Anatomy Of Frog Heart
In amphibians such as the frog the pacemaker is the sinus venosus an enlarged region between the vena cava and the right atrium. The ultimate destination for oxygenated blood within a frog is the carotid arteries which send blood to the brain while the deoxygenated blood goes to the lungs and skin to gather oxygen.
 Frog And Human Anatomy Comparison Ms Pearrow S 7th Grade
Frog And Human Anatomy Comparison Ms Pearrow S 7th Grade
A look inside the heart of a frog looking at key valves and parts of the heart.
Anatomy of frog heart. See figure 6 for reference. Truncus arteriosus it is a tubular structure arise from the right side of. This the cells of the pacemaker are termed leaky meaning that calcium ions leak into the cells.
Posterior vena cava large vein that carries blood from the posterior part of the body towards the heart. Anterior vena cava large vein that carries blood from the anterior part of the body toward the heart. A diagram of a frogs heart.
Oxygen in the water can pass through their porous skin and go directly to the blood. 1heart is approximately pear shaped. Excitation of the frog heart heart is myogenic that is contraction of the heart originates within the muscle itself.
Within a human circulation forms a loop from the heart throughout the different sections of the body. Frog lab i slide 4 bioengineering 3202 human physiology regulation of cellular contraction adjust pretension to improve spacing in contractile elements optimal spacing works at tissue and whole heart levels mv t action potential twitch tension cai transient ca gram cai from ica 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 1 15 2 25 3 35 4 tension of maximum. 2the pericardial cavity is not wide and the pericardium forms double membrane around the heart.
They also have a pair of lungs that allow them to breathe when on land. The thread from the frog heart to the transducer should be quit at horizontal so that you apply tension to the long axis of the heart. C place the transducer at the end of the pan elevated 510 cm above the edge of the dissection pan with the blade oriented perpendicular to the thread.
Sinus venosus on the dorsal surface of heart two precaval and a postcaval fused. Frog heartrana 1heart is approximately pear shaped. Frogs breathe through their skin when underwater.
Frogs have a closed circulatory system containing a three chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle. Leaking of positive ions causes a slow. Heart of frog consists of two additional chambers.
Functions of the frog heart heart pumping organ of the circulatory system has 3 chambers.
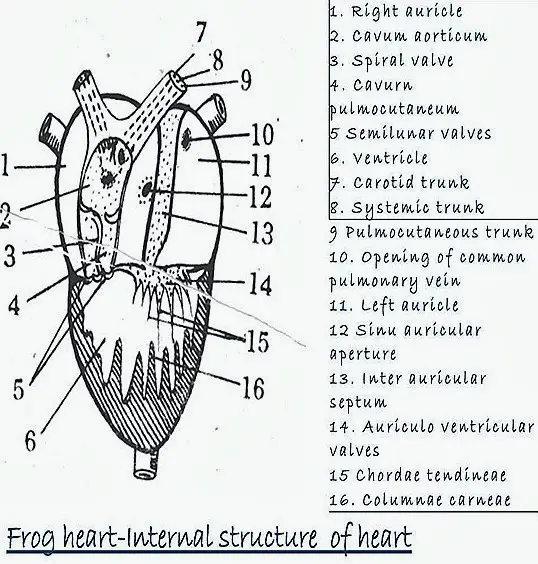 Comparative Anatomy Heart Structure Of Frog And Fish
Comparative Anatomy Heart Structure Of Frog And Fish

 Frog Anatomy Circulatory System
Frog Anatomy Circulatory System
 Animal Circulatory System Frog Fish Earthworm Biology
Animal Circulatory System Frog Fish Earthworm Biology
 Lab 3 Frog Heart At University Of Connecticut Studyblue
Lab 3 Frog Heart At University Of Connecticut Studyblue
Circulatory System Of Toad With Diagram Zoology
 Frog Heart Sinous Venosus Anterior Venae Cavae Posterior
Frog Heart Sinous Venosus Anterior Venae Cavae Posterior
 A Ott Froginfographic 1 By Annika Ott Infographic
A Ott Froginfographic 1 By Annika Ott Infographic
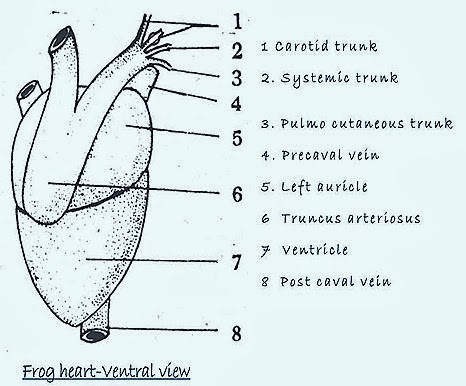 Comparative Anatomy Heart Structure Of Frog And Fish
Comparative Anatomy Heart Structure Of Frog And Fish
Comparative Anatomy Of Vertebrate Hearts
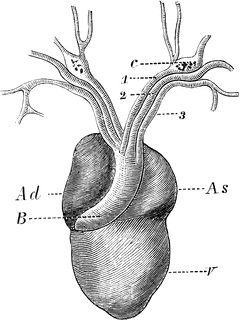
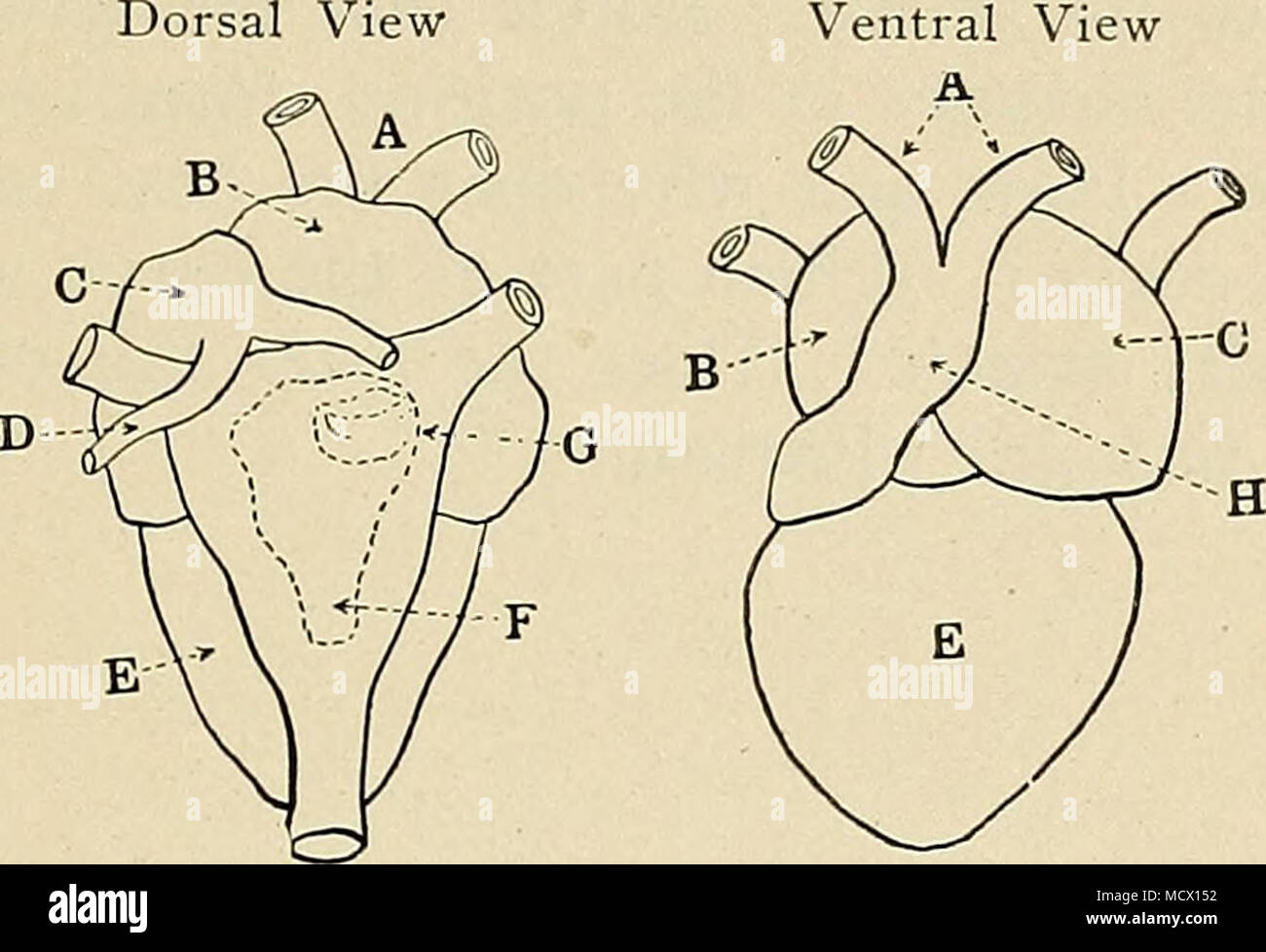 Fig 13 The Gross Anatomy Of Frog S Heart Ventral View
Fig 13 The Gross Anatomy Of Frog S Heart Ventral View
 2 Anatomy Of Frog Part 1 512 1
2 Anatomy Of Frog Part 1 512 1
 Frog Body Parts And Functions Know The Terms In Green
Frog Body Parts And Functions Know The Terms In Green
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-598167278-5b47abf4c9e77c0037f4fedf.jpg) Evolution Of The Human Heart Into Four Chambers
Evolution Of The Human Heart Into Four Chambers
 Biology 2672a Comparative Animal Physiology Circulation
Biology 2672a Comparative Animal Physiology Circulation
 A Ott Froginfographic 1 By Annika Ott Infographic
A Ott Froginfographic 1 By Annika Ott Infographic
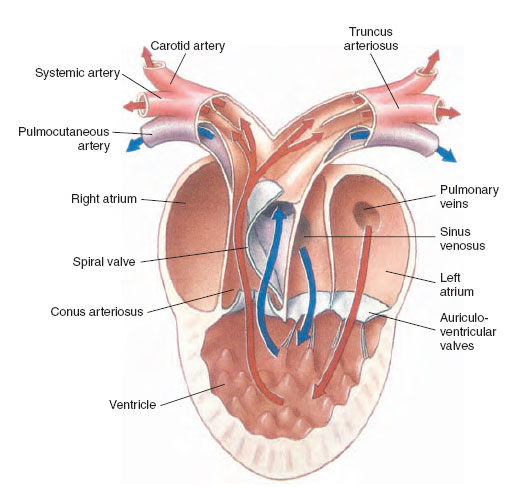 Plan Of Vertebrate Circulatory Systems Circulation
Plan Of Vertebrate Circulatory Systems Circulation
 Frog Dissection Biology Junction
Frog Dissection Biology Junction
 Frog Dissection By Crystal Lee On Prezi
Frog Dissection By Crystal Lee On Prezi
 Amphibian Test Biology 1 Hn With Allen At Pineville High
Amphibian Test Biology 1 Hn With Allen At Pineville High
 Frog Mouth Anatomy Diagram Wiring Diagram Images Gallery
Frog Mouth Anatomy Diagram Wiring Diagram Images Gallery
 The Anatomy Of The Frog Frogs Anatomy Amphibians
The Anatomy Of The Frog Frogs Anatomy Amphibians
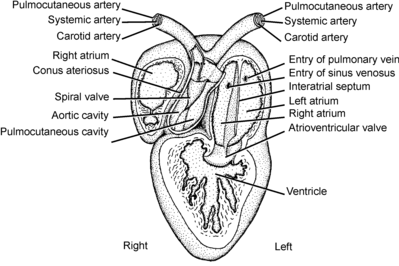 The Organ Systems Circulatory Wikibooks Open Books For An
The Organ Systems Circulatory Wikibooks Open Books For An
 Frog Anatomy External Internal
Frog Anatomy External Internal
 Small Silver Anatomical Heart Pendant
Small Silver Anatomical Heart Pendant
The Vertebrate Heart In Action Nuffield Foundation
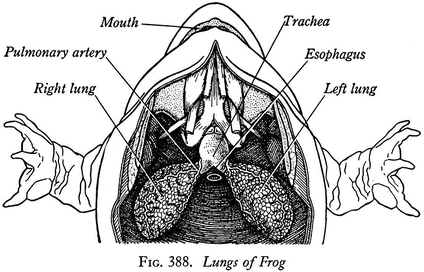 Frog And Human Anatomy Comparison Ms Pearrow S 7th Grade
Frog And Human Anatomy Comparison Ms Pearrow S 7th Grade


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Frog Heart"
Posting Komentar