Anatomy Of Female Pelvic Floor
16 the muscles of the pelvic floor. This paper is intended to review the anatomy and function of the different aspects of the pelvic floor and stress continence control system.
 Life Size Female Pelvis Anatomy Model With Ligaments Vessels Nerves And Pelvic Floor
Life Size Female Pelvis Anatomy Model With Ligaments Vessels Nerves And Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor is a complex group of muscles that exists in both males and females.

Anatomy of female pelvic floor. The female pelvic floor is made of muscles and connective tissue. The pelvic floor is a funnel shaped musculature structure. Female pelvic floor 1.
2 3 most women with incontinence have stress incontinence 4 which is treated using conservative therapy or surgery. Female pelvic cavity ligaments and pelvic fascia iliolumbar ligament from tip of transverse process of l5 to posterior aspect of inner lip of iliac crest. What is the female pelvis.
Innervated by pudendal nerve. Anatomy and pathophysiology introduction. One common type of female pelvic floor dysfunction urinary incontinence is a common condition with prevalence ranging from 85 to 38 depending on age parity and definition.
The female pelvis figure 1a has a wider diameter and a more circular shape than that of the male. Innervated by sacral nerve roots s3 s5. Pelvic muscle exercises as a treatment for incontinence would only be an option for those patients with pelvic muscles having sufficient residual innervation to control those muscles.
This area provides support for the intestines and also contains the bladder and. The pelvic floor muscles support. The pelvis is the lower part of the torso.
The wider inlet facilitates head engagement and parturition. The pelvic floor consists of three muscle layers. The inferior pelvic outlet is closed by the pelvic floor.
Its located between the abdomen and the legs. In the female pelvis the muscles of the pelvic floor are often infiltrated by fibrous tissue and this can frequently be seen even during prenatal stages of development fritsch and frohlich 1994. Innervated by the pudendal nerve.
Deep urogenital diaphragm layer. Anatomy of the female pelvic floor basic knowledge of the anatomy of the female pelvic floor is crucial to correctly interpret pelvic mr images and to fully understand dysfunction associated with pelvic floor weakness. Sacrotuberous ligament from sacrum to tuberosity of the ischium.
Strengthens the lumbo sacral joint. It attaches to the walls of the lesser pelvis separating the pelvic cavity from the inferior perineum region which includes the genitalia and anus.
 Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
 Amazon Com Female Pelvis And Pelvic Floor Model Industrial
Amazon Com Female Pelvis And Pelvic Floor Model Industrial
Human Anatomy Female Pelvic Floor Anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11897/nerves-of-female-pelvis_english.jpg) Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
 Details About Anatomy Model Of Female Pelvis Pelvic Floor Muscles And Reproductive Organs
Details About Anatomy Model Of Female Pelvis Pelvic Floor Muscles And Reproductive Organs
 Female Pelvis And Pelvic Floor 5 Part
Female Pelvis And Pelvic Floor 5 Part
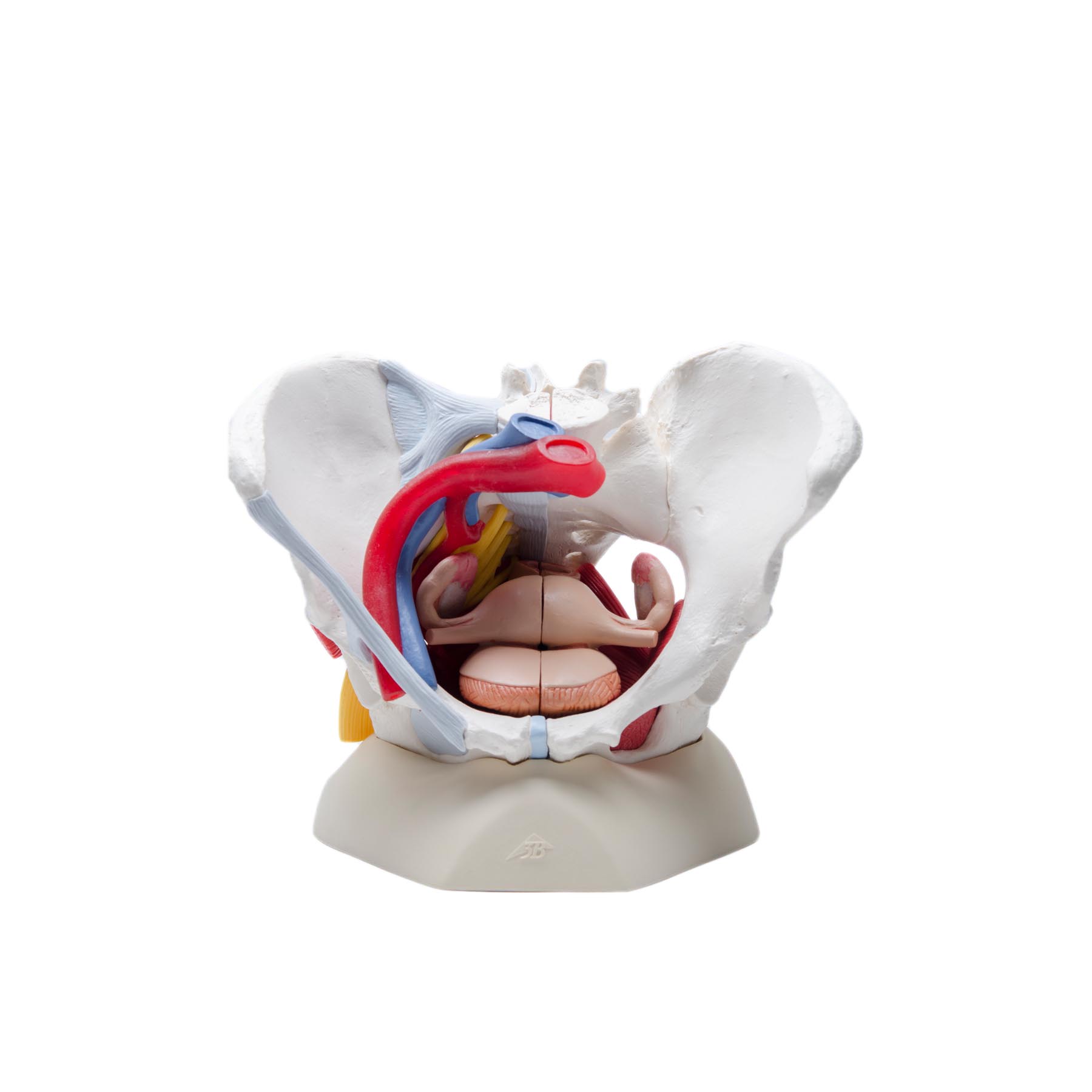 Highly Detailed Female Pelvic Model Magnetic
Highly Detailed Female Pelvic Model Magnetic
 The Ultimate Pelvic Anatomy Resource Pelvic Guru Featured
The Ultimate Pelvic Anatomy Resource Pelvic Guru Featured
 Primary Care Management Of Chronic Pelvic Pain In Women
Primary Care Management Of Chronic Pelvic Pain In Women
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11895/male-pelvic-viscera-and-perineum_english.jpg) Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
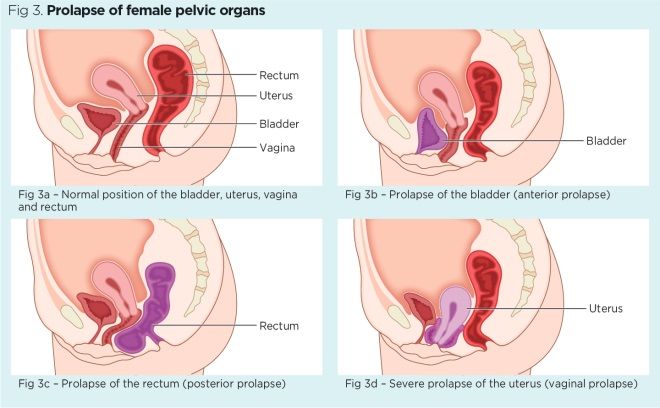 Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
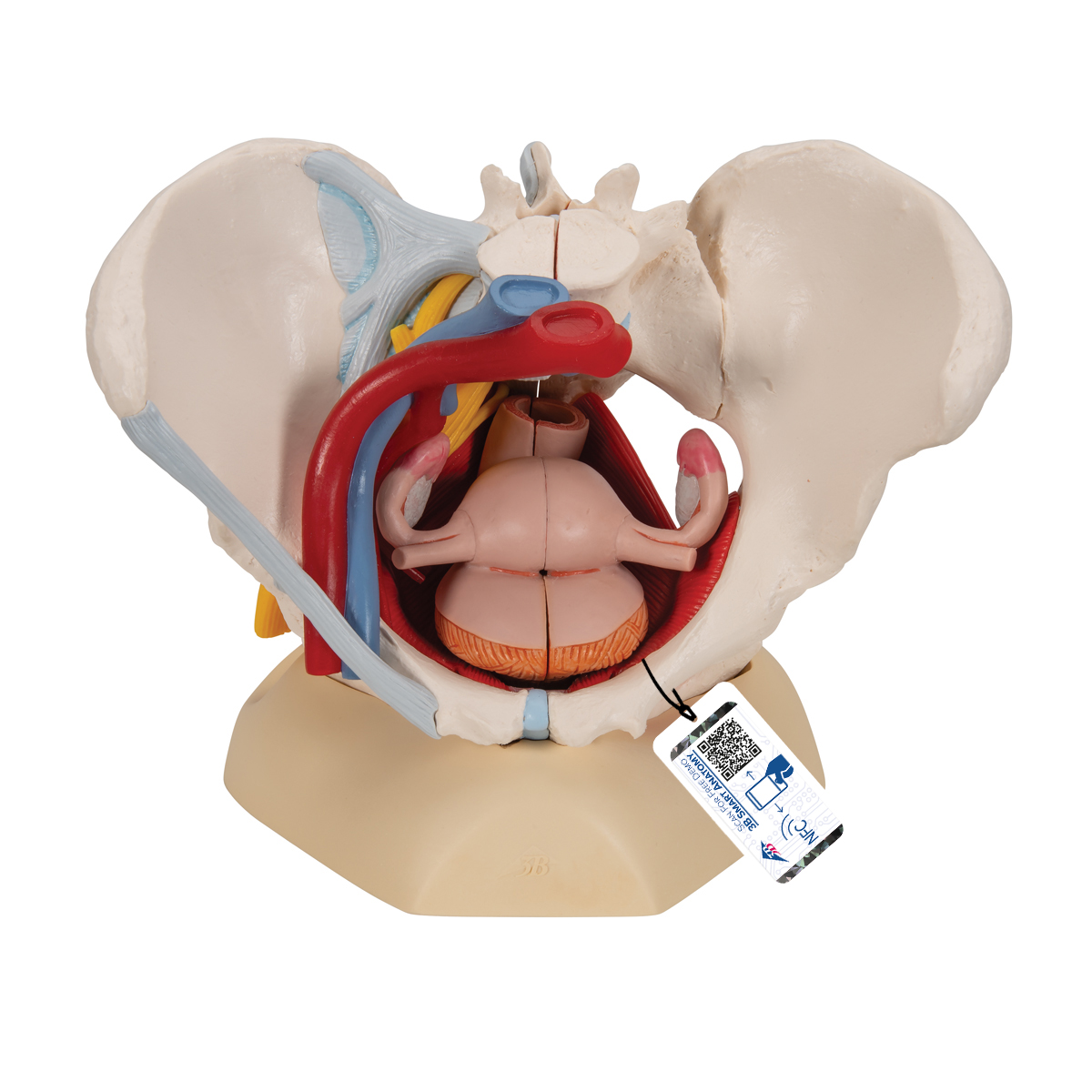 Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Pelvic Models
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Pelvic Models
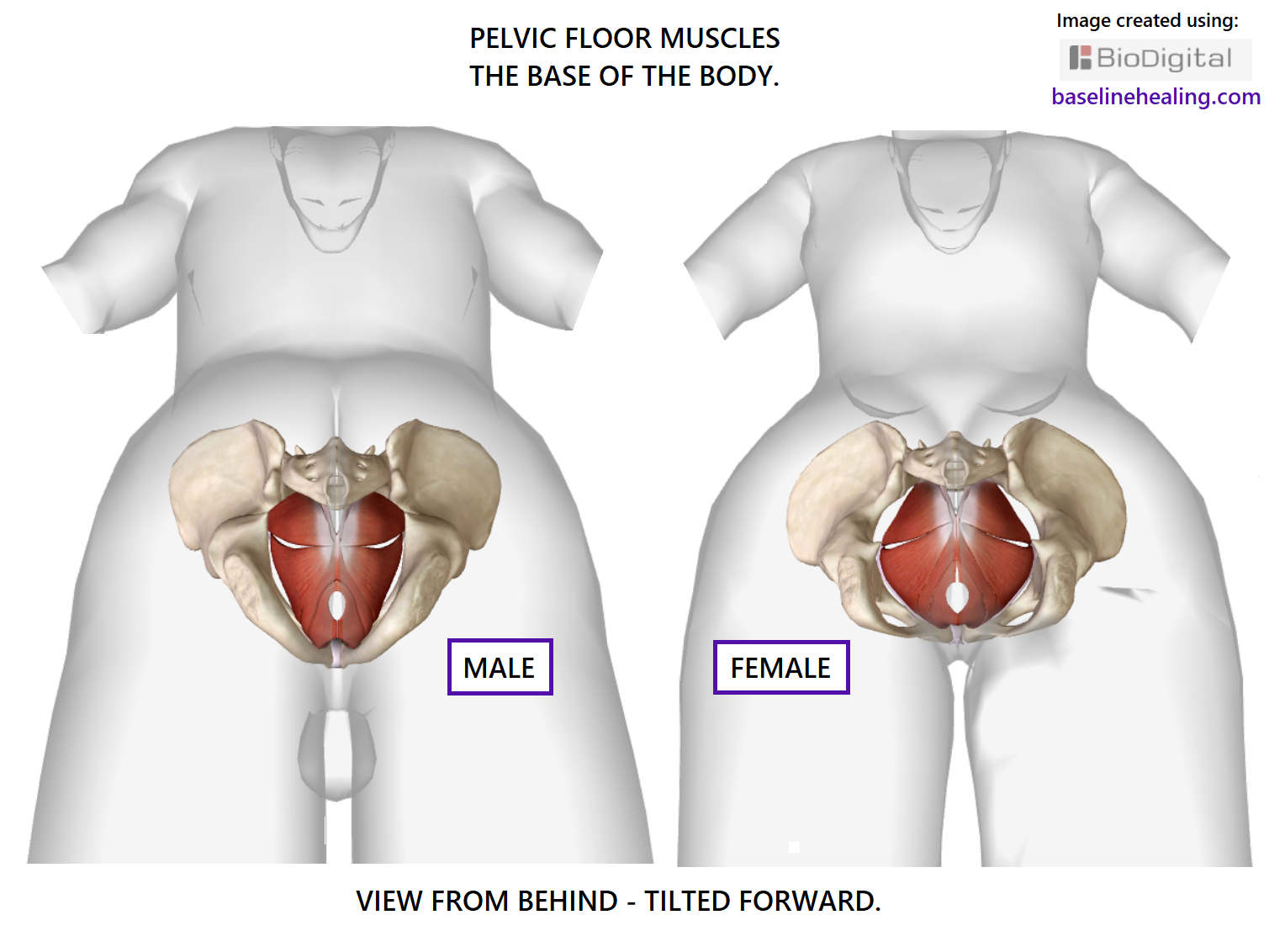 Pelvic Floor Muscles How To Find Your
Pelvic Floor Muscles How To Find Your
 Pelvic Floor Anatomy And Pathology Sciencedirect
Pelvic Floor Anatomy And Pathology Sciencedirect
Pelvic Floor Anatomy Beyond Basics Physical Therapy New
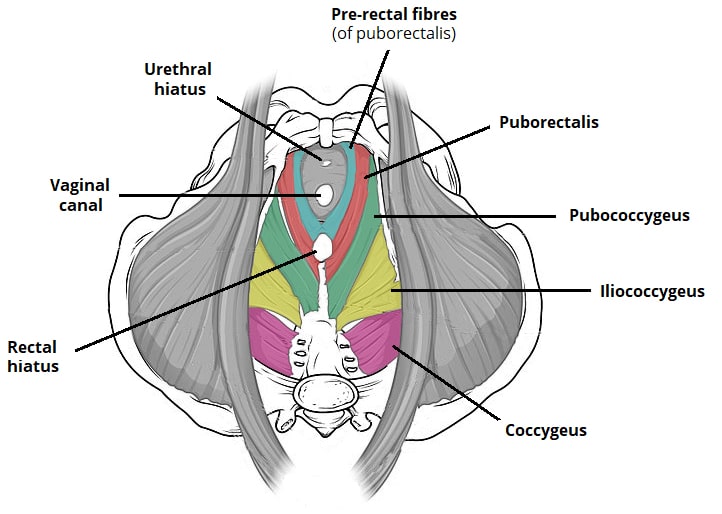 The Pelvic Floor Structure Function Muscles
The Pelvic Floor Structure Function Muscles
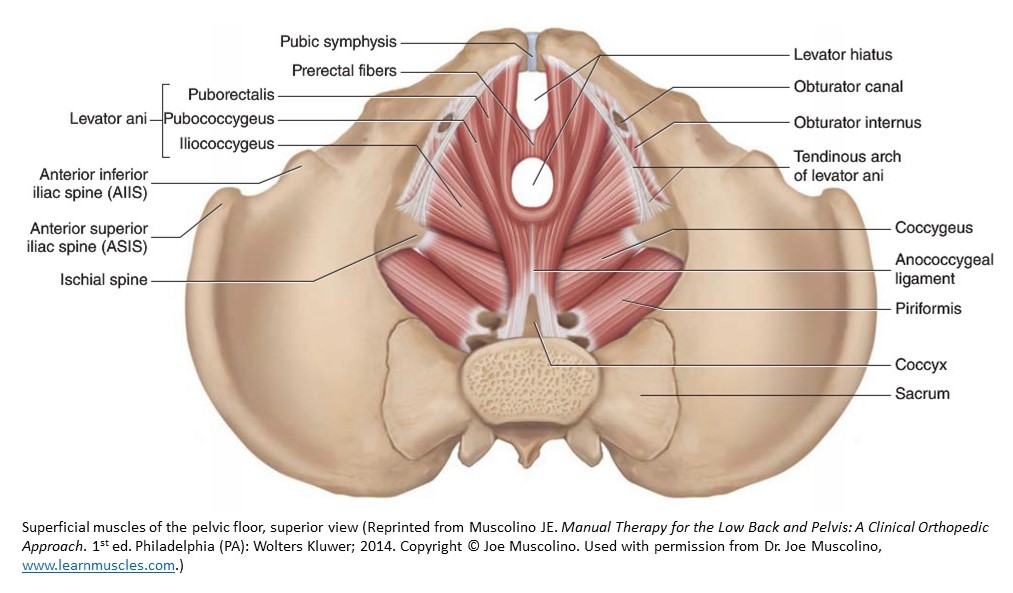 Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Sound Training Advice
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Sound Training Advice
5 Anatomical Detail Of Female Pelvic Anatomy Adapted From
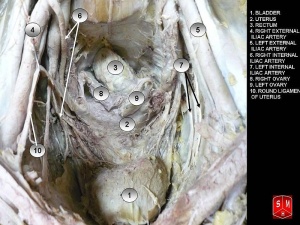
 Pessary Female Pelvic Floor Central
Pessary Female Pelvic Floor Central
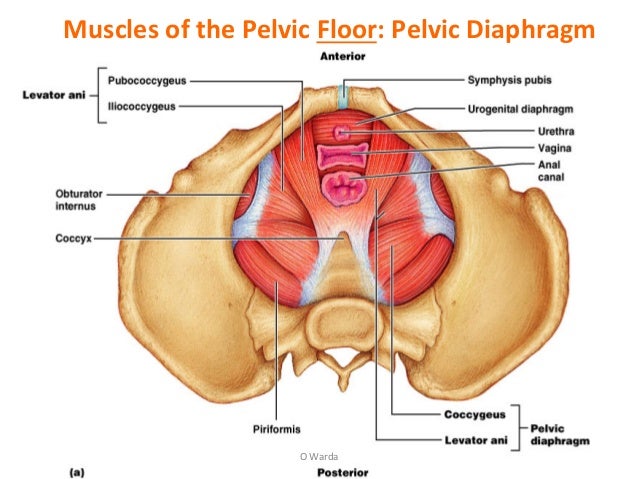 2 Female Pelvic Anatomy Warda Part 2
2 Female Pelvic Anatomy Warda Part 2
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/447/cKqKyPqIrfdkM7JgFJ6LkQ_pelvic-floor-muscles_english.jpg) Diagram Pictures Muscles Of The Pelvic Floor Anatomy
Diagram Pictures Muscles Of The Pelvic Floor Anatomy
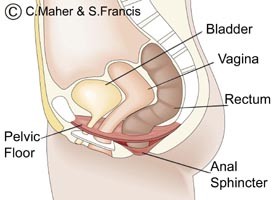
 Normal Anatomy Of The Pelvis And Pelvic Floor Female
Normal Anatomy Of The Pelvis And Pelvic Floor Female
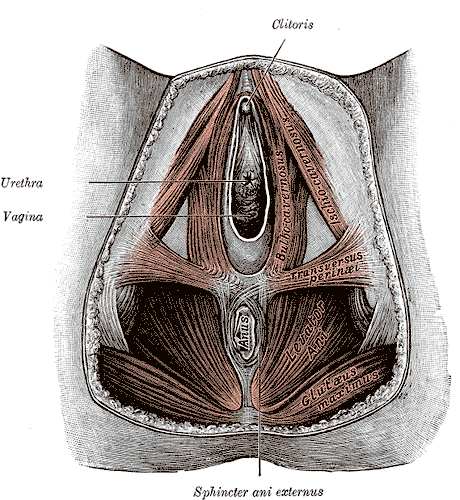 Common Female Pelvic Floor Disorders Pelvic Rehab
Common Female Pelvic Floor Disorders Pelvic Rehab
 Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
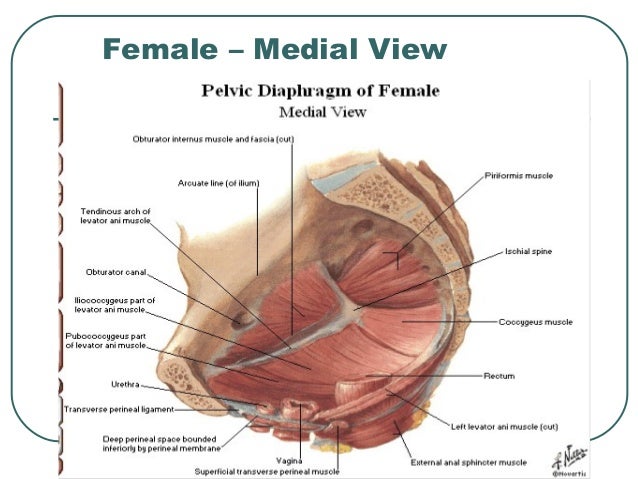
 Pelvic Floor Anatomy Pelvic Diaphragm Part 1
Pelvic Floor Anatomy Pelvic Diaphragm Part 1
 Normal Anatomy Of Female Pelvic Floor Medical Art Works
Normal Anatomy Of Female Pelvic Floor Medical Art Works
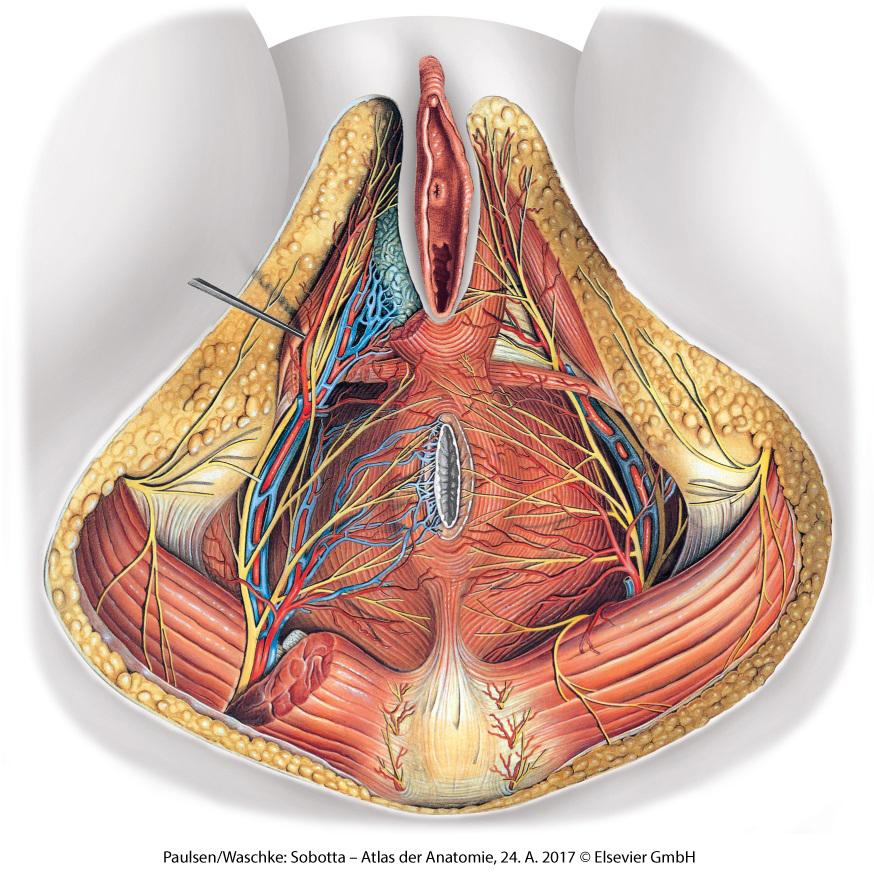
 Information Image Female Perineum Pelvic Floor Muscles
Information Image Female Perineum Pelvic Floor Muscles
Pelvic Floor Anatomy Beyond Basics Physical Therapy New

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Female Pelvic Floor"
Posting Komentar