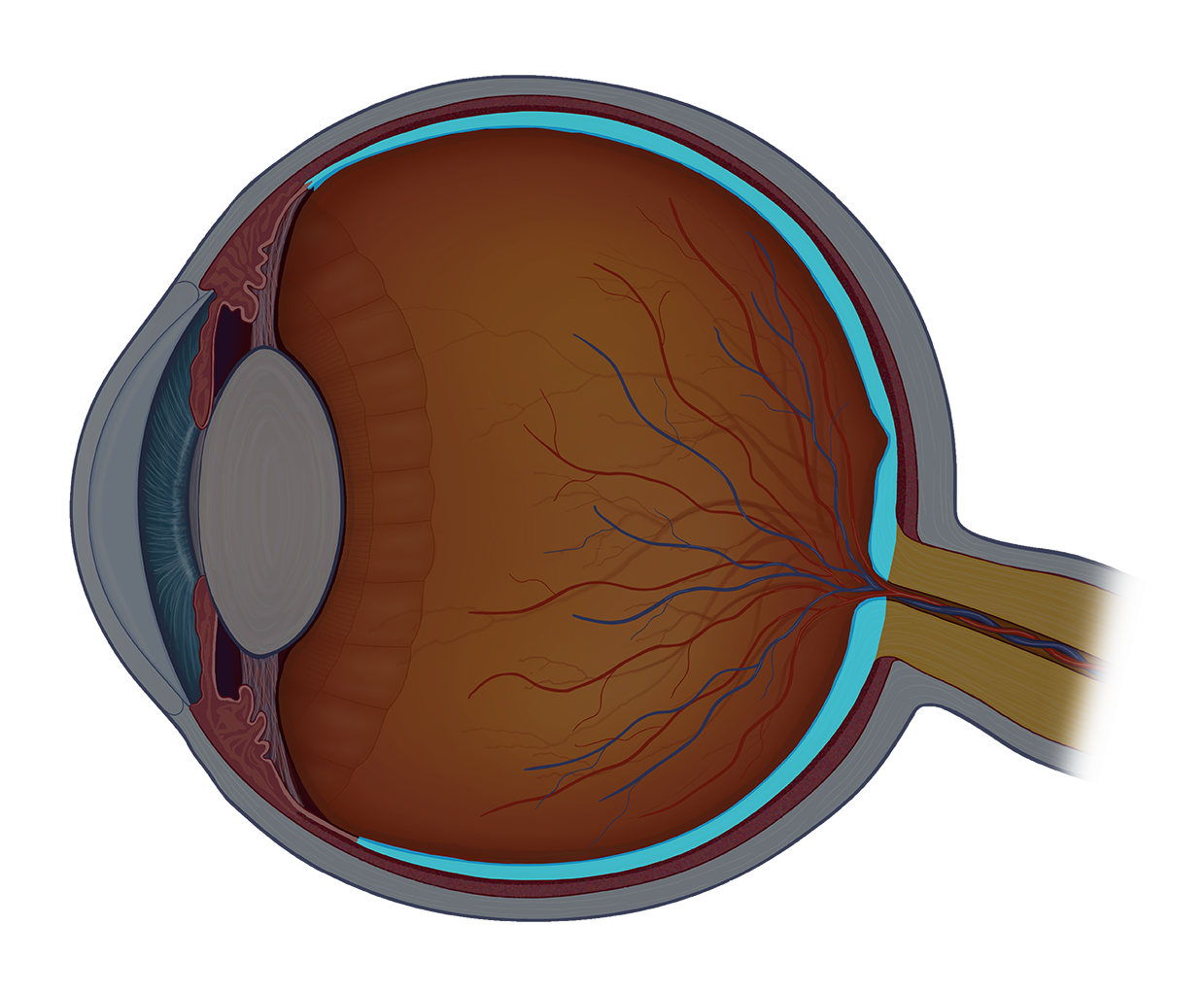
Basic Anatomy Of The Eye
Extraocular muscles help move the eye in different directions. The majority 70 of the bending refracting of light rays is accomplished by the cornea.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg) Structure And Function Of The Human Eye
Structure And Function Of The Human Eye
A closer look at the parts of the eye by liz segre when surveyed about the five senses sight hearing taste smell and touch people consistently report that their eyesight is the mode of perception they value and fear losing most.

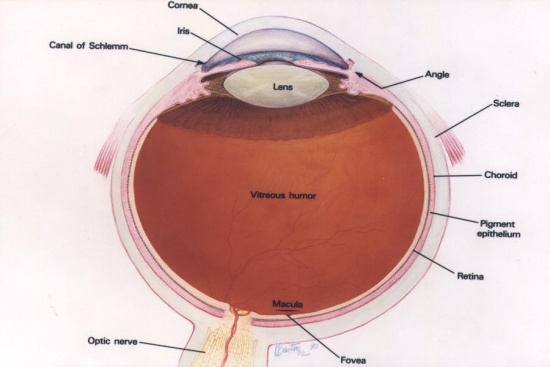
Basic anatomy of the eye. The colored part of the eye. A small area in the retina that contains special light sensitive cells. Muscular structure of the eye that widens and constricts the pupil in correlation with the intensity of light passing through lens suspended behind the pupil controlled by ciliary muscles and focuses light onto the retina.
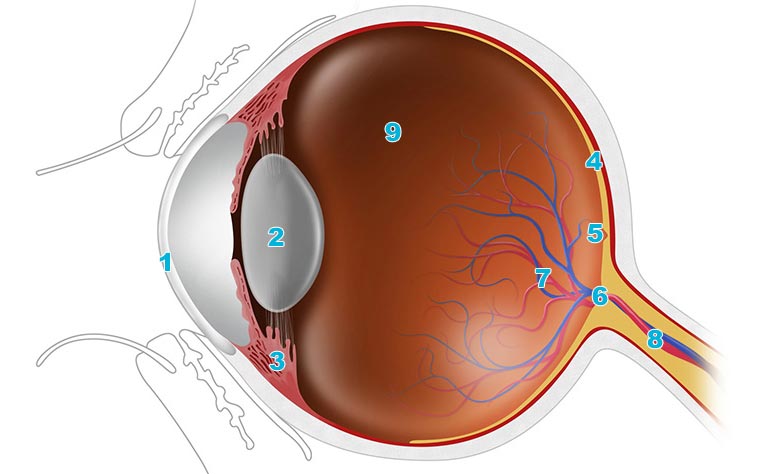
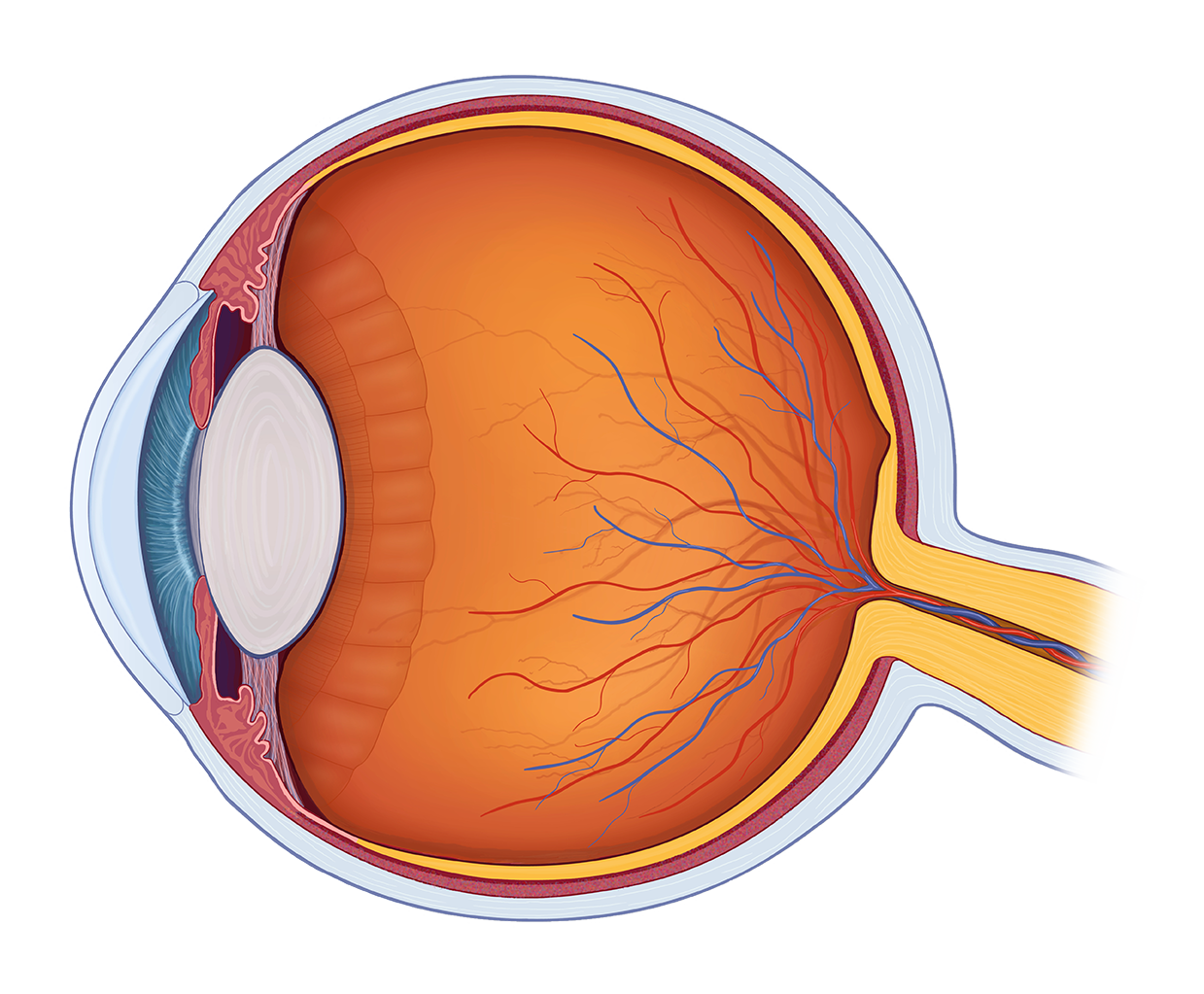
Next light passes through the lens a clear inner part of the eye. The eye is surrounded by the orbital bones and is cushioned by pads of fat within the orbital socket. The cornea transmits and focuses light into the eye.
The tough outermost layer of the eye is called the sclera. Anatomy of the eye. The lens works together with the cornea to focus light correctly on the retina.
There are many parts of the eye. The cornea is shaped like a dome and bends light to help the eye focus. The shape of the cornea does not change with the exception of small changes that occur offer a lifetime.
The anatomy of the eye includes the cornea pupil lens sclera conjunctiva and more. The eye is approximately 1 inch 254 cm wide 1 inch deep and 09 inches 23 cm tall. The crystal clear dome that covers the front of the eye.
Although small in size the eye is a very complex organ. The iris the colored part of the eye controls how much light the pupil lets in. The transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina.
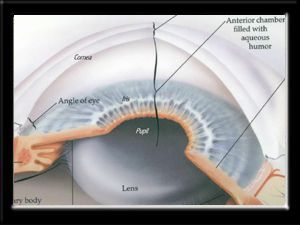
The following page explains basic anatomy of the human eye and highlights some structures in particular and how they relate to cataracts and cataract surgery. Some of this light enters the eye through an opening called the pupil pyoo pul. Nerve signals that contain visual information are transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain.
The iris helps regulate the amount of light that enters the eye. Basic eye anatomy. The retina receives light and sends electrical impulses to the brain that result in sight.
Although the eye is small relative to most organs in the human body it has many distinct anatomical parts all of which contribute to the production of normal vision in one way or another. A thin multi layered membrane which lines the inside back two thirds of the eye. It is composed of millions of visual cells and it is connected by the optic nerve to the brain.
 2 Minute Topic Basic Anatomy Of The Human Eye
2 Minute Topic Basic Anatomy Of The Human Eye
 Anatomy Of The Eye 101 Eyecheck
Anatomy Of The Eye 101 Eyecheck
 1 Basic Anatomy Of The Eye National Eye Institute
1 Basic Anatomy Of The Eye National Eye Institute
 Anatomy Of The Eye Children S Wisconsin
Anatomy Of The Eye Children S Wisconsin
 Structure And Function Of The Eyes Eye Disorders Merck
Structure And Function Of The Eyes Eye Disorders Merck
The Basic Anatomy Of The Eye Salisbury Eyecare Eyewear
 Human Eye Definition Structure Function Britannica
Human Eye Definition Structure Function Britannica
 Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
About Basic Eye Anatomy Gem Clinic Glaucoma Eye
 The General Anatomy Of The Eye Science Diagram Quizlet
The General Anatomy Of The Eye Science Diagram Quizlet
Eye Health Online Course Module 1 Eye Anatomy
/GettyImages-695204442-b9320f82932c49bcac765167b95f4af6.jpg) Structure And Function Of The Human Eye
Structure And Function Of The Human Eye
 Suny Downstate Department Of Ophthalmology Dry Eye Defined
Suny Downstate Department Of Ophthalmology Dry Eye Defined
 Anatomy Of A Normal Human Eye Amdf
Anatomy Of A Normal Human Eye Amdf
 An Easy Guide To Your Eye S Anatomy Lenstore Co Uk
An Easy Guide To Your Eye S Anatomy Lenstore Co Uk
 Clash Of Worlds The Basic Anatomy Of The Eye Eye Anatomy
Clash Of Worlds The Basic Anatomy Of The Eye Eye Anatomy
The Human Visual System Display Interfaces Part 1
Basic Eye Anatomy Cataract Surgery Information
 Basic Eye Anatomy Potthoff Eye Care And Surgery
Basic Eye Anatomy Potthoff Eye Care And Surgery
 Anatomy Of The Eye The Ottawa Hospital
Anatomy Of The Eye The Ottawa Hospital
 Anatomy Of The Eye Retina Centers
Anatomy Of The Eye Retina Centers
Parts Of The Eye American Academy Of Ophthalmology

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Basic Anatomy Of The Eye"
Posting Komentar