Cranial Anatomy
The brainstem can be divided into three levels the midbrain the pons and the medulla. Examination of the cranial nerves allows one to view the brainstem all the way from its rostral to caudal extent.
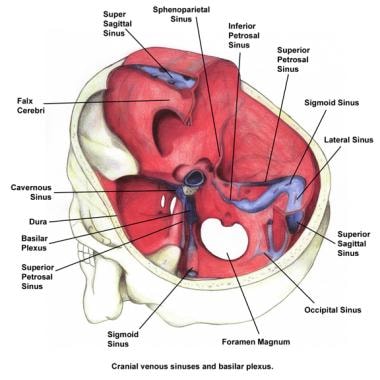 Skull Base Anatomy Overview Anterior Skull Base Middle
Skull Base Anatomy Overview Anterior Skull Base Middle
The vagus nerve has axons that originate from or enter the dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve.

Cranial anatomy. Cranial anatomy the brain is the control center of the nervous system and consequently the human body. The cranial and facial bones and structures. The facial bones underlie the facial structures form the nasal cavity enclose the eyeballs and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.
The paths within the skull are called intracranial and the paths outside the skull are called extracranial. The cranial and facial bones and structures. The brain is in charge of movement memory preservation and involuntary functions in the body.
The brain is in charge of movement memory preservation and involuntary functions in the body. Detailed anatomy of the human skull. The first two nerves olfactory and optic arise from the cerebrum whereas the remaining ten emerge from the brain stem.
Comprised of six bones the frontal sphenoid ethmoid occipital parietal and temporal bones. Cranial anatomy the brain is the control center of the nervous system and consequently the human body. Key points the vagus nerve cranial nerve x sends information about the bodys organs to the brain.
The skull consists of five major bones. There are many holes in the skull called foramina by which the nerves can exit the skull. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case or cranial vault link.
The vagus nerve is responsible for heart rate gastrointestinal peristalsis and sweating to name. These bones are important as they provide an articulation point for the 1st cervical vertebra atlas as well as the facial bones and the mandible jaw bone. The skull of a normal bird usually weighs about 1 of the birds total bodyweight.
Cranial nerves have paths within and outside the skull. The frontal top of head parietal back of head premaxillary and nasal top beak and the mandible bottom beak. The cranium skull is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain.
The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves that arise directly from the brain.
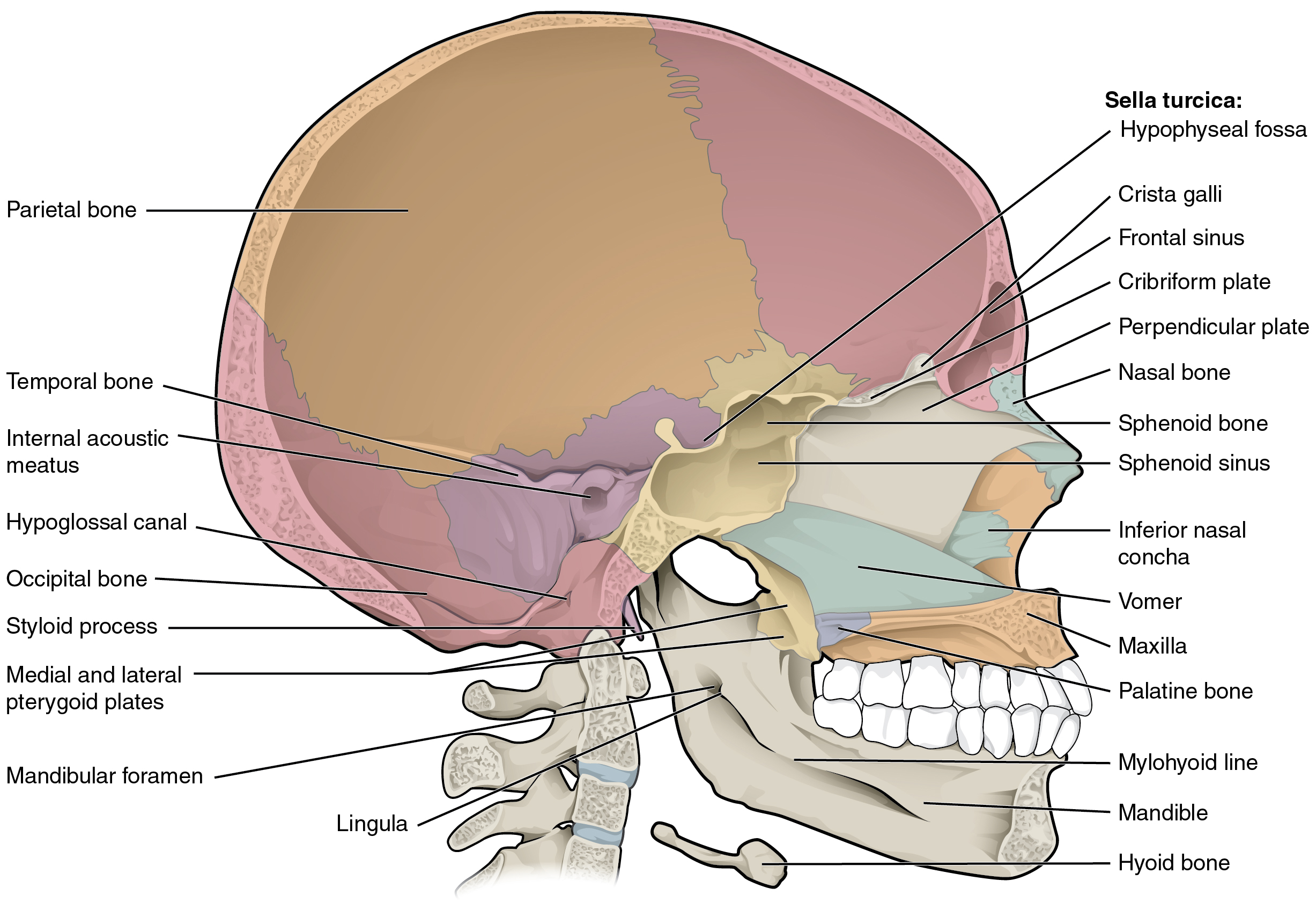 7 2 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
7 2 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
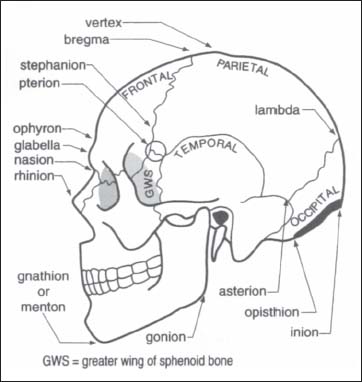 6 Cranial Anatomy And Approaches Neupsy Key
6 Cranial Anatomy And Approaches Neupsy Key
Plos One Cranial Anatomy Of The Gorgonopsian Cynariops
 Part 1 The Axial Skeleton 7 1 The Skull Consists Of 8
Part 1 The Axial Skeleton 7 1 The Skull Consists Of 8
 Bones Of The Head Anatomy Physiology Human Anatomy
Bones Of The Head Anatomy Physiology Human Anatomy
 Skull Anatomical Illustrations
Skull Anatomical Illustrations
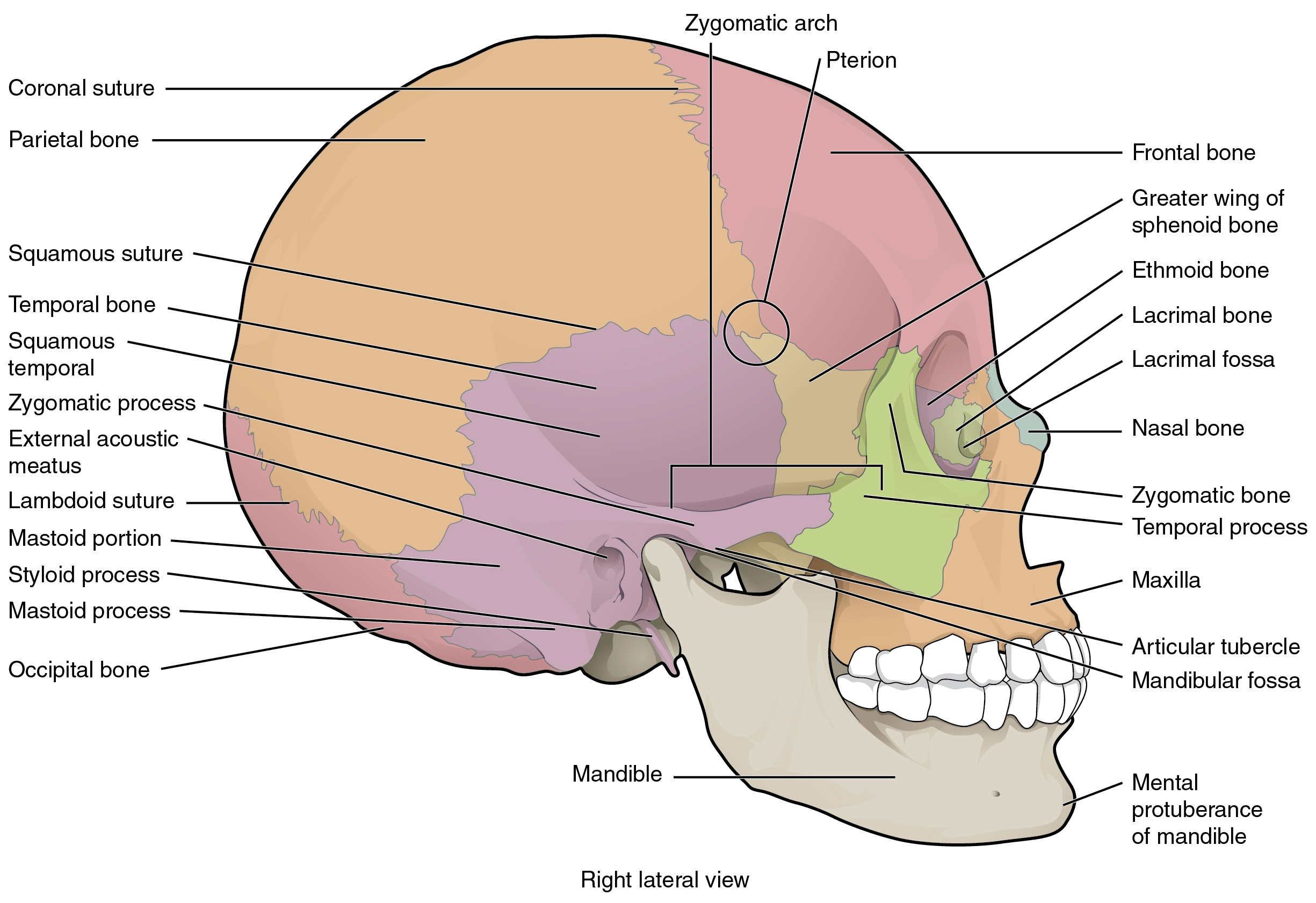 7 2 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
7 2 The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
 Skull Anatomical Illustrations
Skull Anatomical Illustrations
 Cranial Anatomy Of The Basal Synapsid Varanosaurus
Cranial Anatomy Of The Basal Synapsid Varanosaurus
 Skull Anatomy X Ray Stuff Anatomie Knochen Medizin
Skull Anatomy X Ray Stuff Anatomie Knochen Medizin
 Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica
Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/sutura-coronalis/Pu1gDcPU5c8ah4VZapyFwA_Coronal_suture_01.png) Sutures Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub
Sutures Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub

Plos One Cranial Anatomy And Palaeoneurology Of The
 Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric Skull Molding
Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric Skull Molding
 Cranial Nerve Anatomy Cranial Nerves Iowa Head And Neck
Cranial Nerve Anatomy Cranial Nerves Iowa Head And Neck
 Cranial Anatomy Of Plecotus Auritus A 3d Mct Inferior
Cranial Anatomy Of Plecotus Auritus A 3d Mct Inferior
Plos One Cranial Anatomy Of The Gorgonopsian Cynariops
 4d Vision Human Anatomy Cranial Skull Model
4d Vision Human Anatomy Cranial Skull Model

 Cranial Anatomy Of M Wachtleri Pzo 628 Based On Personal
Cranial Anatomy Of M Wachtleri Pzo 628 Based On Personal
Plos One Cranial Anatomy Of The Gorgonopsian Cynariops
 Cranial Nerves Part 1 Normal Anatomy And Function Vetmeet
Cranial Nerves Part 1 Normal Anatomy And Function Vetmeet
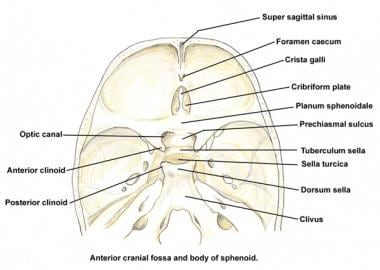 Skull Base Anatomy Overview Anterior Skull Base Middle
Skull Base Anatomy Overview Anterior Skull Base Middle


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Cranial Anatomy"
Posting Komentar