Effector Anatomy
The science of body functions. Illustrated anatomical parts with images from e anatomy and descriptions of anatomical structures.
Biochemistry a small molecule or protein that alters biochemical processes in a cell.
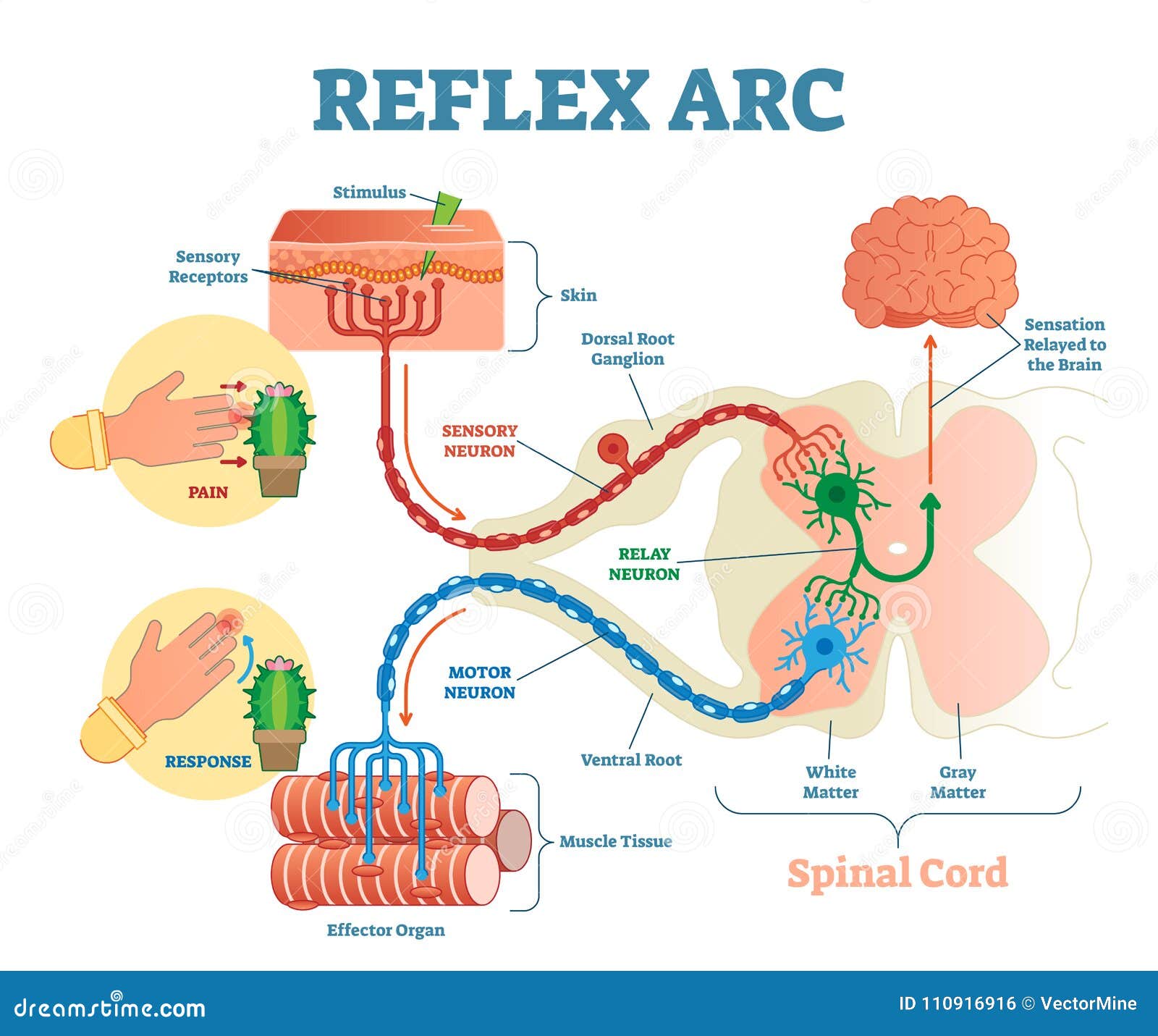
Effector anatomy. Effector general anatomy definition. Effector biology in some cases proteins can be considered to function as effector molecules especially in cellular signal transduction cascades. The term effector is used in other fields of biology.
An effector is any organ or tissue that receives information from the integrating center and acts to bring about the changes needed to maintain homeostasis. The sensors integrating center and effectors are the basic components of every homeostatic response. The study of body structure.
Study of the tissues. Studies the function of the body. Any change or deviation from the normal range of function is opposed or resistedopposed.
Effector effector anatomical parts. Simplest level of structural organization in the body. An effector is the component in a feedback system that causes a change to reverse the situation and return the value to the normal range.
The effector organ is one of the five basic components of a reflex arc. Studies the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another. The motor neuron organizes the action.
A nerve ending that carries impulses to a muscle gland or organ and activates muscle. The sensory receptor recognizes the stimulus and sends it to the sensory neuron. For instance the effector end of a neuron is the terminus where an axon makes contact with the muscle or organ that it stimulates or suppresses.
Keeping the organ system of the body in balance maintaining a stable environment functions of the liver. An organ a gland or muscle that becomes active in response to nerve impulses. How the body parts work and carry out their life sustaining activities.
Filters blood produces bile. One example is the kidney which retains water if blood pressure is too low. The other four components are motor neuron the sensory receptor the sensory neuron and the interneurons.
A muscle gland or organ capable of responding to a stimulus especially a nerve impulse. Body temprature blood pressure ph blood glucose levels.
 Human Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 7 Nervous System Part
Human Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 7 Nervous System Part
 Homeostasis Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation
Homeostasis Chapter 1 The Human Body An Orientation
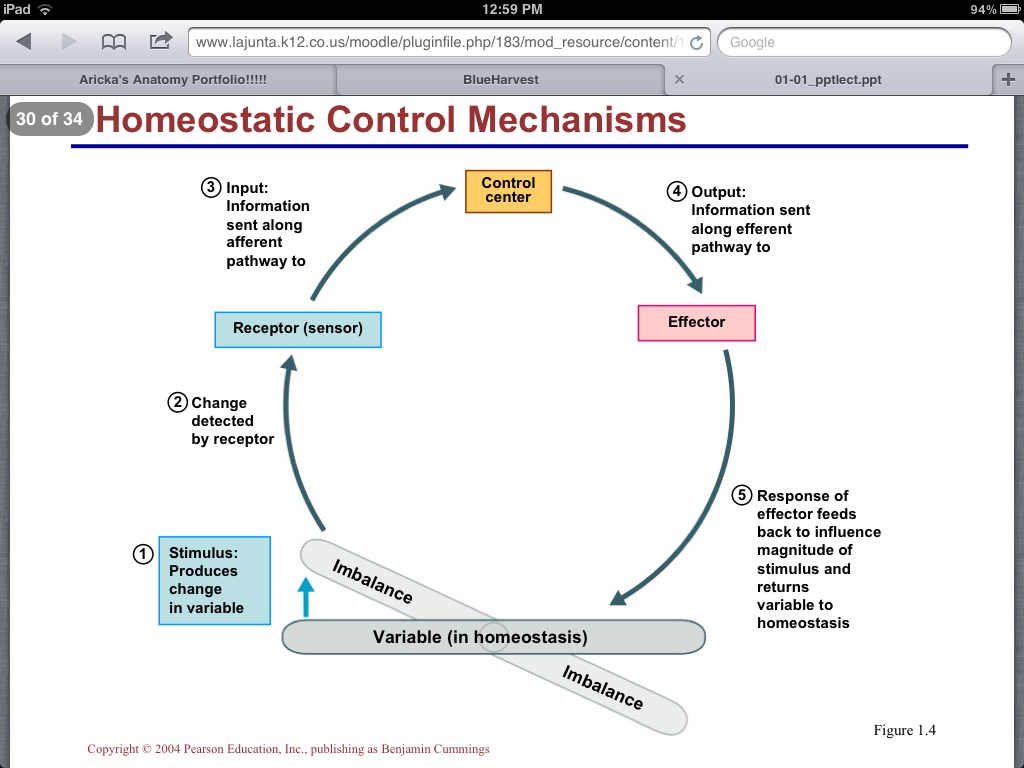 Homeostasis Aricka S Anatomy Blog
Homeostasis Aricka S Anatomy Blog
 Visual Anatomy And Physiology 2nd Edition Martini Test Bank
Visual Anatomy And Physiology 2nd Edition Martini Test Bank
Team Ntu Taida Project Effector 2012 Igem Org
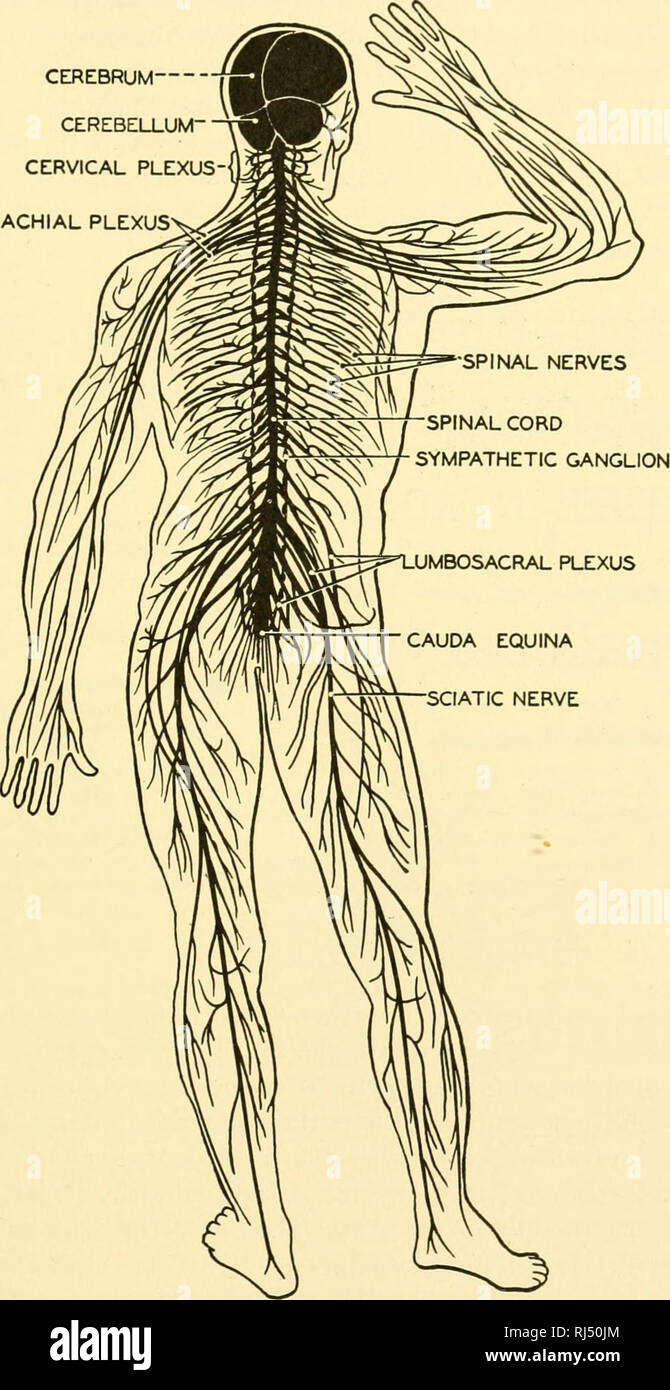 Chordate Anatomy Chordata Anatomy Comparative The
Chordate Anatomy Chordata Anatomy Comparative The
 Homeostasis This Diagram Is Another Example Where The Body
Homeostasis This Diagram Is Another Example Where The Body
Ch 13 Basic Reflex Terminology
Divisions Of The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy And
Sympathetic Division Human Anatomy Organs
 Spinal Reflex Arc Anatomical Scheme Vector Illustration
Spinal Reflex Arc Anatomical Scheme Vector Illustration
 Anatomy Of Robot Manipulator Download Scientific Diagram
Anatomy Of Robot Manipulator Download Scientific Diagram
 Hole S Anatomy Physiology Textbook Used Kolbe Academy
Hole S Anatomy Physiology Textbook Used Kolbe Academy
A P Chapter 11 13 Biology Flashcards Quizlet
 Neuro Review Guide Docx Honors Anatomy Chapters 11 13
Neuro Review Guide Docx Honors Anatomy Chapters 11 13
Are Muscles And Glands Part Of The Central Nervous System
How Do We Make Sense Of Different Components Of Anatomy And
 Autonomic Nervous System Wikipedia
Autonomic Nervous System Wikipedia
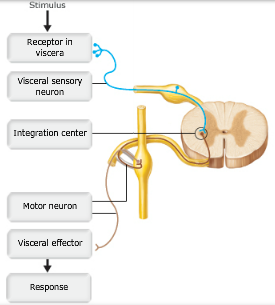 A P Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Flashcards
A P Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Flashcards
 Marieb Essentials Of Human Anatomy Physiology 10th Test
Marieb Essentials Of Human Anatomy Physiology 10th Test
 Anatomy And Physiology Module 9 On Your Own Docx Name Abby
Anatomy And Physiology Module 9 On Your Own Docx Name Abby
 Neuron Synapsis Mind The Graph
Neuron Synapsis Mind The Graph
Anatomy And Physiology I Lec 7 12 Mat4183 Uottawa



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Effector Anatomy"
Posting Komentar