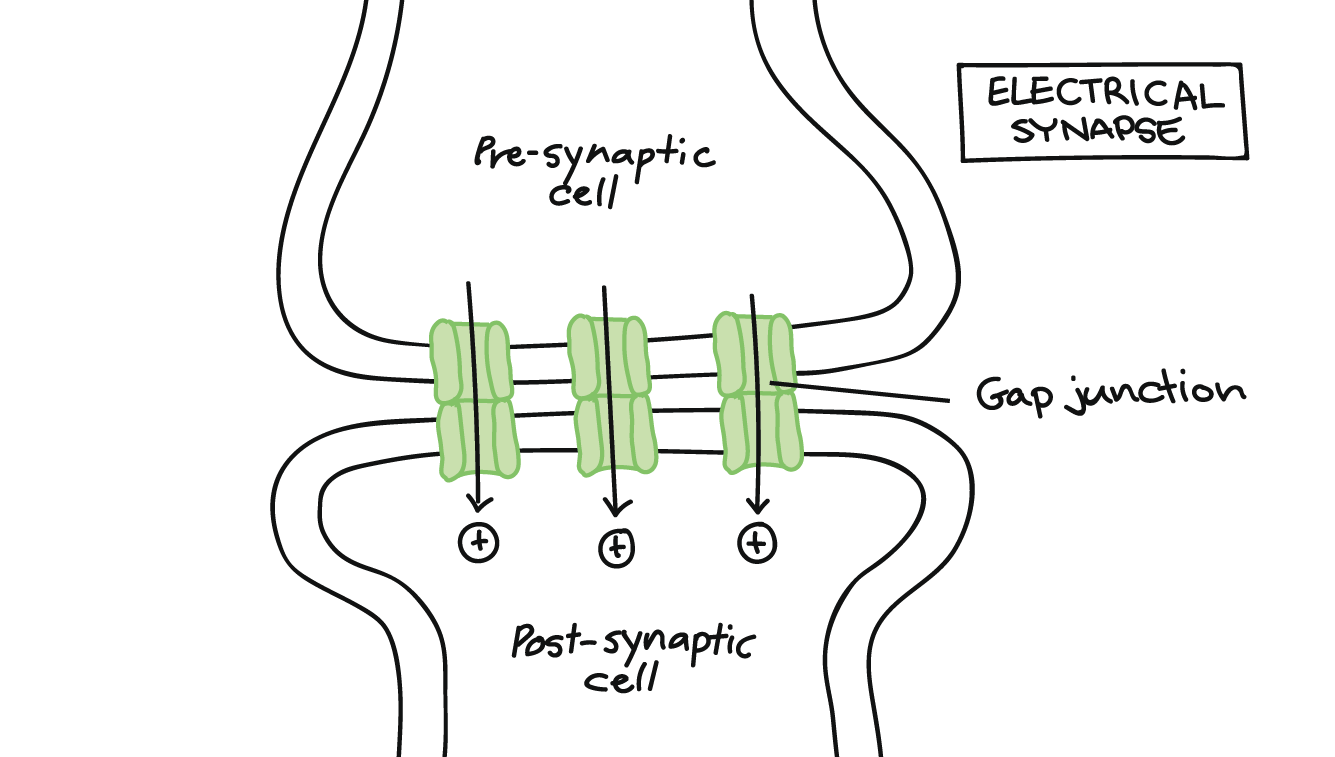 The Synapse Article Human Biology Khan Academy
The Synapse Article Human Biology Khan Academy
 What Are Neurotransmitters Queensland Brain Institute
What Are Neurotransmitters Queensland Brain Institute
Belum ada Komentar untuk "The Anatomy Of A Synapse"
Posting Komentar