Lever Anatomy
Anatomy in a first class lever system the fulcrum or pivot point is located on the lever between the effort force and load or resistance being moved. Start studying types of levers anatomy.
 Lever Arm Archives Learn Muscles
Lever Arm Archives Learn Muscles
About 7085 of the liver volume is occupied by parenchymal hepatocytes.

Lever anatomy. A lever is a rigid rod usually a length of bone that turns about a pivot usually a joint. In the bod found at the elbow joint where the triceps cause extension of fulcrum the part of a lever system that pivots. Levers can be used so that a small force can move a much bigger force.
Bones ligaments and muscles are the structures that form levers in the body to create human movement. Joints are the fulcrum resistance the load. The liver also detoxifies chemicals and metabolizes drugs.
A lever is a rigid bar that moves on a fixed point called the fulcrum when a force is applied to it. Effort and load are on opposite sides of the fulcrum. Joints are the fulcrum the load to be moved by a lever system.
A small effort can be used to advantage over larger weight when using a larger lever arm. Its tilted slightly in the bodys cavity with the left portion above the stomach and the right portion above the first. A lever is a rigid body that rotates around a pivot point and exerts force on an object preventing its tendency to rotate 1st class lever.
The operation of most skeletal muscles involves leverage using a lever to move an object. In simple terms a joint where two or more bones join together forms the axis or fulcrum and the muscles crossing the joint apply the force to move a weight or resistance. Histology the study of microscopic anatomy shows two major types of liver cell.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Muscles and bones act together to form levers. The livers main job is to filter the blood coming from the digestive tract before passing it to the rest of the body.
Usually this involves the force applied to move the resistance or weight. Parenchymal cells and nonparenchymal cells. There are four parts to a lever lever arm pivot effort and load.
This is called mechanical advantage. The part of a lever system that pivots. The liver is a half moon shaped organ thats fairly straight on the bottom.
Seesaws and crowbars are non anatomical examples of first class lever systems. Nonparenchymal cells constitute 40 of the total number of liver cells but only 65 of its volume.
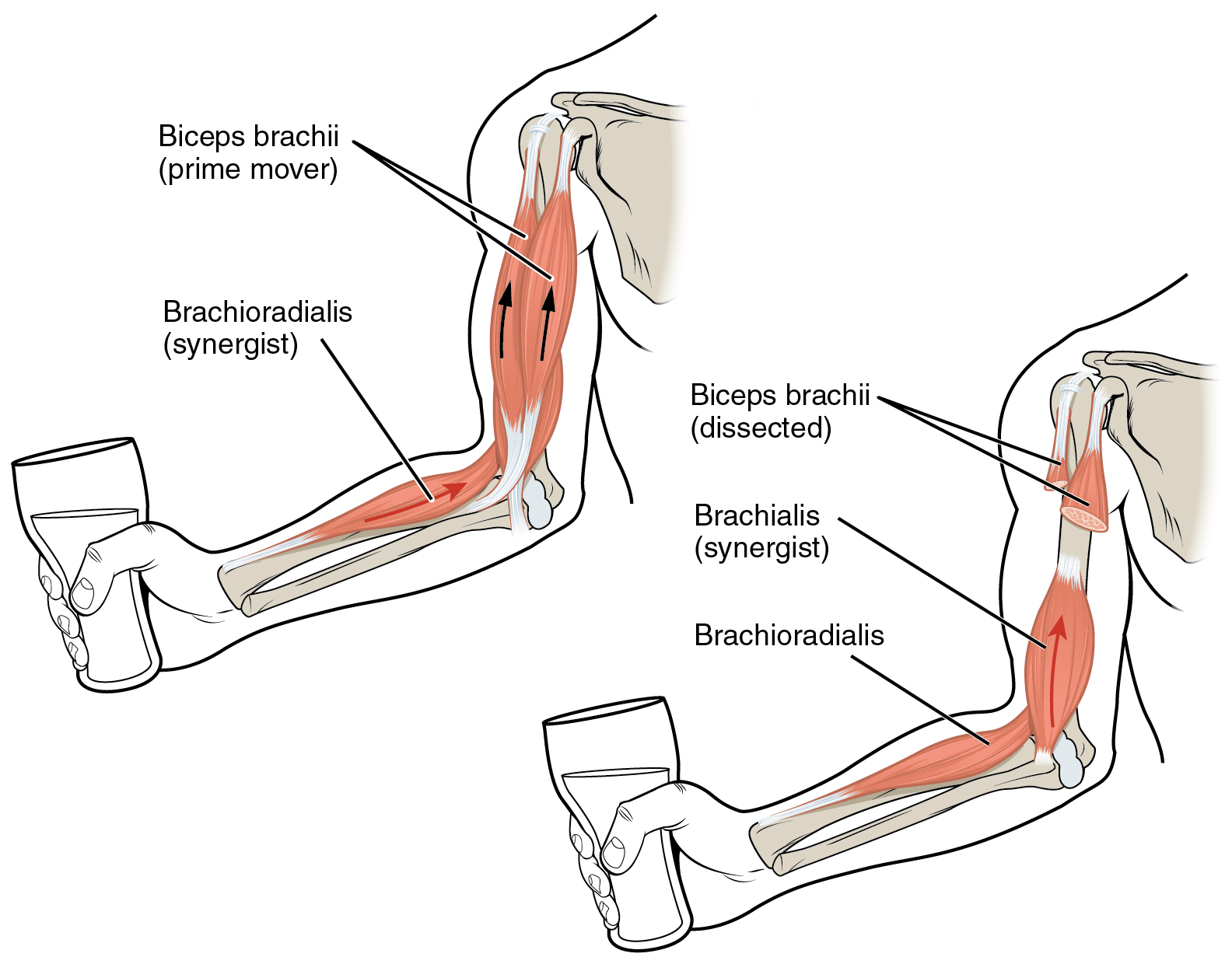 Interactions Of Skeletal Muscles Their Fascicle Arrangement
Interactions Of Skeletal Muscles Their Fascicle Arrangement
 1 Gives Examples Of Bone Joint Muscle Lever Systems From
1 Gives Examples Of Bone Joint Muscle Lever Systems From
 Class 1 Lever Model In Action A An Illustration Of The
Class 1 Lever Model In Action A An Illustration Of The
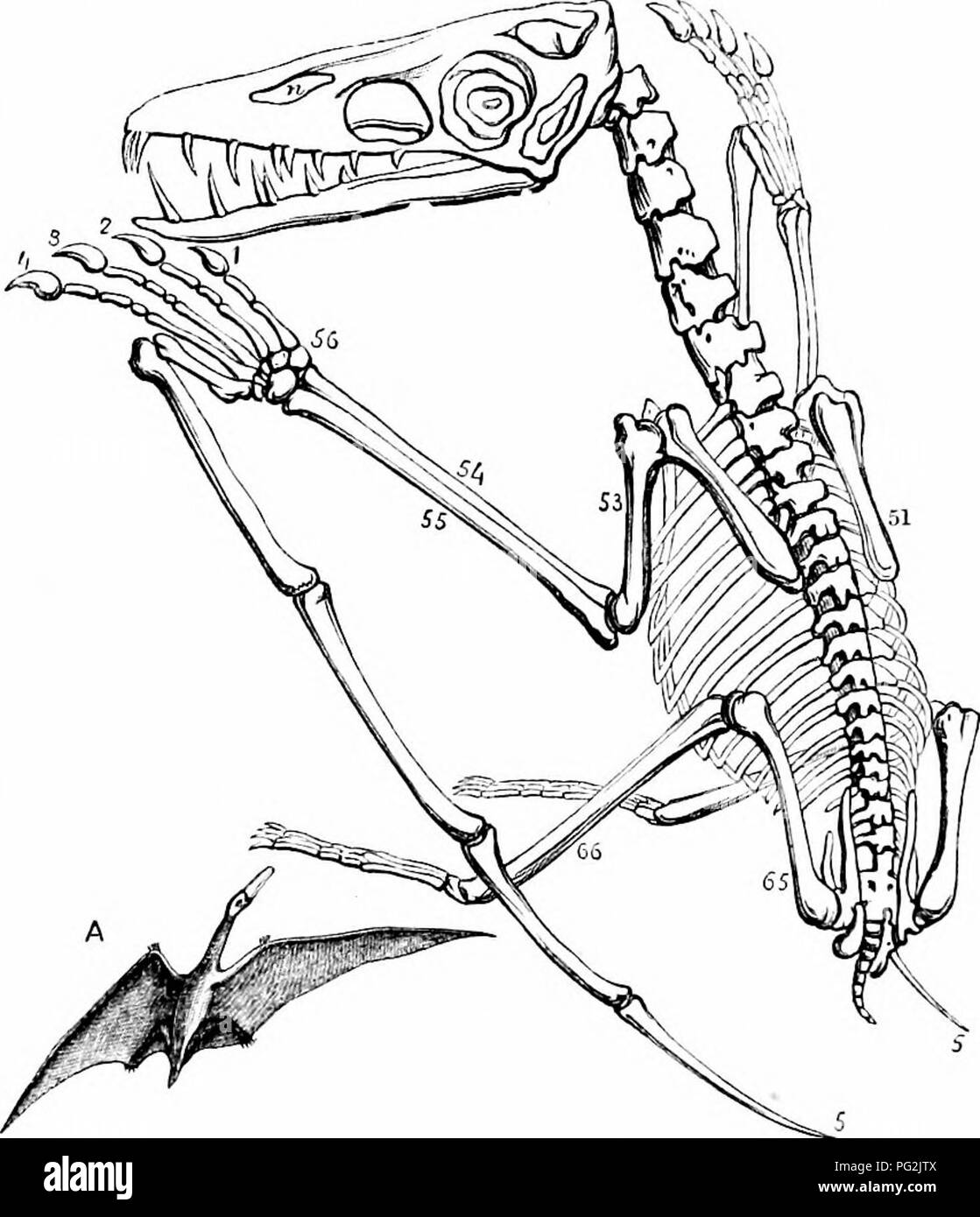 On The Anatomy Of Vertebrates Vertebrates Anatomy
On The Anatomy Of Vertebrates Vertebrates Anatomy
 Crossfit Anatomy Of Levers Part 4 Third Class Levers
Crossfit Anatomy Of Levers Part 4 Third Class Levers
Levers Work To Create Movement In The Human Body Human
 The Anatomical Record Anatomy Anatomy 14 R M Strong
The Anatomical Record Anatomy Anatomy 14 R M Strong
 How To Elbow Lever Progession Tutorial Body Weight Training Muscle Anatomy Easyflexibility
How To Elbow Lever Progession Tutorial Body Weight Training Muscle Anatomy Easyflexibility
 Dynamics Of Breathing Yoga Anatomy 2nd Edition
Dynamics Of Breathing Yoga Anatomy 2nd Edition
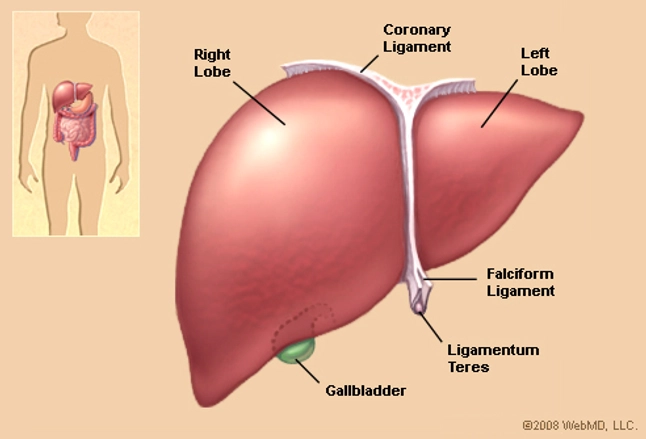 Liver Anatomy Picture Function Conditions Tests
Liver Anatomy Picture Function Conditions Tests
 Levers 12 Ses 2013 Biophysical Principles
Levers 12 Ses 2013 Biophysical Principles
 Levers In Regards To Anatomy Youtube
Levers In Regards To Anatomy Youtube
 Aerial Straps Flight Training Fitness
Aerial Straps Flight Training Fitness
 Anatomy Of The Elbow Elbow Anatomy
Anatomy Of The Elbow Elbow Anatomy
 Chapter 10 Anatomy Of The Muscular System
Chapter 10 Anatomy Of The Muscular System
 System Of Levers 1st 2nd And 3rd Class Most Of The
System Of Levers 1st 2nd And 3rd Class Most Of The
Within A Musculoskeletal Lever System The Joint Acts As
 Elements Of Design Ektfl8 Decorative Tank Toilet Lever
Elements Of Design Ektfl8 Decorative Tank Toilet Lever
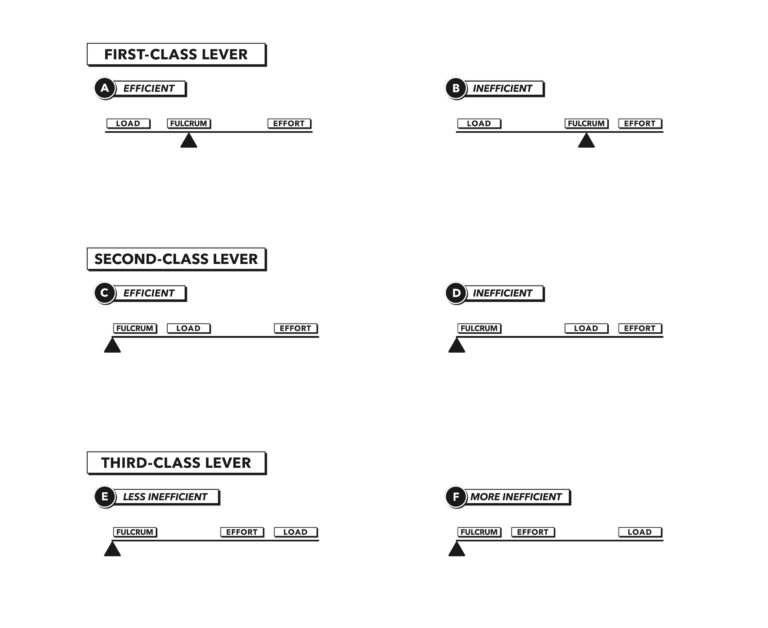 Crossfit Anatomy Of Levers Part 6 Lever Efficiency
Crossfit Anatomy Of Levers Part 6 Lever Efficiency
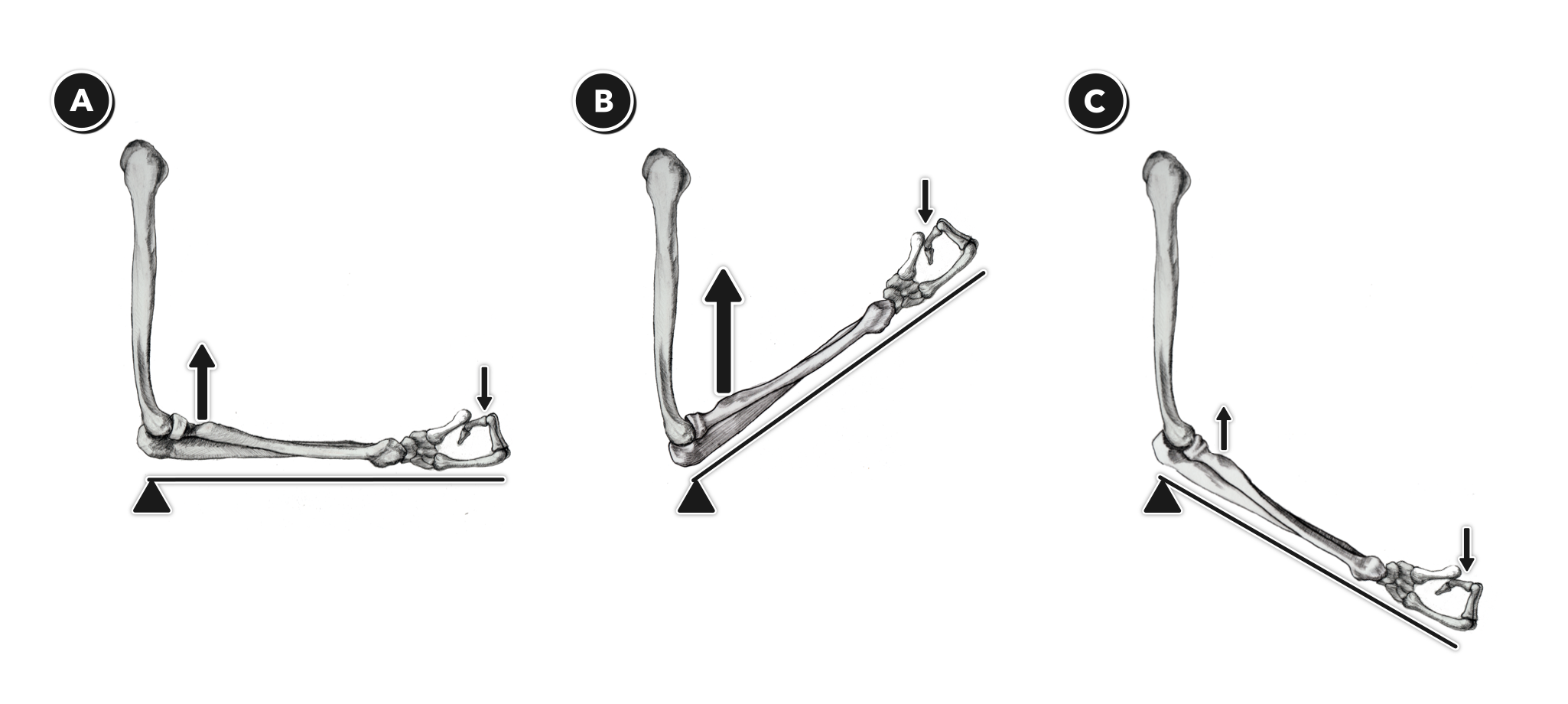
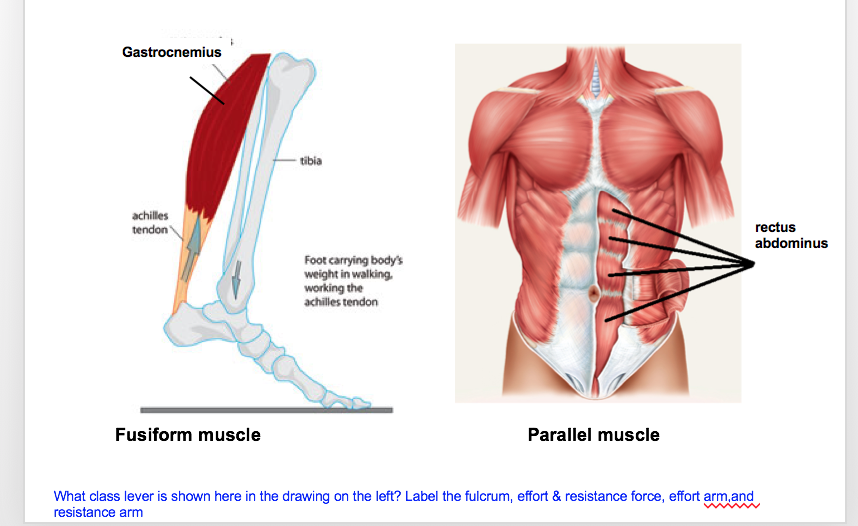 Solved What Class Lever Is Shown Here In The Drawing On T
Solved What Class Lever Is Shown Here In The Drawing On T
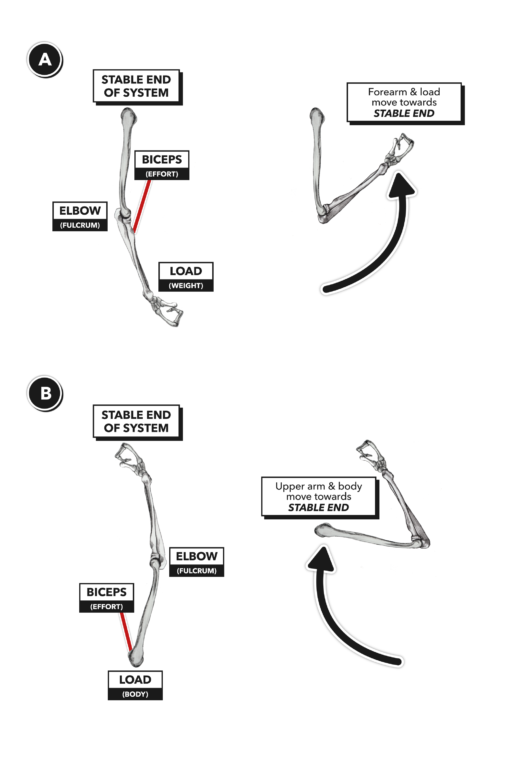 Crossfit Anatomy Of Levers Part 7 Lever Changes
Crossfit Anatomy Of Levers Part 7 Lever Changes
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Lever Anatomy"
Posting Komentar