Horse Eye Anatomy
The exterior of the eye comprises the conjunctiva which is divided into the palpebral and bulbar portions and the eyelids. While all anatomical features of equids are described in the same terms as for other animals by the international committee on veterinary gross anatomical nomenclature in the book nomina anatomica veterinaria there are many horse specific colloquial terms used by equestrians.
They eye of a horse can tell you a lot about his attitude at the moment.

Horse eye anatomy. The anatomy of the equine eye. This additional eyelid is a whitish pink color and it is found under the other eyelids in the inside corner of the eye near the nose. Horses have large eyelashes or cilia on their upper eyelid margin and none on the lower lid.
The eyeball of the horse is not perfectly spherical but rather is flattened anterior to posterior. The upper lid has lashes. The equine eye is a complex and elegantly designed organ that functions to allow capture of light and conversion of light into an electrical stimulus which is then transmitted to the brain and interpreted into vision.
Equine anatomy refers to the gross and microscopic anatomy of horses and other equids including donkeys and zebras. Unlike humans horses also have a third eyelid or nictitating membrane which originates from the inside corner and closes horizontally across the eye. If the eye is opened wide and you see the white of the eye surrounding the dark circle.
The eyes of a horse are protected not only by the same types of eyelids that people have but also by the nictitating membrane which is sometimes called the third eyelid. The equine eye includes the eyeball and the surrounding muscles and structures termed the adnexa. Anatomy of the equine eye.
This additional eyelid is a whitish pink color and it is found under the other eyelids in the inside corner of the eye near the nose. A horses eye should always appear soft and dark with the exception of some blue eyed horses or some appaloosas who have white showing at all times. The eyes of a horse are protected not only by the same types of eyelids that people have but also by the nictitating membrane which is sometimes called the third eyelid.
However research has found the horse does not have a ramped retina as was once thought. Long sensory hairs or vibrissae provide sensation to the skin surrounding the eyes of horses. This function is reflected in the structure of the eye.
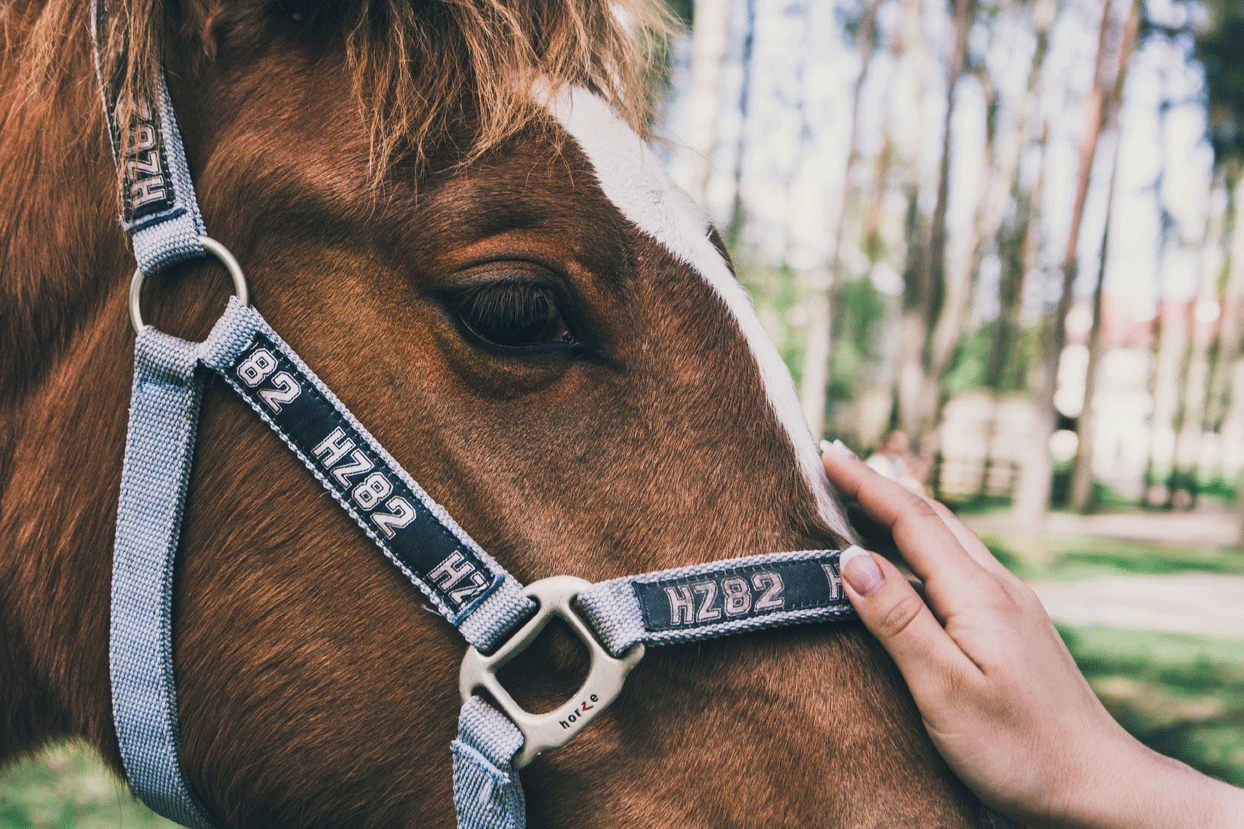 Course Equine Anatomy And Health Considerations Avalon
Course Equine Anatomy And Health Considerations Avalon
 The Structure Of The Eye Video Khan Academy
The Structure Of The Eye Video Khan Academy
 Physical Examination Of The Eye Eye Diseases And Disorders
Physical Examination Of The Eye Eye Diseases And Disorders
 The Equine Eye Expert Advice On Horse Care And Horse Riding
The Equine Eye Expert Advice On Horse Care And Horse Riding
 Iris And Periocular Recognition In Arabian Race Horses Using
Iris And Periocular Recognition In Arabian Race Horses Using
 How To Draw Animals Horses Their Anatomy And Poses
How To Draw Animals Horses Their Anatomy And Poses
 Understanding Equine Vision And Eye Disease Horse Journals
Understanding Equine Vision And Eye Disease Horse Journals
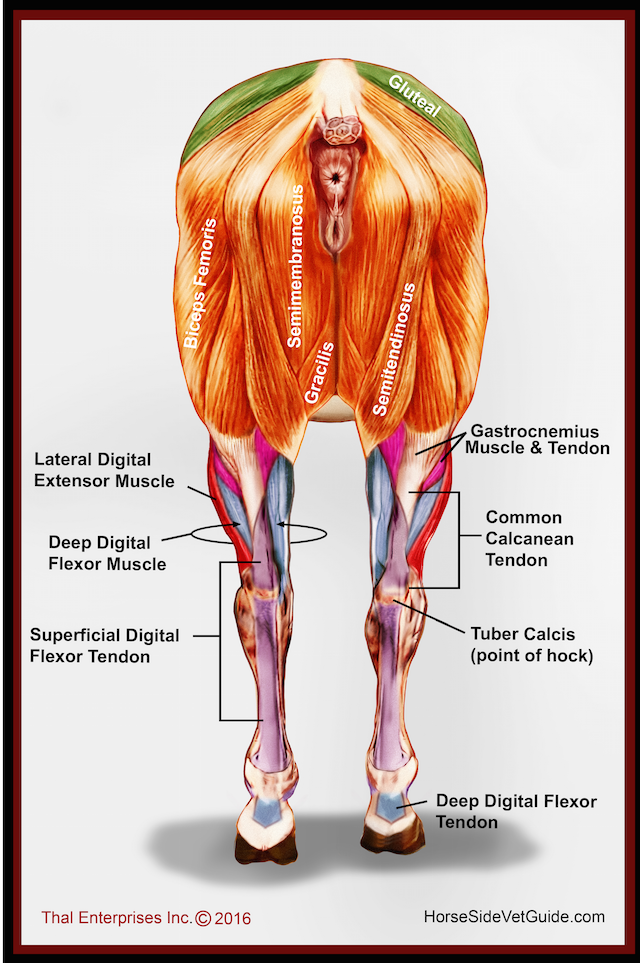 Vitals Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
Vitals Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
Wise Old Eyes Horses Animals Pixoto
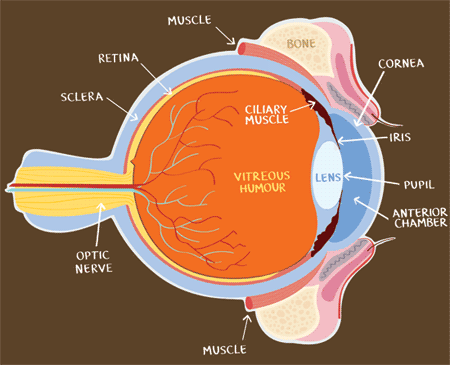 Moon Blindness Uveitis In Horses Natural Chinese Herbal
Moon Blindness Uveitis In Horses Natural Chinese Herbal
 Eye Opener Anatomy Comparison Of The Eye Between Animals
Eye Opener Anatomy Comparison Of The Eye Between Animals
 Anatomy Of The Horse Klaus Dieter Budras 9783899936667
Anatomy Of The Horse Klaus Dieter Budras 9783899936667
 Equine Eye Anatomy And Physiology The Horse
Equine Eye Anatomy And Physiology The Horse
 Horse Anatomy Pictures Think Like A Horse Rick Gore
Horse Anatomy Pictures Think Like A Horse Rick Gore
 Management Of Equine Eye Injuries Canberra Equine Hospital
Management Of Equine Eye Injuries Canberra Equine Hospital
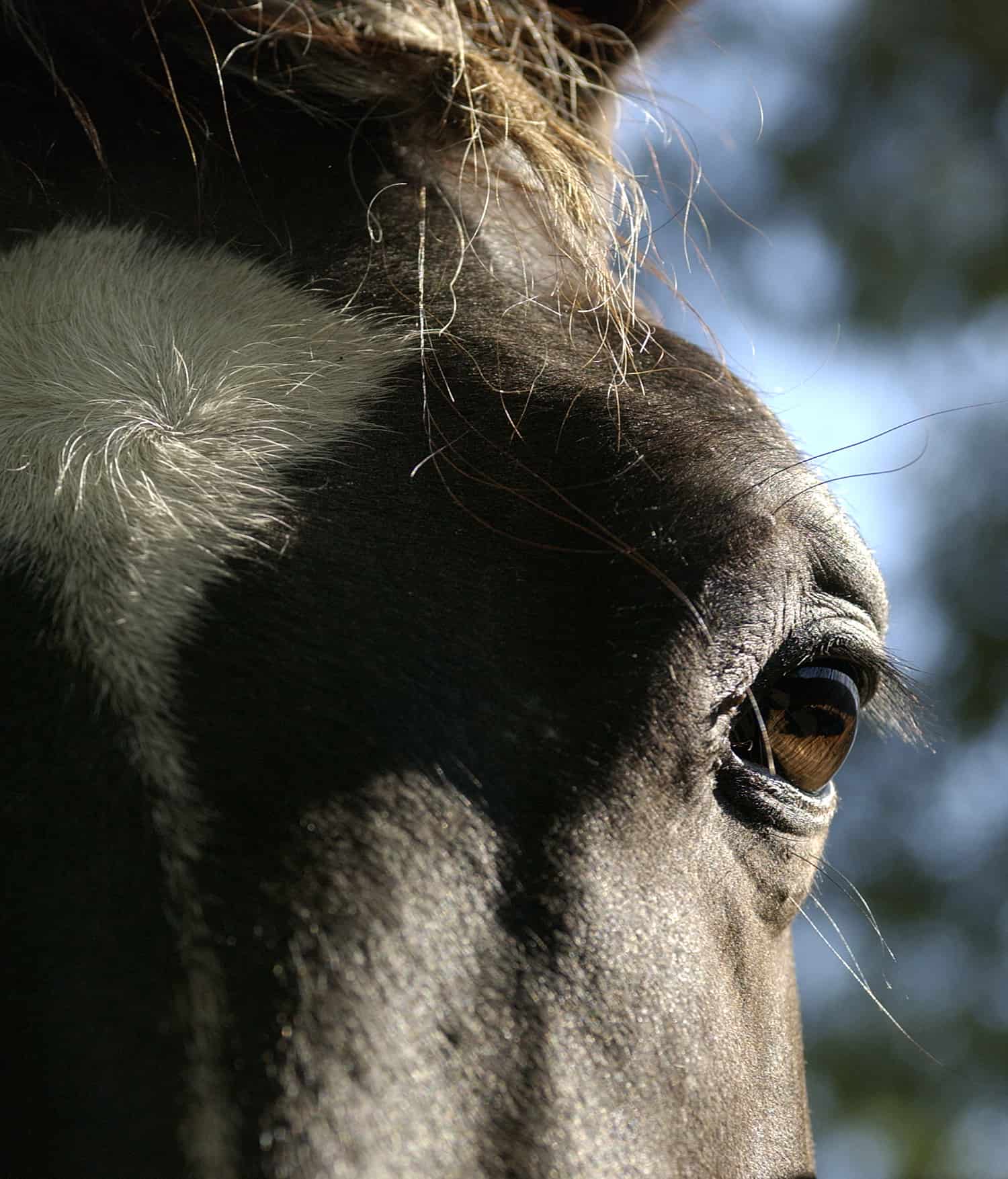 Equine Eye Anatomy And Physiology The Horse
Equine Eye Anatomy And Physiology The Horse
 Eye Structure And Function In Cats Cat Owners Merck
Eye Structure And Function In Cats Cat Owners Merck
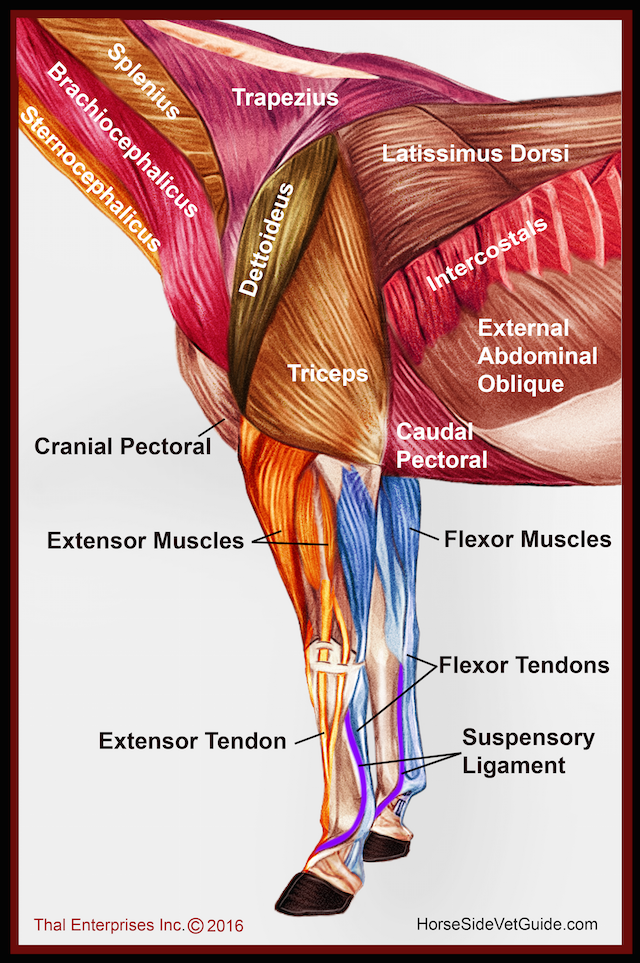 Vitals Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
Vitals Anatomy Horse Side Vet Guide
The Eye A Window To The Soul Scarsdale Vets
 Understanding Equine Vision And Eye Disease Horse Journals
Understanding Equine Vision And Eye Disease Horse Journals
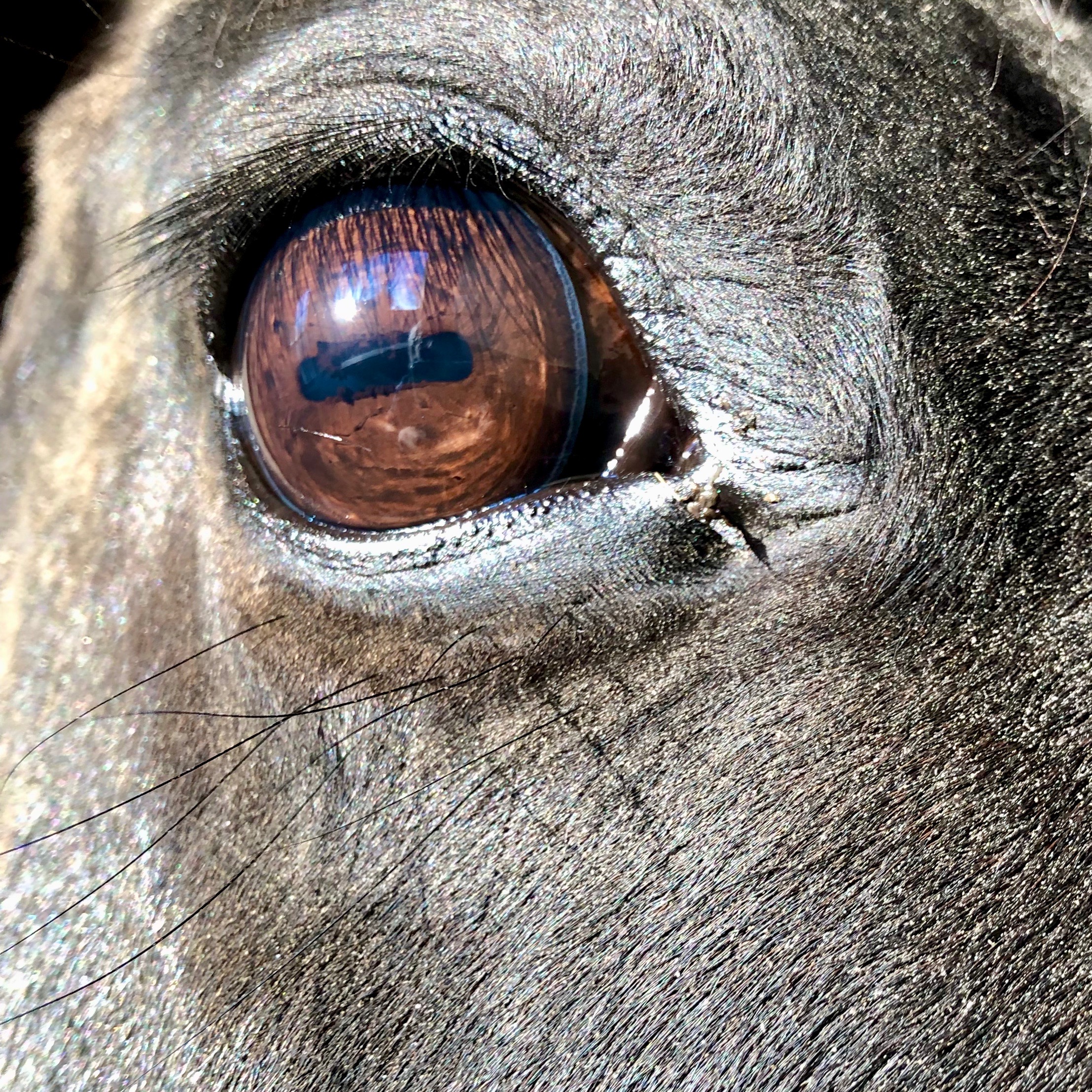 Horse Color Vision The Cooperative Horse
Horse Color Vision The Cooperative Horse



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Horse Eye Anatomy"
Posting Komentar