Anatomy Of Mouth Floor
The oral cavity is bounded at the sides and in front by the alveolar process containing the teeth and at the back by the isthmus of the fauces. Anatomy of a mouth.
Review of imaging anatomy and pathology the floor mouth source.

Anatomy of mouth floor. Men are diagnosed with floor of mouth cancer three to four times more often than women. Muscular diaphragm comprised of the bilateral mylohyoid muscles. Mouth also called oral cavity or buccal cavity in human anatomy orifice through which food and air enter the body.
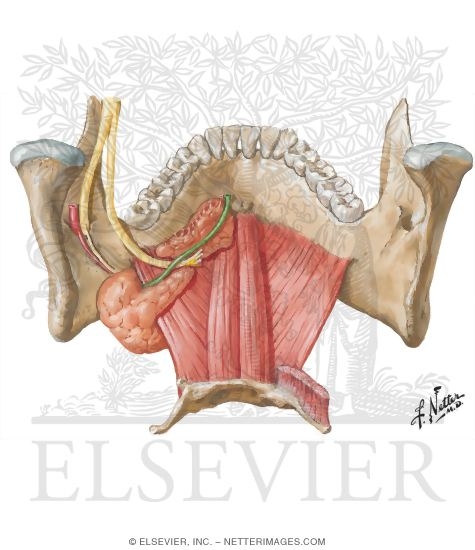
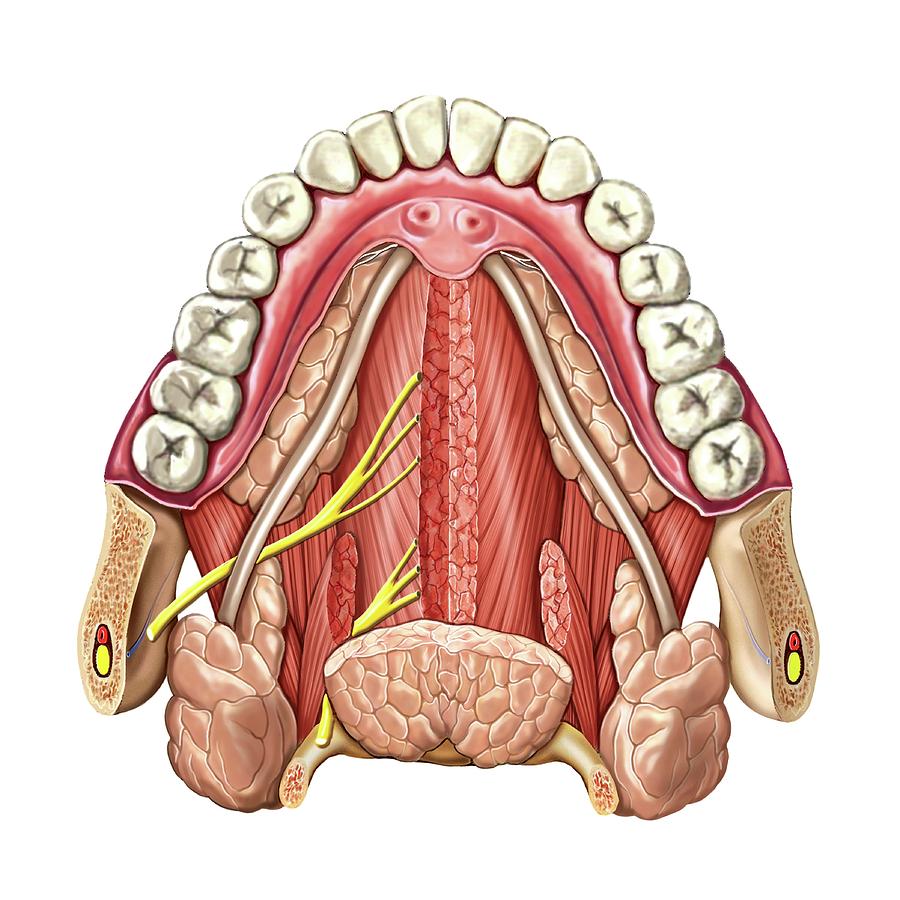
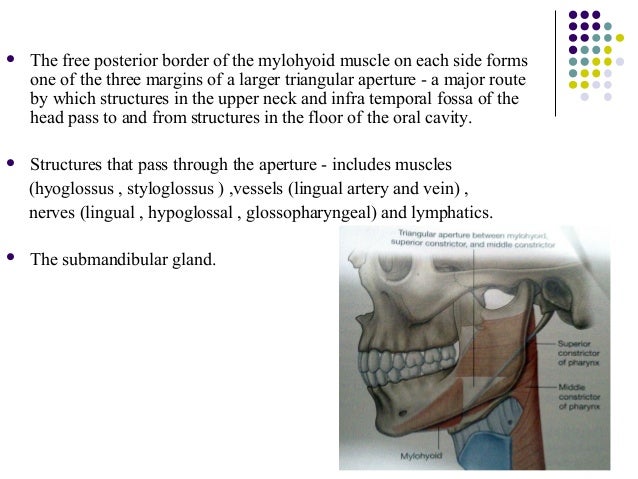
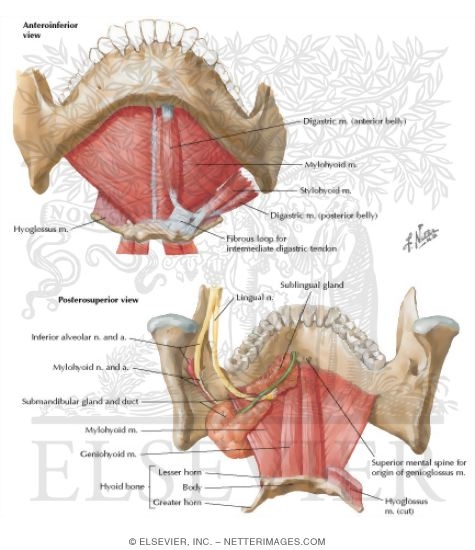
Gross anatomy the floor of mouth is a u shaped space which extends and includes from the oral cavity mucosa superiorly and the mylohyoid muscle sling 23. The floor of mouth is an oral cavity subsite and is a common location of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. For purposes of surgical planning the floor of the mouth is defined as the space between the mucosal surface and the mylohyoid muscle sling and comprising both structures 1.
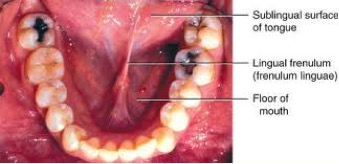
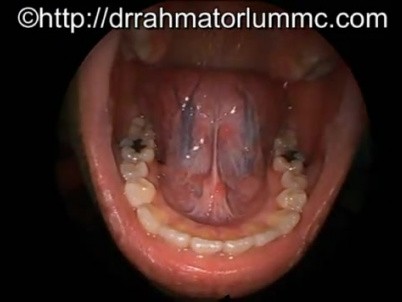
The mouth opens to the outside at the lips and empties into the throat at the rear. The vestibule is the area between the teeth lips and cheeks. The floor of mouth is a horseshoe shaped area under the tongue between the sides of the lower jawbone the mandible.
Geniohyoid muscles pull the larynx forward during swallowing. The mouth oral cavity consists of several components including the teeth gingiva gums tongue palate cheeks lips and floor of the mouth. With the exception of the teeth the mouth is lined by mucous membranes.
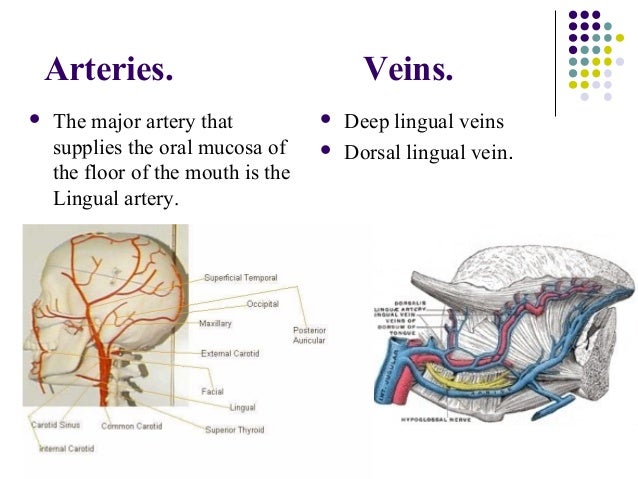
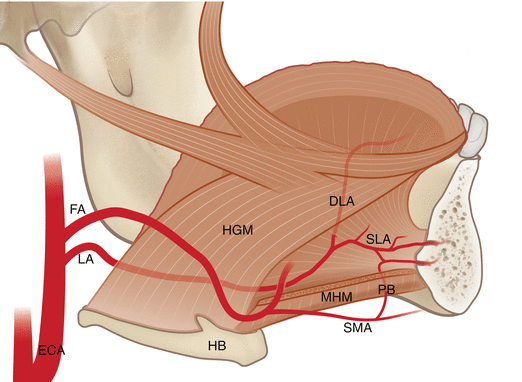
Its boundaries are defined by the lips cheeks hard and soft palates and glottis. During a dental implant procedure in the anterior zone of the mandible perforation of the lingual cortex may invade the floor of the mouth and hence damage structures within the sublingual space. The floor of the mouth is richly vascularised by a number of branches of submental and sublingual arteries.
Floor of the mouth lined with smooth thin mucous membrane stratified squamous epithelium boundaries. Pillar inferior mylohyoid muscle superior mucous membrane lining wwwindiandentalacademyco m 3. The teeth are held within the jaw bones and serve several important functions beyond allowing you to chew.
The mouth consists of 2 regions the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. It provides structural support to the floor of the mouth and pulls the larynx forward during swallowing. Part of the mandible either sides body of mandible posterior base of the ant.
Anatomy of the mouth. Anatomy of the floor of the mouth the floor of the mouth is a horizontally aligned u shaped space situated in the part of the oral cavity that lies beneath the tongue. Cancer of the floor of mouth accounts for 28 35 percent of all mouth cancers.
The floor the floor of the oral cavity consists of several structures.
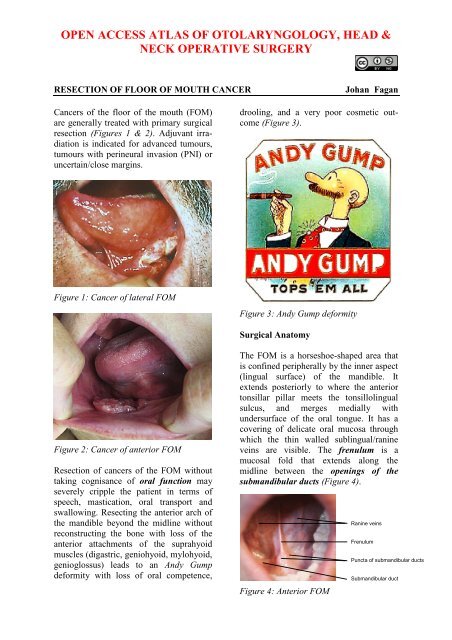 Resection Of Floor Of Mouth Cancers Vula University Of
Resection Of Floor Of Mouth Cancers Vula University Of
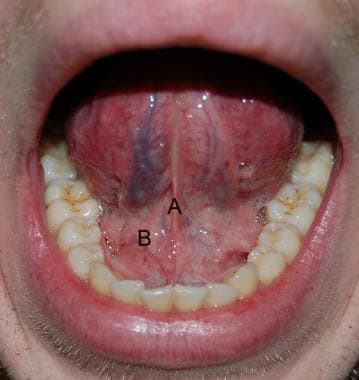 Mouth Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Oral Vestibule
Mouth Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Oral Vestibule
 Clinical Aspects Of The Sublingual Mass Note That The
Clinical Aspects Of The Sublingual Mass Note That The
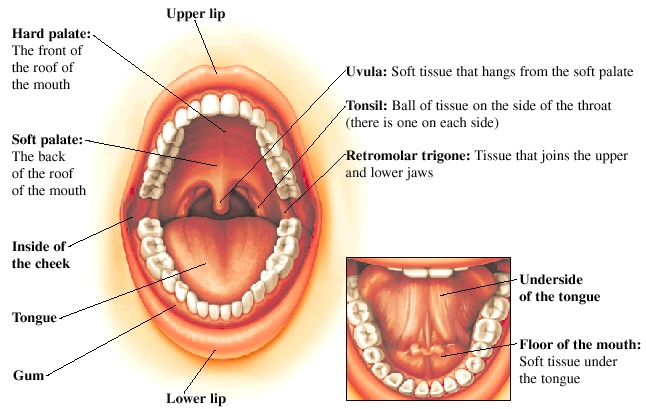
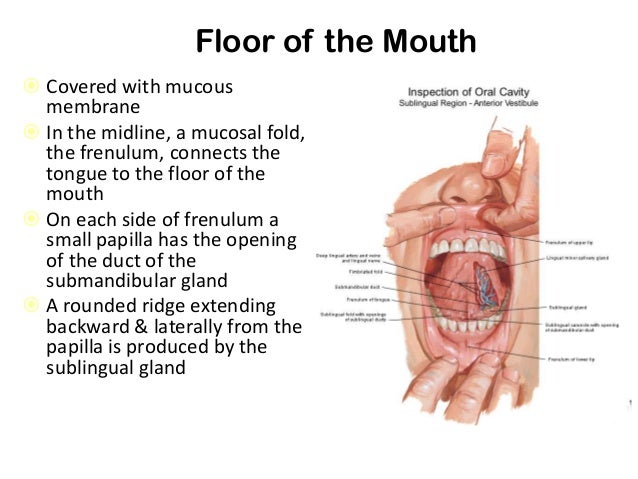 Anatomy Of Oral Region And Pharynx
Anatomy Of Oral Region And Pharynx
 Tongue And Oral Floor Artwork Stock Image C021 2359
Tongue And Oral Floor Artwork Stock Image C021 2359
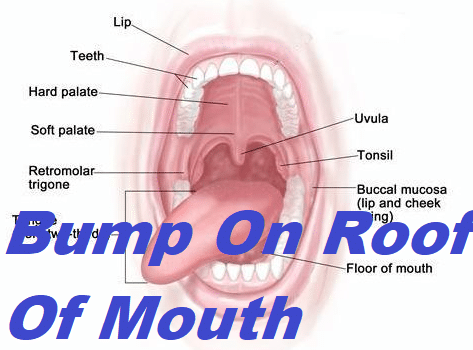 Bump On Roof Of Mouth Grow Health
Bump On Roof Of Mouth Grow Health
 The Oral Cavity Dentistry Osd 101 Gross Anatomy With
The Oral Cavity Dentistry Osd 101 Gross Anatomy With
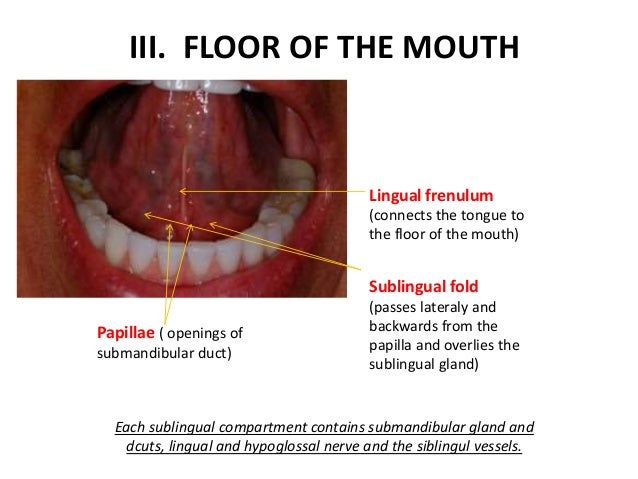 Dr Mustafa Haddad Anatomy Of Oral Cavity
Dr Mustafa Haddad Anatomy Of Oral Cavity
Lingual Nerve Block Selective Anesthesia For Tongue And
 Human Digestive System Britannica
Human Digestive System Britannica
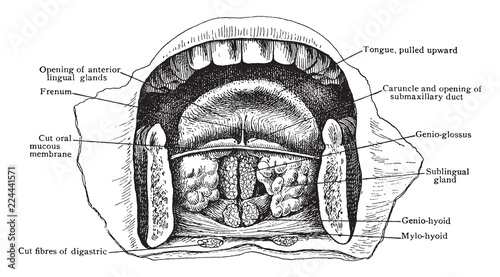 Anterior Part Of Floor Of Mouth Vintage Illustration Buy
Anterior Part Of Floor Of Mouth Vintage Illustration Buy
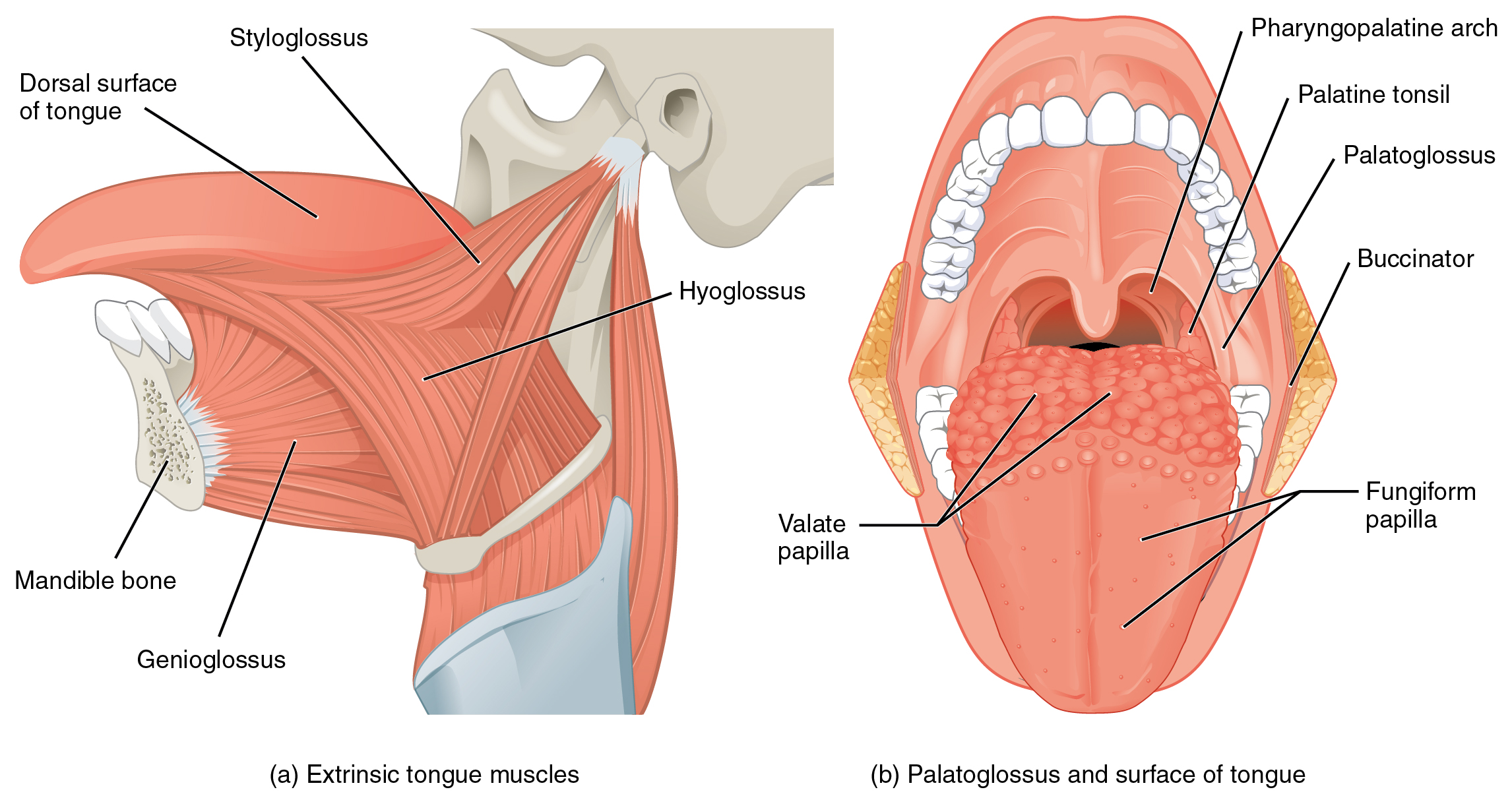 11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
Why Does The Bottom Of Your Mouth Feel Hard When You Press
 The Inner Cortex And Lingual Periosteum Of The Mandible And
The Inner Cortex And Lingual Periosteum Of The Mandible And
 Buccal Mucosa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Buccal Mucosa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Beyond Five What Is The Oral Cavity
Beyond Five What Is The Oral Cavity
 Submandibular Region And Floor Of Mouth Human Anatomy
Submandibular Region And Floor Of Mouth Human Anatomy
 Oral Mucosa Ppt Video Online Download
Oral Mucosa Ppt Video Online Download

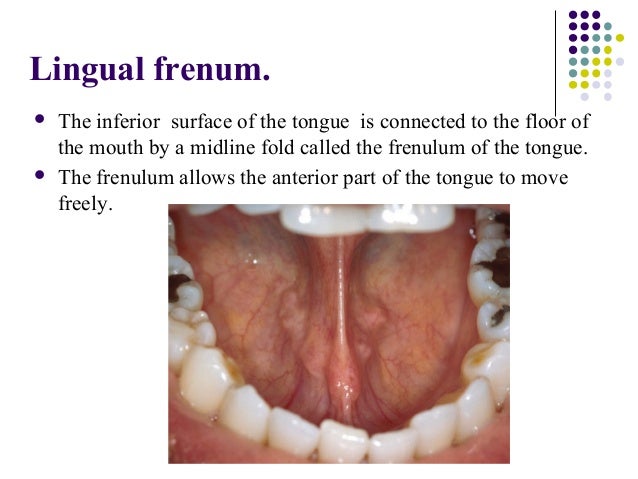




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Mouth Floor"
Posting Komentar