Connective Tissue Anatomy
Nearly all the fat in the body. Sparsely distributed chondrocytes in matrix.
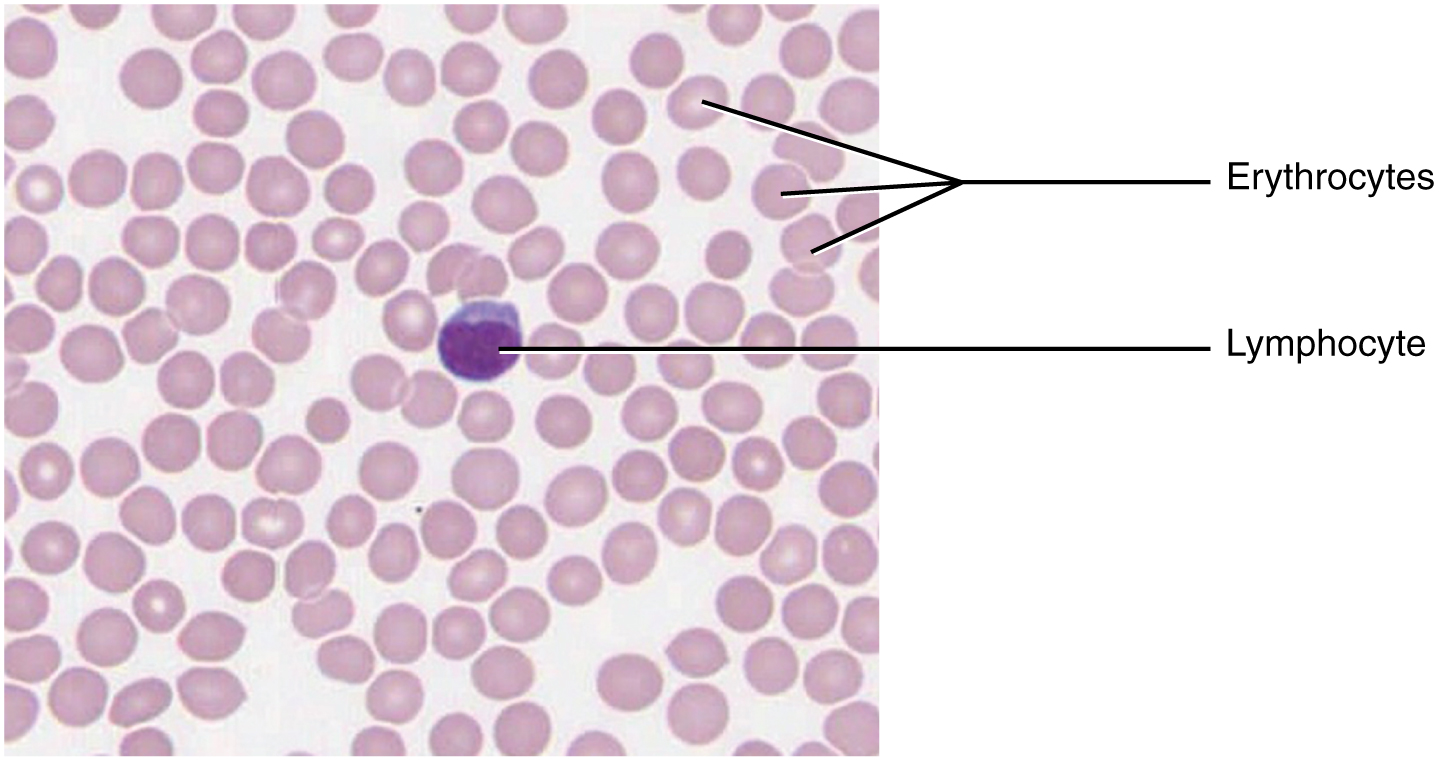 4 3 Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And
4 3 Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And
A type of loose connective tissue proper.
Connective tissue anatomy. Adipocytes account for most of volume. Skeletal voluntary muscles smooth muscles and the cardiac muscle in the heart. Although it is the most abundant and widely distributed of the primary tissues the amount of connective tissue in a particular organ varies.
Eachosteon consists of a central canal which contains blood vessels and nerves surrounded by concentric rings lamellae of hard matrix and collagen fibers. Collagen resist tension thick has 3 strands reticular provides structural support thin elastic enables recoil of stretched tissues. Loose connective tissue is named so because of the weave and type of its constituent fibers.
Muscle tissue which responds to stimulation and contracts to provide movement is divided into three major types. Three fibers in connective tissue. Like to the timber framing of a house the connective tissue provides structure and support throughout the body.
These canals consist of blood vessels that branch off the central vessels. Regular irregular and elastic. Matrix is dominated by chondroitin sulfate and collagen.
Dense regular connective tissue fibers are parallel to each other enhancing tensile strength and resistance to stretching in the direction of the fiber orientations. Connective tissue binds the cells and organs of the body together and performs many functions especially in the protection support and integration of the body. Ligaments and tendons are made of dense regular connective tissue.
Produces both the fibers and the ground substance of the extracellular matrix. Most abundant type of cartilage. Human anatomy and physiology tissues.
It holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues. Connective tissue ct is a one of the four main classes of tissues. There are three major categories of dense connective tissue.
In vertebrates the most common type of connective tissue is loose connective tissue. Found in the upper portion of the respiratory tract trachea and bronci ends of bones and ribs skeleton of a fetus. Highly vascularized fat that breaks down to provide heat to the blood.
Branching off the central canal at right angles are perforating canals. These fibers form an irregular network with spaces between the fibers. Four types of connective tissue 2342 all develop from mesenchyme 3295 different degrees of blood flow 3457 extracellular matrix full of ground substance and fibers 3594.
 Connective Tissue Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Connective Tissue Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
 Muscle Tissue Anatomy Physiology Nutrition With External
Muscle Tissue Anatomy Physiology Nutrition With External
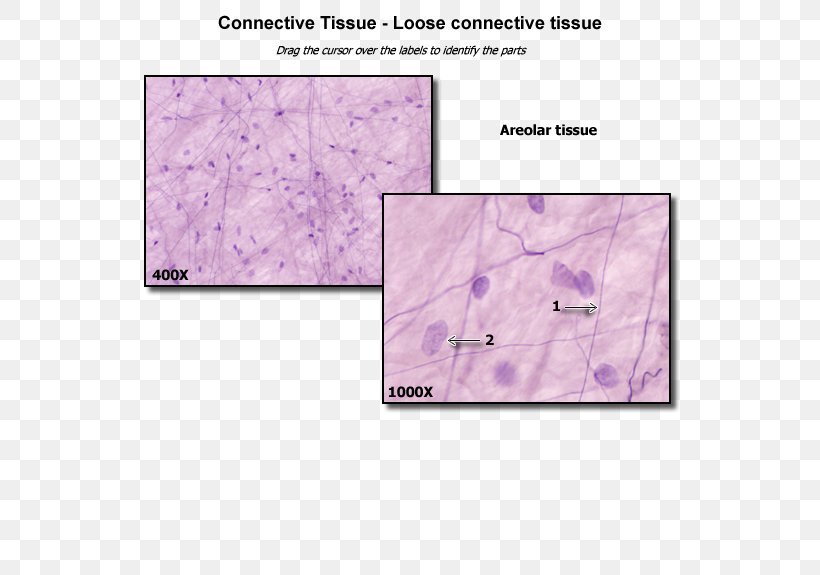 Loose Connective Tissue Anatomy Dense Connective Tissue Png
Loose Connective Tissue Anatomy Dense Connective Tissue Png
 Which Connective Tissue Composes The Dermis Of The Skin
Which Connective Tissue Composes The Dermis Of The Skin
 Extraperitoneal Retroperitoneal Subperitoneal
Extraperitoneal Retroperitoneal Subperitoneal
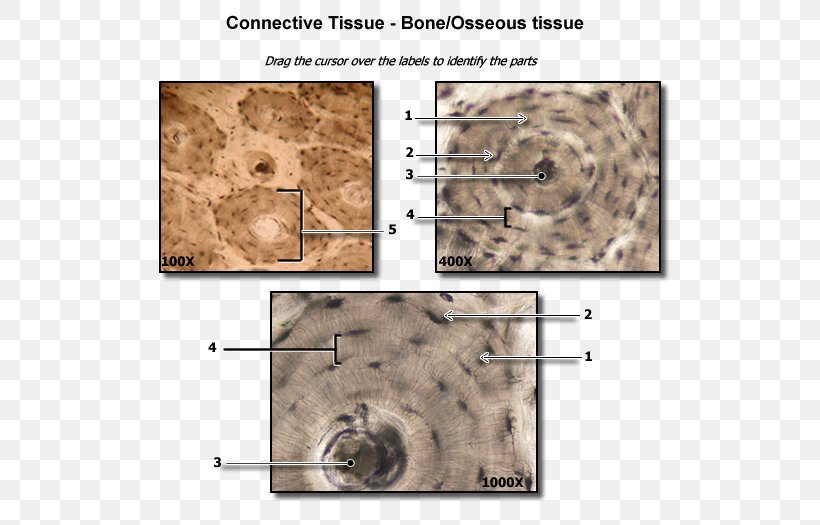 Dense Connective Tissue Bone Anatomy Png 550x525px
Dense Connective Tissue Bone Anatomy Png 550x525px
 Connective Tissues Anatomy Language Histology
Connective Tissues Anatomy Language Histology
 Areolar Tissue Google Search Loose Connective Tissue
Areolar Tissue Google Search Loose Connective Tissue
 Chapter 4 Tissues Textbook And Lecture Notes For Human
Chapter 4 Tissues Textbook And Lecture Notes For Human
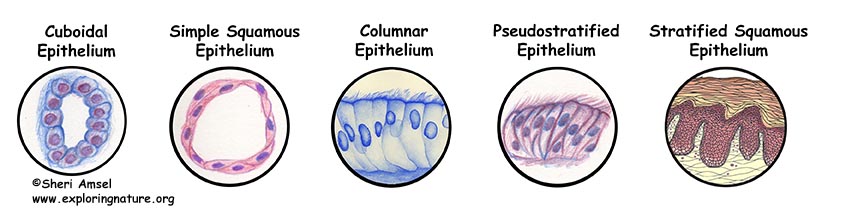 Tissues Epithelium Muscle Connective Tissue And Nervous
Tissues Epithelium Muscle Connective Tissue And Nervous
 Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture Notes Summer 2017
Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture Notes Summer 2017
 Visual Anatomy Physiology First Edition Martini Ober
Visual Anatomy Physiology First Edition Martini Ober
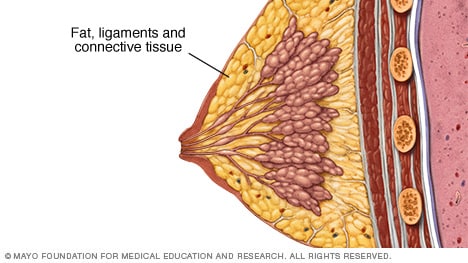 Slide Show Female Breast Anatomy Mayo Clinic
Slide Show Female Breast Anatomy Mayo Clinic

Connective Tissue Anatomy And Physiology

 Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
 Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue Sinoe Medical Homepage
Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue Sinoe Medical Homepage
 Human Body Tissue Anatomy Body Human Thebestofglp08
Human Body Tissue Anatomy Body Human Thebestofglp08
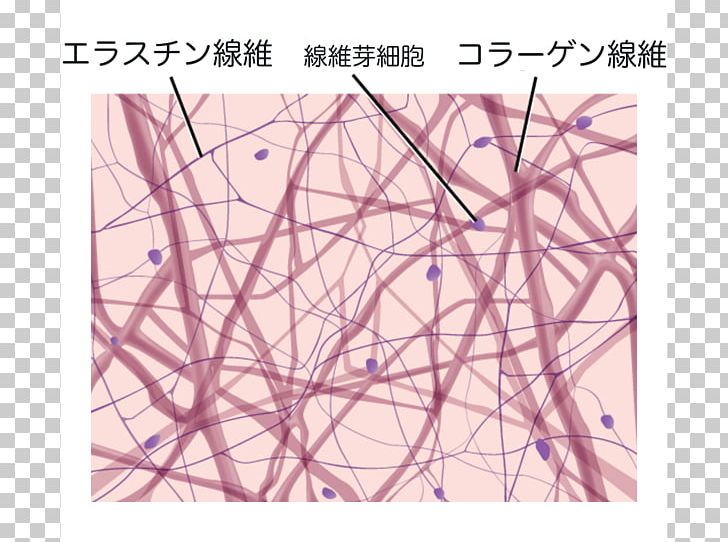 Loose Connective Tissue Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Anatomy And Physiology Tissues Page 3 Of 4 Nursing Crib
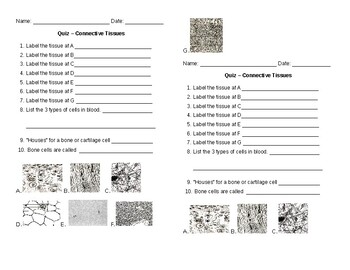 Anatomy Connective Tissue Quiz
Anatomy Connective Tissue Quiz
 Tissues Part 4 Types Of Connective Tissues Crash Course A P 5
Tissues Part 4 Types Of Connective Tissues Crash Course A P 5


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Connective Tissue Anatomy"
Posting Komentar