Anatomy Of Sleep Apnea
Nonetheless upper airway muscle tone is a component of the pathogenesis of sleep apnea but it is only important in patients who have underlying abnormal upper airway anatomy. The goal of this review is to advance the understanding of the muscular and soft tissue palatal anatomy as it relates to palatal surgery for sleep apnea and the phenotypic variations that generate the shape and collapsibility of the retropalatal airway.
 Sleep Apnea Dentist Des Plaines Il Roseroot Dental 847 699 3370
Sleep Apnea Dentist Des Plaines Il Roseroot Dental 847 699 3370
Obstructive sleep apnea pathophysiology anatomy hypoglossal nerve pcrit ventilator control pharyngeal risk factors key points the oropharynx is the most common site of airway collapse in obstructive sleep apnea osa and enlarged parapharyngeal fat pad thicker lateral pharyngeal walls and increased tongue volume play key roles.
Anatomy of sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea osa is a common disorder characterized by repetitive narrowing or collapse of the pharyngeal airway during sleep. Sleep apnea is often diagnosed with an overnight sleep test called a polysomnogram or sleep study. It bypasses the obstruction of the upper airway which is the primary cause of the disorder.
Obstructive osa central csa and a combination of the two called mixed. Wide thick or long tongue. Though the condition is called sleep apnea each individual pause in breath is known as an apnea.
Tracheostomy as a last resort option. Enlarged tonsils or adenoids. Sleep apnea has many different possible causes.
Here are just some examples of causes for sleep apnea from anatomical point of view. The disorder is associated with major comorbidities including excessive daytime sleepiness and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Individuals with normal upper airway anatomy do not develop obstructive apneas or hypopneas during sleep even though they have a reduction in muscle tone and a reduction in the caliber of their upper airway 6 7.
In adults the most common cause of obstructive sleep apnea is excess weight and obesity which is associated with soft tissue of the mouth and. There are three forms of sleep apnea. Osa is the most common form.
This was the mainstay of treatment in severe sleep apnea before the invention of cpap therapy in 1981. Sleep apnea obstructive sleep apnea consists of episodes of partial or complete closure of the upper airway that occur during sleep and lead to breathing cessation defined as a period of apnea 10 sec. Risk factors for osa include being overweight a family history of the condition allergies a small airway and enlarged tonsils.
Obstructive sleep apnea is a condition that is marked by halted or interrupted breathing during sleep. Because this happens during sleep many people with osa do not realize that they have this condition.
/https%3A%2F%2Fd1n5s2tett0dwr.cloudfront.net%2F78CMZGpjxi3qV-t7IDe2gOD6zYk%3D%2F1000x370%2Fd3b3by4navws1f.cloudfront.net%2Fshutterstock_119606590-2.jpg) Sleep Apnea New Haven Ct Guilford Ct Stratford Ct
Sleep Apnea New Haven Ct Guilford Ct Stratford Ct
 Sleep Apnea Treatment Ft Lauderdale Stop Snoring Miami
Sleep Apnea Treatment Ft Lauderdale Stop Snoring Miami
 Obstructive Sleep Apnea A Pathophysiology And
Obstructive Sleep Apnea A Pathophysiology And
Role Of Orthodontist In Obstructive Sleep Apnea An
About Sleep Apnea At Home Sleep Solutions
Positional Therapy For Sleep Apnea Singular Sleep
What Is Sleep Apnea Veteran Disability And Long Term
 Stroke Awareness Month Untreated Sleep Apnea And Stroke
Stroke Awareness Month Untreated Sleep Apnea And Stroke
 Sleep Apnea Treatment In Tysons Smile Makers Dental Center
Sleep Apnea Treatment In Tysons Smile Makers Dental Center
 Sleep Apnea Va Palo Alto Health Care System
Sleep Apnea Va Palo Alto Health Care System
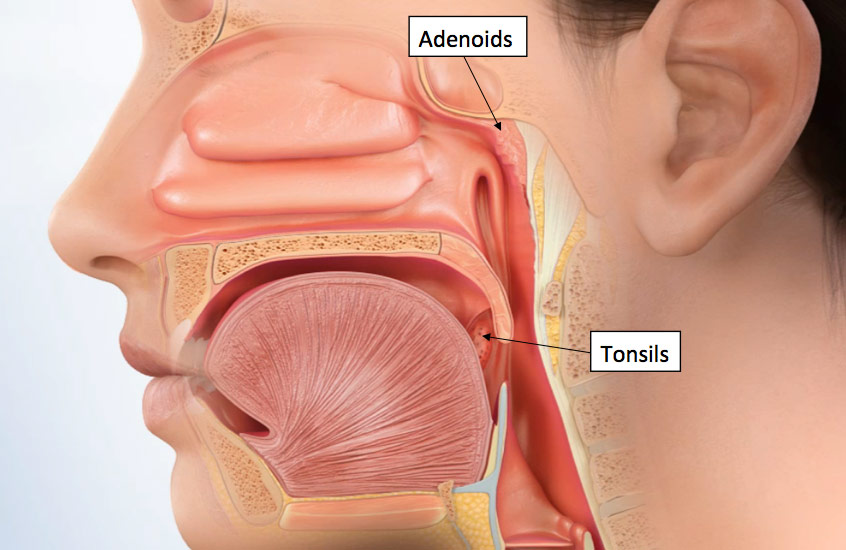 Snoring In Children Can Obstructive Sleep Apnea Be
Snoring In Children Can Obstructive Sleep Apnea Be
 What Is Sleep Apnea Mayo Clinic News Network
What Is Sleep Apnea Mayo Clinic News Network
 What Is Sleep Apnea Healthy Sleep Solutions
What Is Sleep Apnea Healthy Sleep Solutions
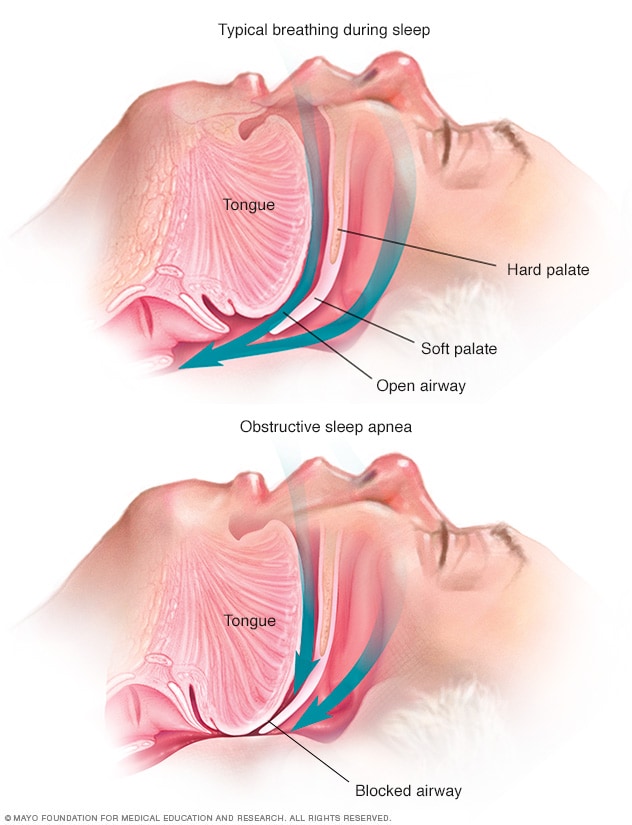 Obstructive Sleep Apnea Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Houston Texas Area Snoring And Sleep Apnea Treatment
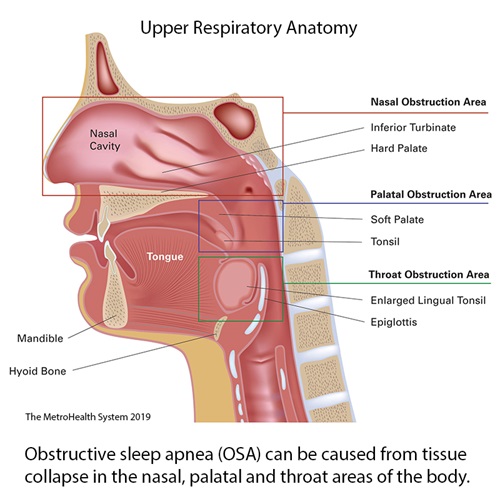 About Obstructive Sleep Apnea Osa The Metrohealth System
About Obstructive Sleep Apnea Osa The Metrohealth System
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sleep-apnea-overview-3014774-v1-5c5dbe9a46e0fb00017dd118.png) Sleep Apnea Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And Treatment
Sleep Apnea Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And Treatment
 What Can Happen When Sleep Apnea Goes Undiagnosed Everyday
What Can Happen When Sleep Apnea Goes Undiagnosed Everyday
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/does-sleep-apnea-go-away-3015020-FINAL2-6a8a000dfb8c40508fc8bedce8836ded.png) Does Sleep Apnea Go Away Risk Factors And Prognosis
Does Sleep Apnea Go Away Risk Factors And Prognosis
 Obstructive Sleep Apnea Wikipedia
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Wikipedia
 Sleep Apnea Psychiatry Medbullets Step 2 3
Sleep Apnea Psychiatry Medbullets Step 2 3
 Sleep Apnea How Is It Related To Heart Disease And What Can I Do About It
Sleep Apnea How Is It Related To Heart Disease And What Can I Do About It

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Sleep Apnea"
Posting Komentar