Macula Anatomy
Anatomy of internal ear in senses. The macula in humans has a diameter of around 55 mm 022 in and is subdivided into the umbo foveola foveal avascular zone fovea parafovea and perifovea areas.
 Macular Degeneration Baton Rouge La Ophthalmologist
Macular Degeneration Baton Rouge La Ophthalmologist
Photopic color vision are primary functions of this area.
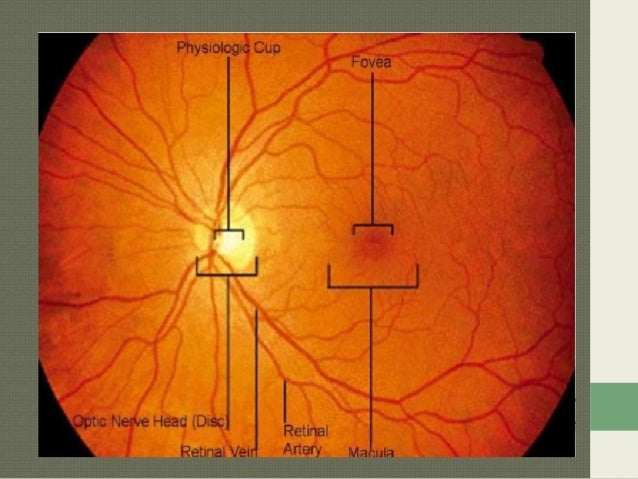
Macula anatomy. In the center of the macula is the fovea perhaps the most important part of the eye. The macula is a circular area of diameter 55 mm with a center located 17 degrees or 40 50 mm temporal and 053 08mm inferior to the center of the optic disc. The normal central retinal artery black arrow is located nasal to the central retinal vein green arrow in the optic disc.
The bundle of nerve fibers at the back of the eye that carry visual messages from the retina to the brain. When the gaze is fixed on any object the centre of the macula the centre of the lens and the object are in a straight line. The macula is a small but important area in the center of the retina.
A number of eye problems can affect the macula and can lead to vision loss if they are not treated. An area of the eye near the center of the retina where visual perception is most acute. Macula lutea macula lutea is a 55 mm circular area deeper red than rest.
Anatomy of macula 1. It is one hundred times more sensitive to detail than the peripheral retina. The fovea is the area of best visual acuity.
Vestibule of sensory cells called a macula which is about 2 mm 008 inch in diameter. Vestibular structures of sensory cells called a macula. Contents anatomy of macula lutea embryology blood supply macular function tests.
The light sensing nerve cells rods and cones located in the retina. It is marked by the presence of multiple cyst like cystoid formations which cause edema swelling in the macular area resulting in blurred or decreased central vision. Cystoid macular edema cme is a painless disorder affecting the macula.
It contains a large amount of conesnerve cells that are photoreceptors with high acuity. The portion of the eye at the center of the retina that processes sharp clear straight ahead vision. The macula is responsible for the sharp straight ahead vision that is used for seeing fine detail reading driving and recognizing faces.
Macula lutea in anatomy the small yellowish area of the retina near the optic disk that provides central vision. The macula or macula lutea is an oval shaped pigmented area near the center of the retina of the human eye and some other animalian eyes. Mechanical senses of hair cells known as maculae.
You need the macula to clearly see details of objects in front of you like faces and written text. The macula is the pigmented part of the retina located in the very center of the retina.
 Diagram Showing The Anatomy Of The Eye Including The
Diagram Showing The Anatomy Of The Eye Including The
 Anatomy Review Optical Coherence Tomography Scans
Anatomy Review Optical Coherence Tomography Scans
 Human Eye Macula Of Retina Muscle Anatomy Png Clipart
Human Eye Macula Of Retina Muscle Anatomy Png Clipart
 Fundoscopic Appearances Of Retinal Pathologies Geeky Medics
Fundoscopic Appearances Of Retinal Pathologies Geeky Medics
 Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
 Anatomy Of The Eye Oregon Optometric Physicians
Anatomy Of The Eye Oregon Optometric Physicians
 Screening For Macular Degeneration Optical Experts Doctor
Screening For Macular Degeneration Optical Experts Doctor
 What Is Macular Degeneration Amdf
What Is Macular Degeneration Amdf
 Eye Anatomy How Youniggasook Od Ciliary Body Retina Iris
Eye Anatomy How Youniggasook Od Ciliary Body Retina Iris
 Anatomy Final Eye Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy Final Eye Flashcards Quizlet
 Macula Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Macula Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
 Retina Diseases Las Vegas Nv Nevada Retina Center
Retina Diseases Las Vegas Nv Nevada Retina Center
 Vector Structure Of The Human Eye Anatomy And Medicine Iris
Vector Structure Of The Human Eye Anatomy And Medicine Iris
 Macular Degeneration Women S Voices For Change
Macular Degeneration Women S Voices For Change
 Retinoblastoma Anatomy Of The Eye Memorial Sloan
Retinoblastoma Anatomy Of The Eye Memorial Sloan
 New Anatomy And Physiology Of Macula Pptx Visual System
New Anatomy And Physiology Of Macula Pptx Visual System
 Anatomy And Structure Of The Eye Brightfocus Foundation
Anatomy And Structure Of The Eye Brightfocus Foundation
 Retina Macula Lutea Choroid Anatomy Eyeball Anatomy Eye
Retina Macula Lutea Choroid Anatomy Eyeball Anatomy Eye
 About Basic Eye Anatomy Gem Clinic Glaucoma Eye
About Basic Eye Anatomy Gem Clinic Glaucoma Eye
 How The Eye Works As A Camera Amdf
How The Eye Works As A Camera Amdf
 Anatomy Of The Human Eye Affected By Age Related Macula
Anatomy Of The Human Eye Affected By Age Related Macula
 Macular Hole Scott E Pautler M D Tampa
Macular Hole Scott E Pautler M D Tampa
 Colorado Retina Patient Education
Colorado Retina Patient Education
 Retina Farmington Retina Specialist Ct Consulting
Retina Farmington Retina Specialist Ct Consulting


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Macula Anatomy"
Posting Komentar