Anatomy Of Placenta
The placenta is a temporary organ that connects the developing fetus via the umbilical cord to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake thermo regulation waste elimination and gas exchange via the mothers blood supply. This includes the different types of villi and the most important cellular components of the villi such as villous trophoblast hofbauer cells mesenchymal cells and endothelium.
 Anatomy Of Human Placenta A Fetal Side The Amnion
Anatomy Of Human Placenta A Fetal Side The Amnion
Placenta anatomy physiology introduction.
Anatomy of placenta. Anatomy of a normal placenta. Anatomy of the placenta. The fetus epithelial duct called umbilical cord attaches to at least one flat surface whereas the reverse surface grows out of the mothers female internal reproductive organ throughout the gestation time period.
And to produce hormones which support pregnancy. Gross anatomy typically the placenta is discoid in shape. The placenta signifies the second or embryonic period of pregnancy.
Placenta anatomy when its delivered it appears like a flat spherical organ thats distributed with thick blood vessels. Pmc images search for placenta anatomy figure 1 anatomy of placenta and fetal membranes at term the location of membranes amnion and chorion surrounding the fetus as well as the umbilical cord and placenta are shown. Medlineplus medical encyclopedia image skip navigation.
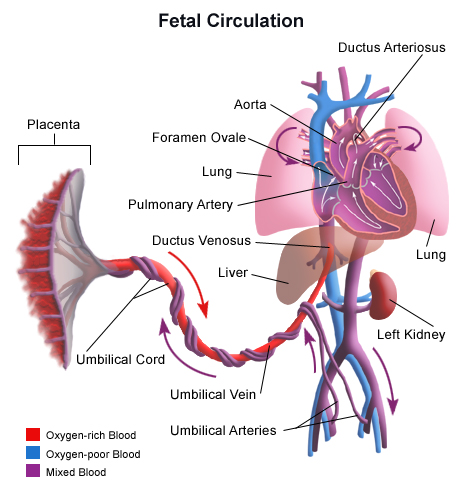
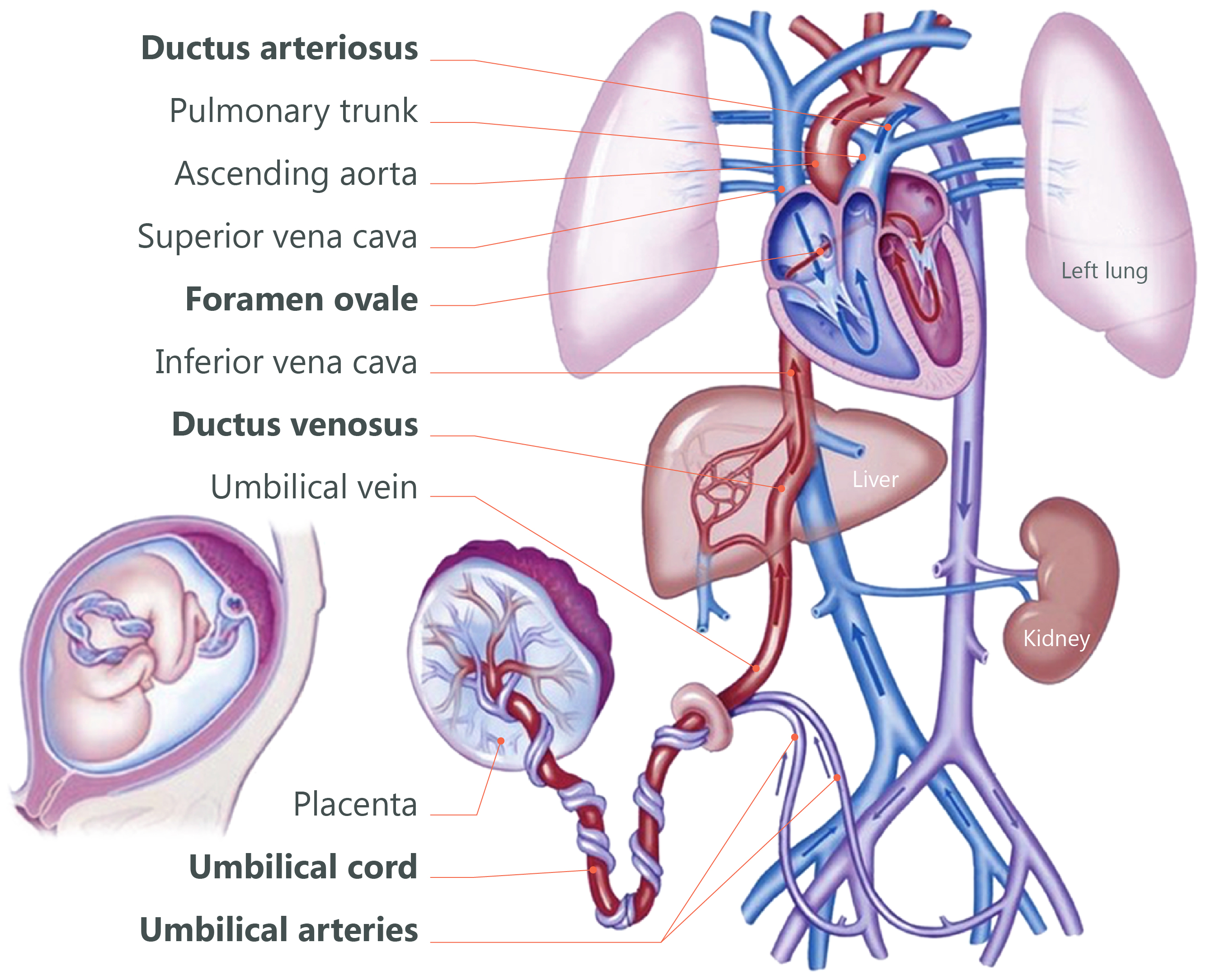
The placenta provides the fetus with oxygen and nutrients and takes away waste such as carbon dioxide via the umbilical cord. To fight against internal infection. In some types.
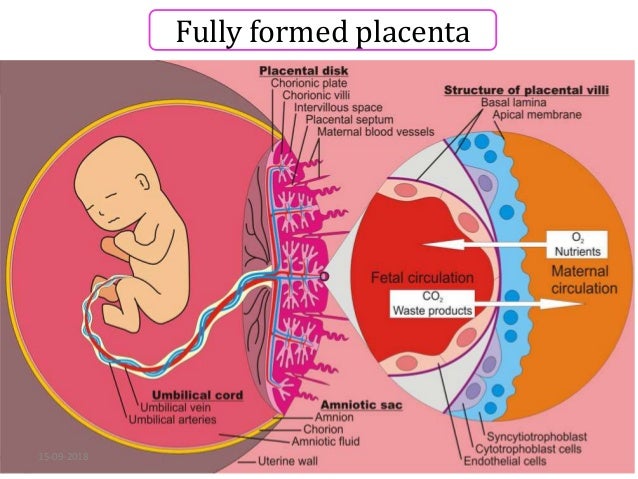
The placenta at term weighs 470 g and measures 22 cm in diameter with a thickness of 20 25 cm 3. The physical contact surfaces used within the process. In this diagram the placenta is roughly four months old and various fundamental structures can be recognized namely the umbilical cord the amnion the chorionic plate the already advanced branching of the villi the basal plate and the cotyledon.
The macroscopic anatomy of the delivered placenta as well as the microscopic anatomy and histology of this organ are also described. The human placenta is a hemochorial placenta which means that maternal blood is in direct contact with fetal trophoblast. The placenta consists of a foetal portion formed by the chorion.
The syncytiotrophoblast invades maternal venous sinuses relatively early and invades the spiral arterioles on the 17th or 18th day after conception. The placenta normally lies along the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus and may extend to the lateral wall with increasing gestational age 1.
 How Do They Diagnose Placenta Accreta Socratic
How Do They Diagnose Placenta Accreta Socratic
 Placental Anatomy And Its Functions
Placental Anatomy And Its Functions
Determinants Of Placenta Previa A Case Control Study
 Human Fetus Placenta Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty Free
Human Fetus Placenta Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty Free
 Chorioangioma Of Placenta Intechopen
Chorioangioma Of Placenta Intechopen
 Placenta What Is It And How It Works Biology Dictionary
Placenta What Is It And How It Works Biology Dictionary
 Anatomy Of The Placenta Doctor Stock
Anatomy Of The Placenta Doctor Stock
 Anatomy Of The Placenta Adapted From Openstax College 2013
Anatomy Of The Placenta Adapted From Openstax College 2013
Development Of The Placental Villi
Anatomy And Function Of The Placenta Miller Medical Legal
 Cord Clamping Concord Neonatal
Cord Clamping Concord Neonatal
 The Placenta And Your Baby S Nutrients Naomi Paschall Md
The Placenta And Your Baby S Nutrients Naomi Paschall Md
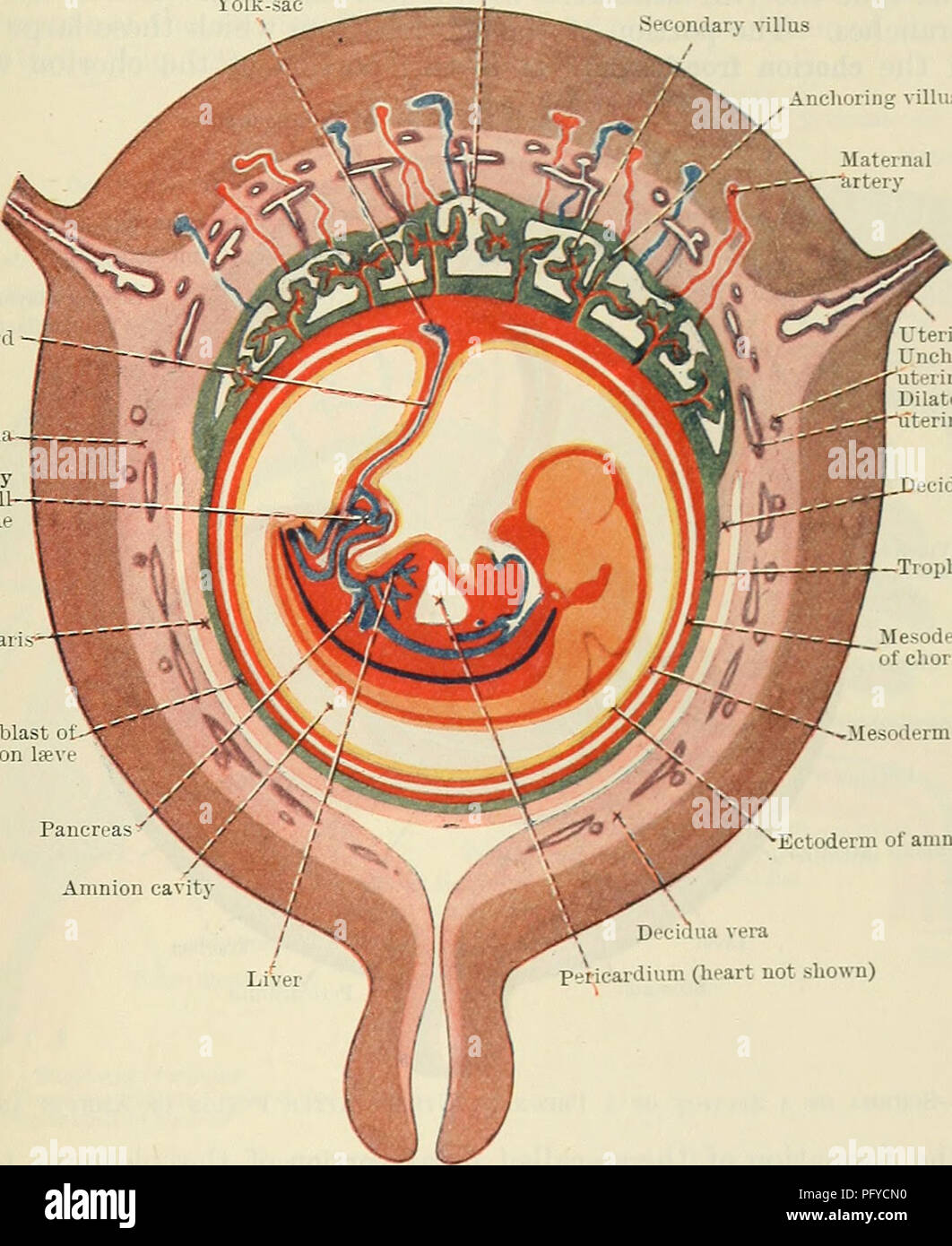 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy The Placenta 59
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy The Placenta 59
 The Placenta And The Fetus Structure And Function
The Placenta And The Fetus Structure And Function
 Pepper Anatomy What S Inside Your Chili Pepperscale
Pepper Anatomy What S Inside Your Chili Pepperscale
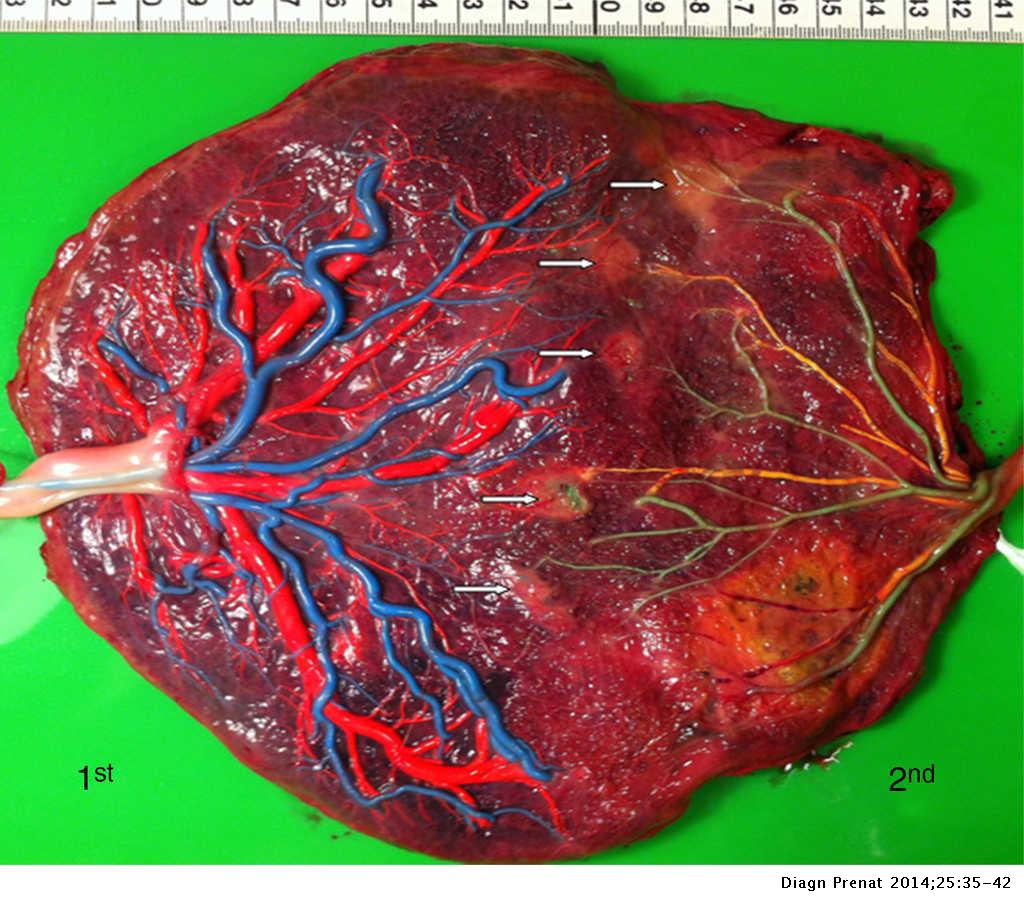 Monochorionic Twin Placentas Injection Technique And
Monochorionic Twin Placentas Injection Technique And
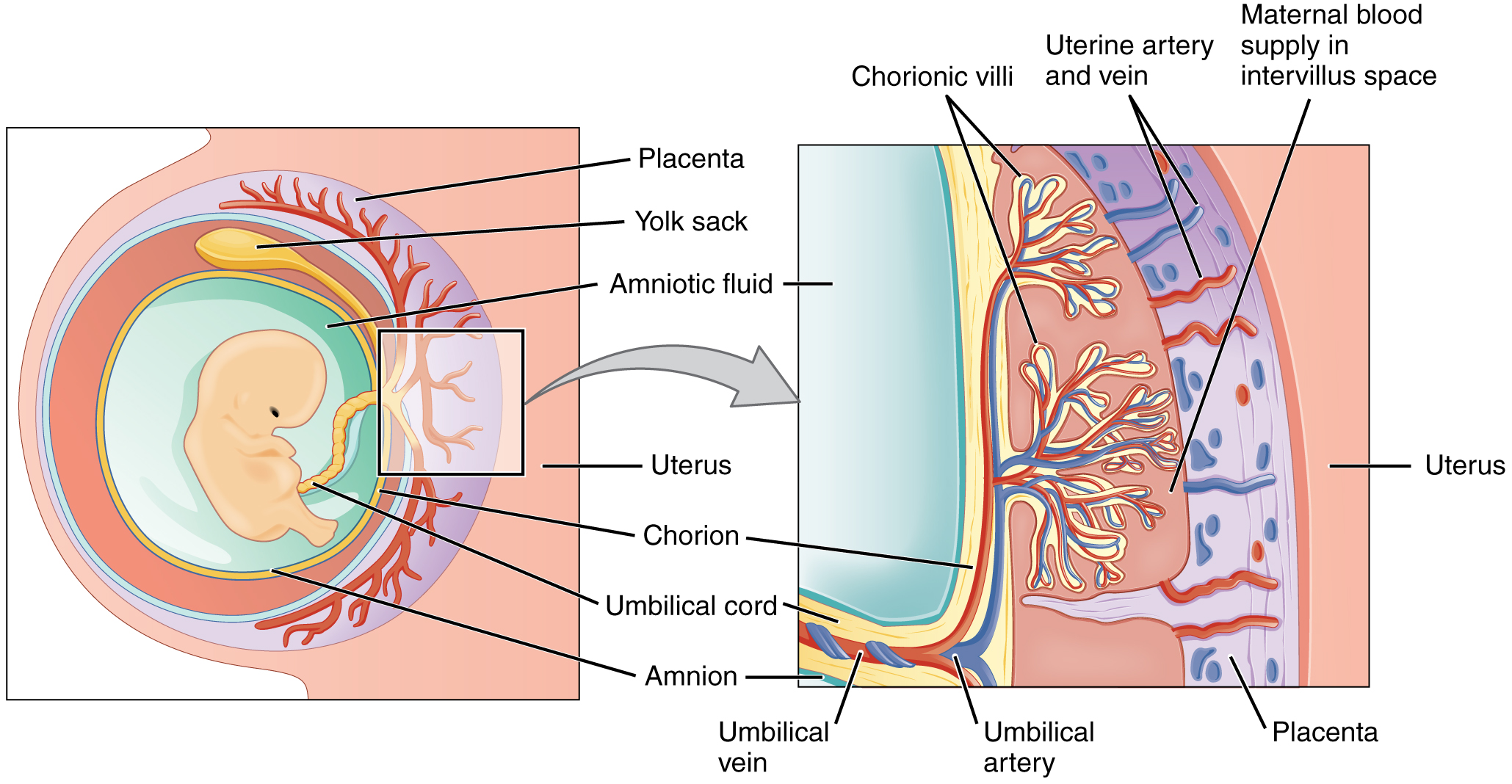 28 2 Embryonic Development Anatomy And Physiology
28 2 Embryonic Development Anatomy And Physiology
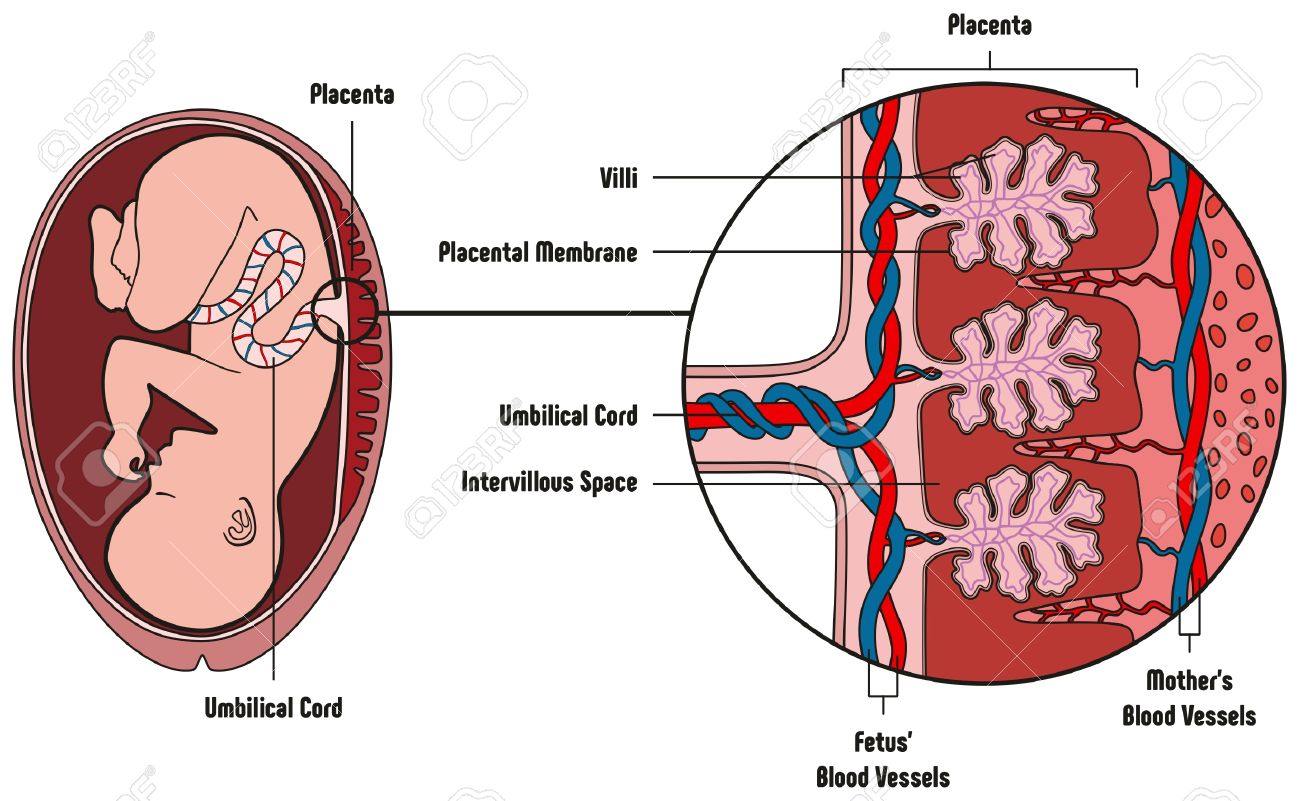 Human Fetus Placenta Anatomy Diagram With All Part Including
Human Fetus Placenta Anatomy Diagram With All Part Including
 Baby And Placenta Placenta Removal Vintage Anatomy Poster
Baby And Placenta Placenta Removal Vintage Anatomy Poster
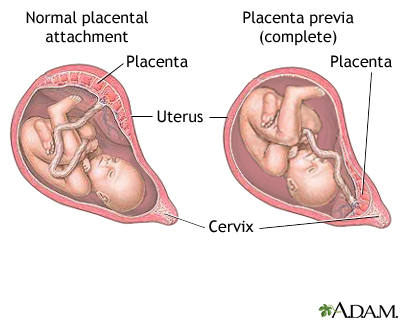 Placenta Previa Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Placenta Previa Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
 Placenta Anatomy In 2019 Anatomy Art Anatomy Drawing Anatomy
Placenta Anatomy In 2019 Anatomy Art Anatomy Drawing Anatomy
 Placenta Development Embryology
Placenta Development Embryology


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Placenta"
Posting Komentar