Dog Leg Anatomy
Two thirds of a dogs body weight is carried on their front legs. The bones and ligaments can easily be cracked stretched or twisted when impact is applied through running jumping or by virtue of an accident or jolting impact as listed below.
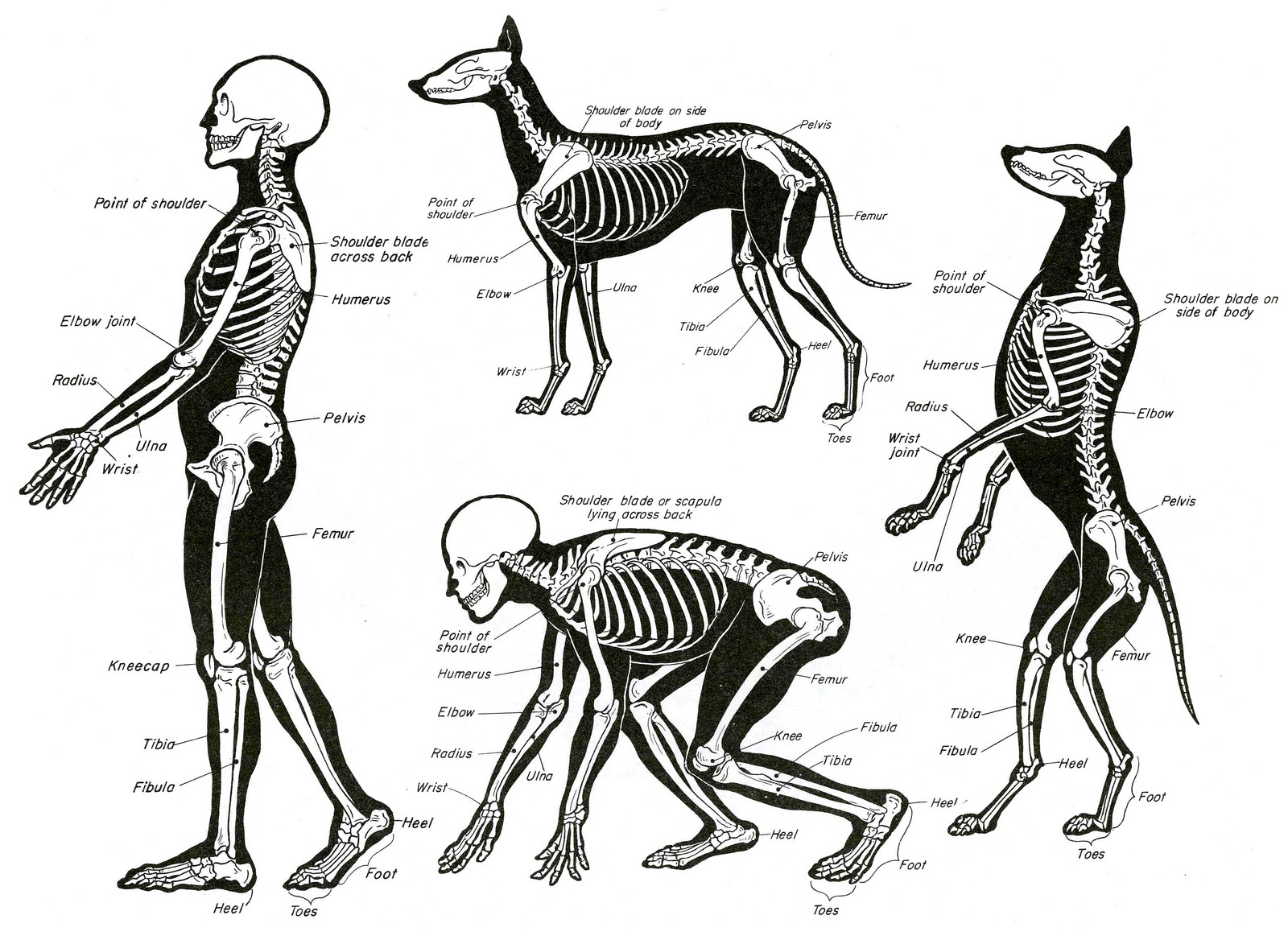 Combative Anatomy How To Fight A Dog Exigent Circumstances
Combative Anatomy How To Fight A Dog Exigent Circumstances
The forearm may have feathering on the back.

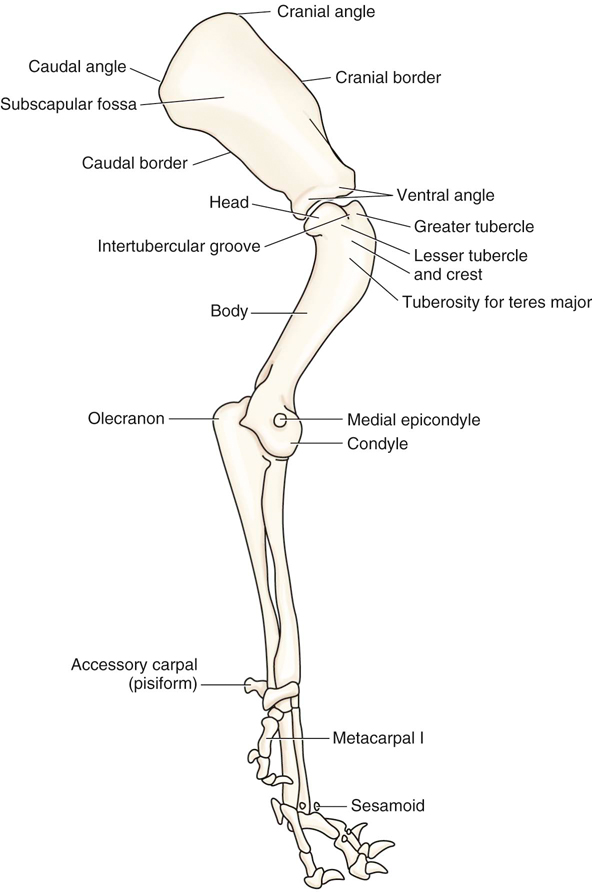
Dog leg anatomy. The rear legs of the dog begin with the femur bone which extends to a pair of bones known as the tibia and the fibula. These further extend to the heel bone known as tarsus the paw bone known as metatarsus and the toe bone phalange. The dog is carried around by the forelegs and the hind legs.
Dog leg problems can be classified to further understand how they should be dealt with and treated. Understanding and knowing your dogs leg anatomy will help learn the possible weaknesses injuries and the best ways how to treat them. The forelegs and hind legs of a dog are as different as human arms and legs.
The elbow is the first joint in the dogs leg located just below the chest on the back of the foreleg. Dogs legs are comprised of bones muscles ligaments and tendons. These dog leg injuries include bone fractures bone cracks ligament tears ligament damage cuts bruises and joint pain.
Only one third is carried on their hind legs. Understanding the dog leg anatomy is also important as this is an area that is very much prone to injury. Much as the hind legs have got larger muscles which make them stronger they only carry around one third of its body weight.
The anatomy of a dogs hind leg and foreleg differs just as a human arm and leg differ according to for dummies. Dog leg anatomy just like humans have arms and legs dogs have forelegs and hind legs. The long bone that runs after the elbow on the foreleg is the forearm.
Like your arms its comprised of the ulna and radius. It ends at the elbow the elbow is the first joint in the dogs leg located just below the chest on the back of the foreleg. In reality the anatomy of a dogs leg is very complex.
However the muscles on their hind legs are larger and therefore stronger. The upper arm on the foreleg is right below the shoulder and is comprised of the humerus bone. The forelegs or front legs carry two thirds of its body weight.
Directly below the shoulder of the foreleg is the humerus bone which ends at the elbow the first joint located just below the chest on the back of the foreleg.
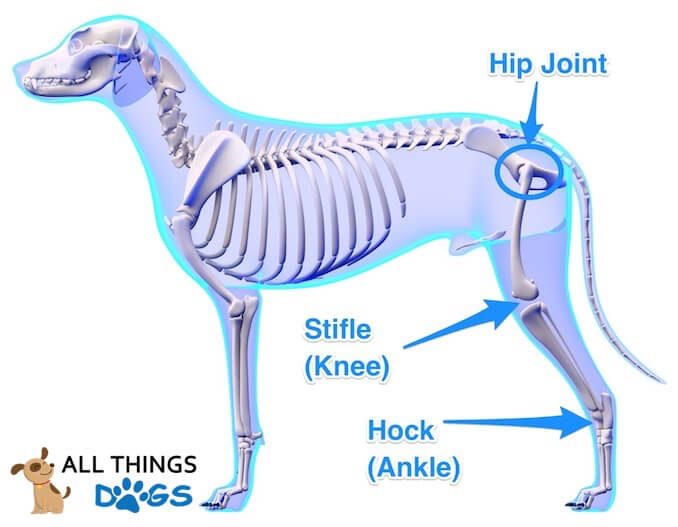 A Visual Guide To Dog Anatomy Muscle Organ Skeletal
A Visual Guide To Dog Anatomy Muscle Organ Skeletal
Injury Of The Cranial Cruciate Ligament Ccl In The Dog
 Anatomy Of The Dog Elbow With Lateral Zoom Wall Art Canvas
Anatomy Of The Dog Elbow With Lateral Zoom Wall Art Canvas
 Dog Leg Anatomy Explained Injury Types And Treatments
Dog Leg Anatomy Explained Injury Types And Treatments
 Yoga Anatomy Using Muscle Awareness To Lower Your Heels In
Yoga Anatomy Using Muscle Awareness To Lower Your Heels In
 Dasksha Dog Leg Brace For Hind Leg 1 Pair Used For Sprains Hind Leg Support For Arthritis Stability After Injury Dog Hock Ankle Support
Dasksha Dog Leg Brace For Hind Leg 1 Pair Used For Sprains Hind Leg Support For Arthritis Stability After Injury Dog Hock Ankle Support
 Muscle Bone Structure Charts Dog Anatomy Dog Leg Grey
Muscle Bone Structure Charts Dog Anatomy Dog Leg Grey
 Dog Leg Anatomy Explained Injury Types And Treatments
Dog Leg Anatomy Explained Injury Types And Treatments
 Lymphadenectomy Overview Of Surgical Anatomy Removal Of
Lymphadenectomy Overview Of Surgical Anatomy Removal Of
 A Visual Guide To Dog Anatomy Muscle Organ Skeletal
A Visual Guide To Dog Anatomy Muscle Organ Skeletal
 Lymphadenectomy Overview Of Surgical Anatomy Removal Of
Lymphadenectomy Overview Of Surgical Anatomy Removal Of
 Alternatives To Surgery For Ligament Injuries In Dogs
Alternatives To Surgery For Ligament Injuries In Dogs
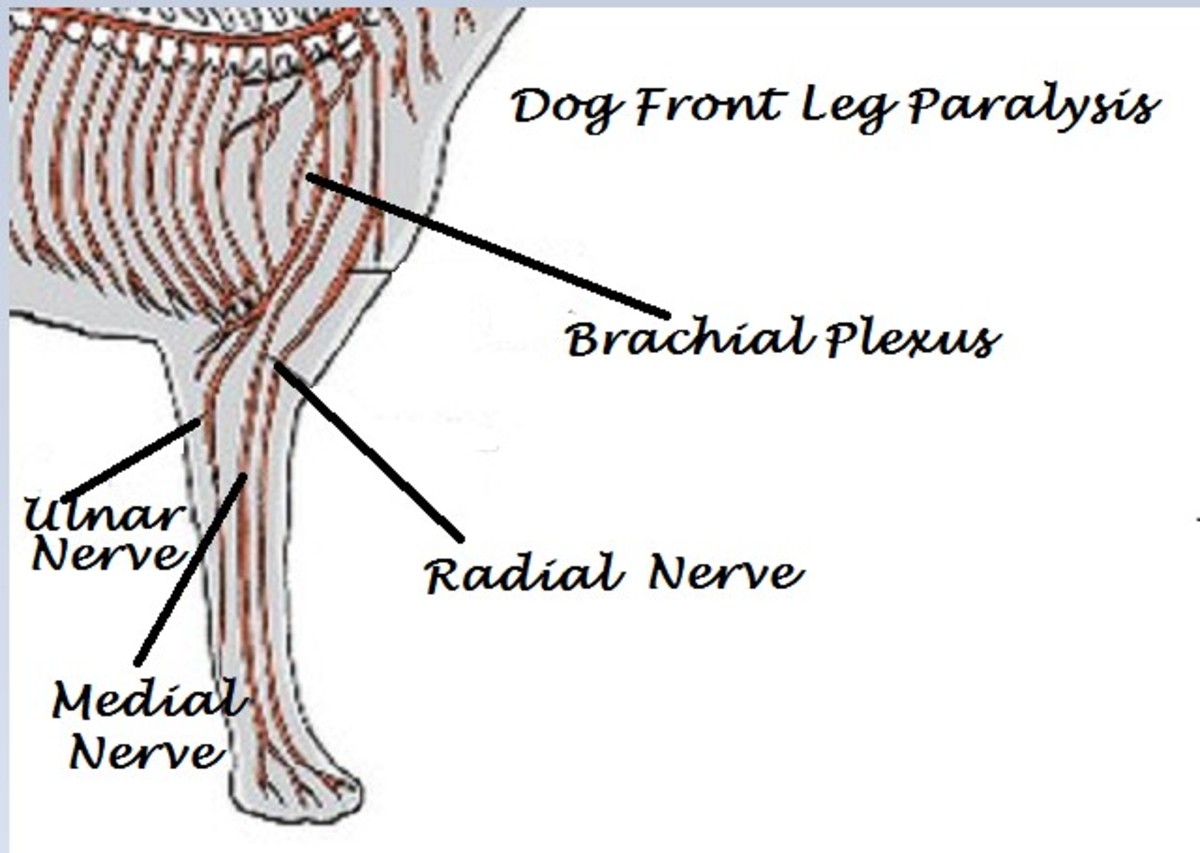 Causes Of Front Leg Paralysis In Dogs Pethelpful
Causes Of Front Leg Paralysis In Dogs Pethelpful
 Labeled Atlas Of Anatomy Illustrations Of The Dog
Labeled Atlas Of Anatomy Illustrations Of The Dog
 The Anatomy Of Your Dog Or Cat Dog Anatomy Dog Leg Leg
The Anatomy Of Your Dog Or Cat Dog Anatomy Dog Leg Leg
 Amazon Com Bbyt Dog Canine Hip Joint Skeleton Model
Amazon Com Bbyt Dog Canine Hip Joint Skeleton Model
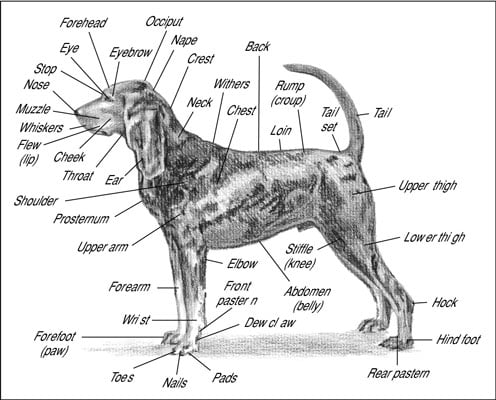 Dog Anatomy From Head To Tail Dummies
Dog Anatomy From Head To Tail Dummies
 Labeled Atlas Of Anatomy Illustrations Of The Dog
Labeled Atlas Of Anatomy Illustrations Of The Dog



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Dog Leg Anatomy"
Posting Komentar