Anatomy Of The Tonsils
This results in fever difficulty swallowing sore throat ear pain loss of voice and throat tenderness. The tonsil consists of a mass of lymphoid follicles supported by.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-to-do-about-cryptic-tonsils-1191883-5c7013cfc9e77c00010d6bcb.png) What To Do About Cryptic Tonsils
What To Do About Cryptic Tonsils
Each tonsil is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes covered by pink mucosa like on the adjacent mouth lining.
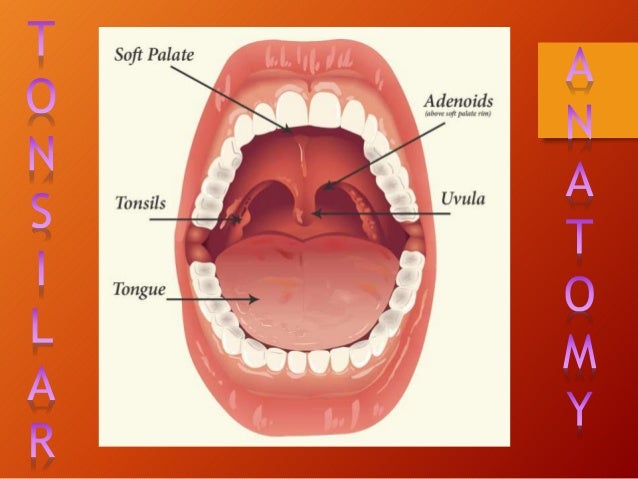
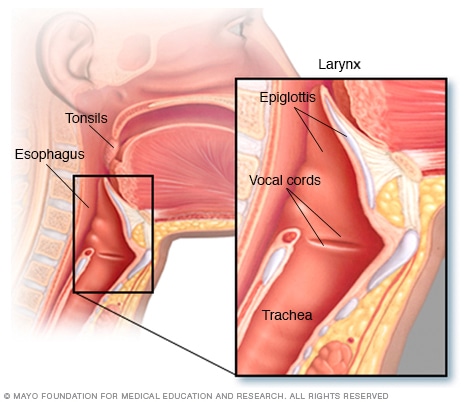
Anatomy of the tonsils. Tonsil small mass of lymphatic tissue located in the wall of the pharynx at the rear of the throat of man and other mammals. Tonsils are collections of lymphoid tissue that can be seen in the mouth. The tonsils are part of the lymphatic system which helps to fight infections.
They are made up of lymphatic tissue a type of tissue that helps filter infection and bacteria from the body. Tonsillitis occurs when bacterial or viral organisms cause inflammation of the tonsillar tissue. Tonsil and adenoid anatomy overview.
These are a pair of oval shaped masses protruding from each side of the oral pharynx behind the mouth cavity. Tonsils play a role in the bodys immune response. Malt can also be found in the bowel in peyers patches.
These organs play an important role in the immune system. Tonsils are located on either side of the tongue in the back of the mouth. Different parts of the throat adenoids.
In man the term is used to designate any of three sets of tonsils most commonly the palatine tonsils. The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract which is known as waldeyers tonsillar ring and includes the adenoid tonsil two tubal tonsils two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils. Anatomy of tonsils there are three sets of tonsils in the back of the mouth the adenoids the palantine and the lingual tonsils.
Recurrent tonsillitis sometimes results in the need for a tonsillectomy. Anatomy development the tonsils are part of malt mucosa associated lymphoid tissue. Running through the mucosa of each tonsil are pits called crypts.
In general malt is relatively undeveloped at birth with low cellularity. These tonsils are found in pairs one on each side of the body and are typically small in size. These are known as the palatine tonsils.
Tonsils start to develop around 14 15th week of embryonic life. The tonsils begin developing early in the third month of fetal life. The adenoid is a median mass of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue.
 Anatomy Of Tonsil And Oropharynx
Anatomy Of Tonsil And Oropharynx
 Duke Anatomy Labs 23 24 Bisected Head
Duke Anatomy Labs 23 24 Bisected Head
Pediatric Center Penn State Hershey Medical Center
 Palatine And Pharyngeal Tonsils Google Search Lingual
Palatine And Pharyngeal Tonsils Google Search Lingual
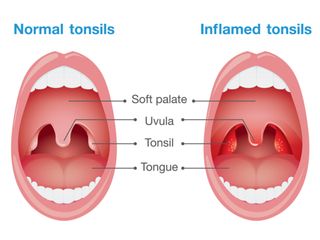 Tonsils Facts Function Treatment Live Science
Tonsils Facts Function Treatment Live Science
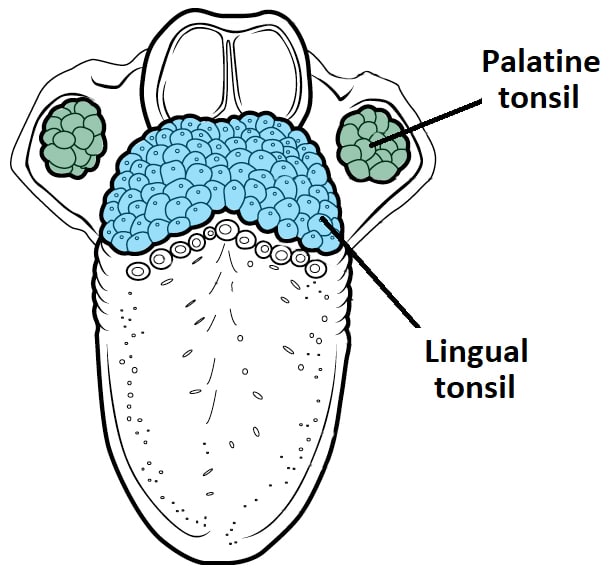 The Tonsils Waldeyer S Ring Lingual Pharyngeal
The Tonsils Waldeyer S Ring Lingual Pharyngeal
Duke Anatomy Labs 23 24 Bisected Head
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2096/YTcQGRhXZfKaQCVTiC0Izg_Palatine_Tonsils_02.png) Tonsils Anatomy Histology And Clinical Points Kenhub
Tonsils Anatomy Histology And Clinical Points Kenhub
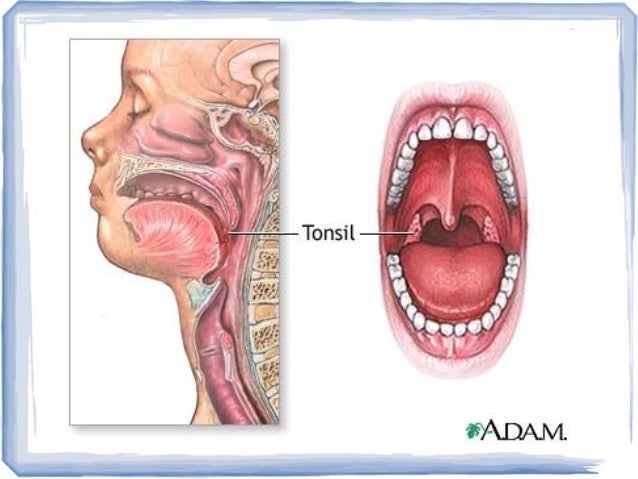 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Palatine Tonsil
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Palatine Tonsil
 21 1 Anatomy Of The Lymphatic And Immune Systems Anatomy
21 1 Anatomy Of The Lymphatic And Immune Systems Anatomy
 Tonsillectomy And Adenoidectomy Iowa Head And Neck Protocols
Tonsillectomy And Adenoidectomy Iowa Head And Neck Protocols

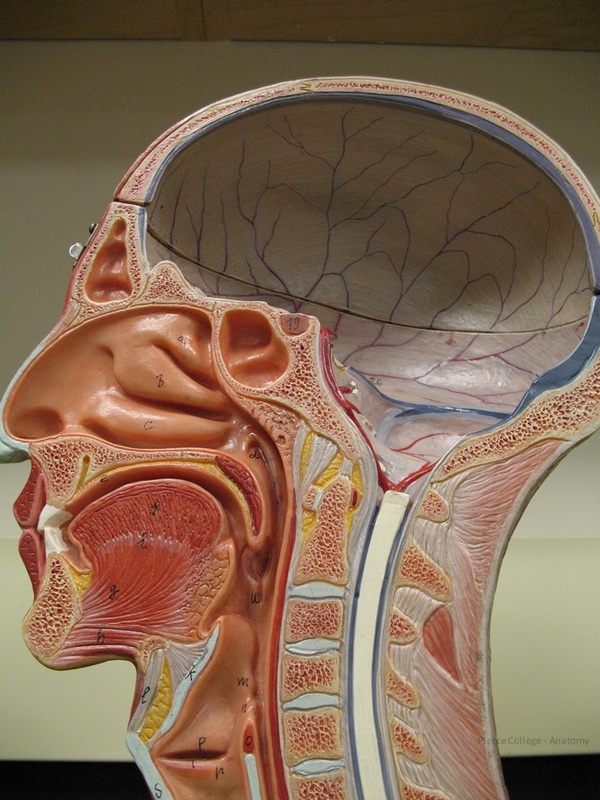 Tonsils Somso Pierce College Anatomy
Tonsils Somso Pierce College Anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2095/NtRyxn7ADpjbonfYTBwog_Tonsillar_Crypt_01.png) Tonsils Anatomy Histology And Clinical Points Kenhub
Tonsils Anatomy Histology And Clinical Points Kenhub
 Tonsillectomy And Adenoidectomy In Children Anatomy Gross
Tonsillectomy And Adenoidectomy In Children Anatomy Gross
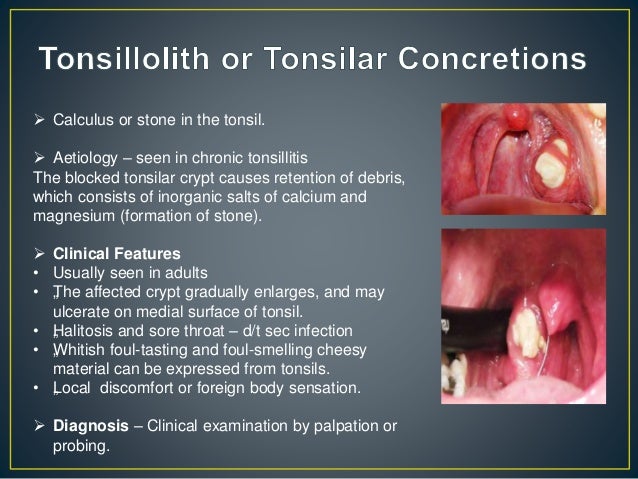 Palatine Tonsil Its Anatomy Diseases And Their Management
Palatine Tonsil Its Anatomy Diseases And Their Management
 Anatomy Of Tonsil Cancer Headandneckcancerguide Org
Anatomy Of Tonsil Cancer Headandneckcancerguide Org
 Oropharynx An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Oropharynx An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
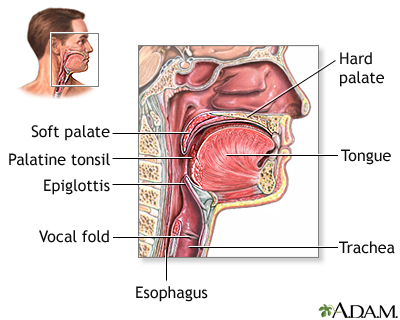 Pharyngitis Sore Throat Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
Pharyngitis Sore Throat Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
 Lingual Tonsillectomy Sleep Doctor
Lingual Tonsillectomy Sleep Doctor
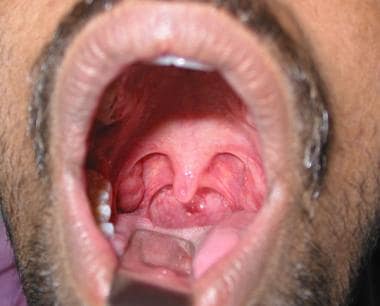 Tonsil And Adenoid Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Tonsil And Adenoid Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
 Anatomy Of The Tonsils Midsagittal Section Part 1 Diagram
Anatomy Of The Tonsils Midsagittal Section Part 1 Diagram
Palatine Tonsils Useful Notes On Palatine Tonsils Human



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of The Tonsils"
Posting Komentar