Fossa Anatomy
The occipital bones including temporal bone sphenoid bone parietal bone and the frontal bone put up to its concave wall. The antecubital fossa is the shallow depression located in front of the median cubital vein of your arm.
 Anatomy Group D Temporal Fossa
Anatomy Group D Temporal Fossa
Cerebral fossa any of the depressions on the floor of the cranial cavity.
Fossa anatomy. Glenoid cavity glenoid fossa the concavity in the head of the scapula that receives the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint. It has a mongoose like head relatively longer than that of a cat although with a muzzle that is broad and short and with large but rounded ears. The cubital fossa is triangular in shape and thus has three borders.
In anatomy a hollow or depressed area. Condylar fossa condyloid fossa either of two pits on the lateral portion of the occipital bone. Gross anatomy it is located superior and posterior to the torus tubarius the posterior projection of.
A trench or channel. Amygdaloid fossa the depression in which the tonsil is lodged. The popliteal fossa is a diamond shaped area located on the posterior aspect of the knee.
It is the main path by which vessels and nerves pass between the thigh and the leg. Lateral border medial border of the brachioradialis muscle. Medial border lateral border of the pronator teres muscle.
The fossa of rosenmüller also known as the posterolateral pharyngeal recess is the most common site of origin for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. In this article we shall look at the anatomy of the popliteal fossa its borders contents and clinical correlations. Fossa a concavity in a surface especially an anatomical depression pit.
The median cubital vein joins the two longest vessels that run up the length of your arm. Blood vessels are located deep to the nerves within the fossa and include. Superior border hypothetical line between the epicondyles of the humerus.
The superomedial aspect of the popliteal fossa is bounded by the semimembranosus and. The popliteal fossa is 25 cm wide and mainly consists of fat tissue. The fossa appears as a diminutive form of a large felid such as a cougar but with a slender body and muscular limbs and a tail nearly as long as the rest of the body.
The temporal fossa is a shallow depression on the temporal lines and one of the be massive marks on the skull.
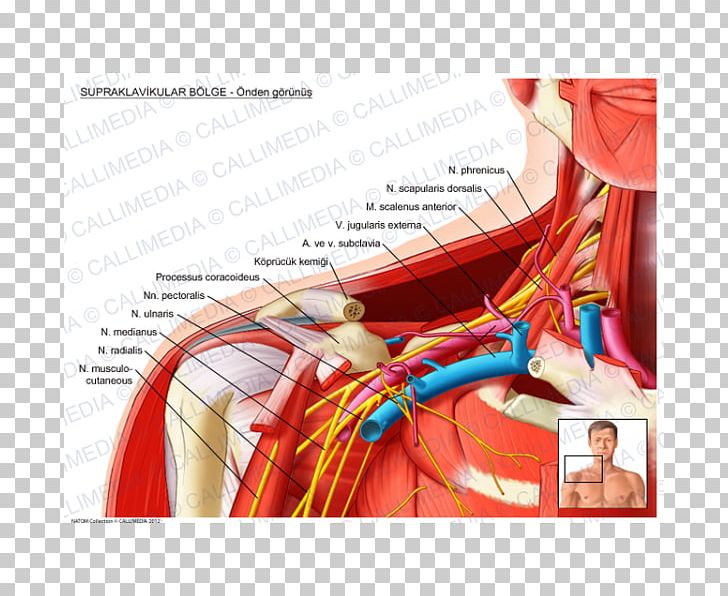 Supraclavicular Fossa Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes Anatomy
Supraclavicular Fossa Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes Anatomy
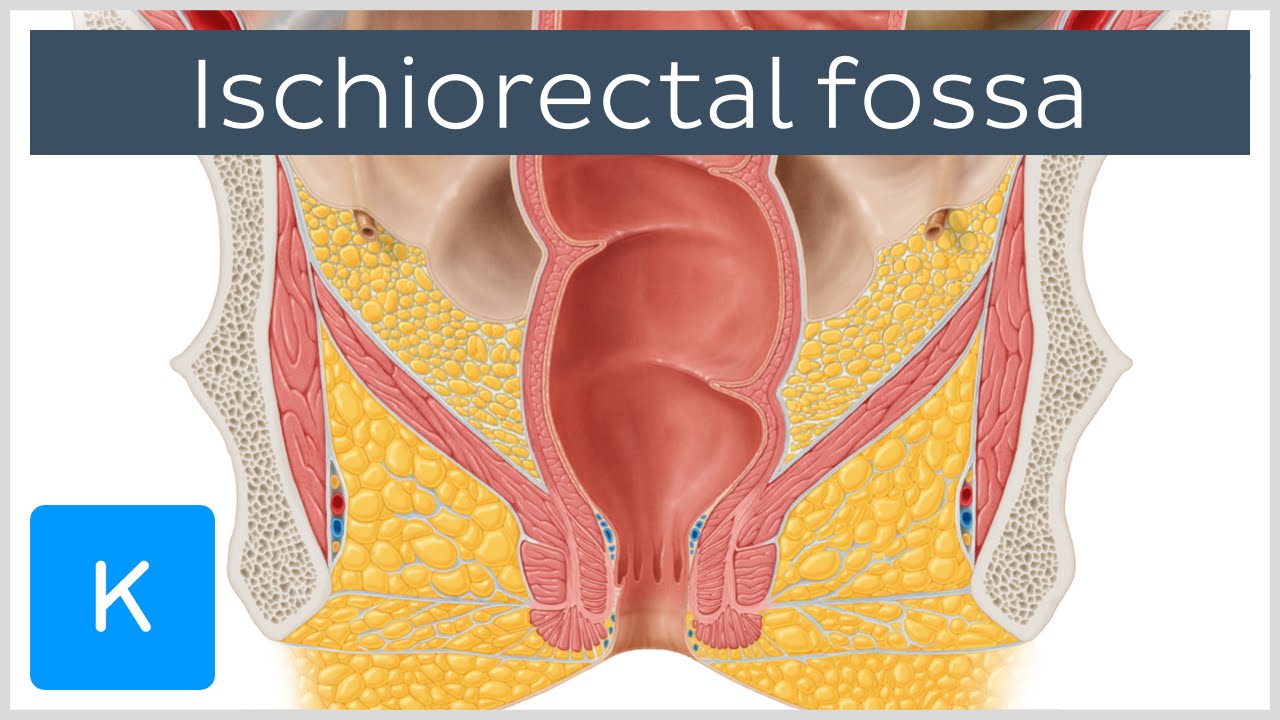
 Anatomy Of The Ischiorectal Fossa Human Anatomy Kenhub
Anatomy Of The Ischiorectal Fossa Human Anatomy Kenhub
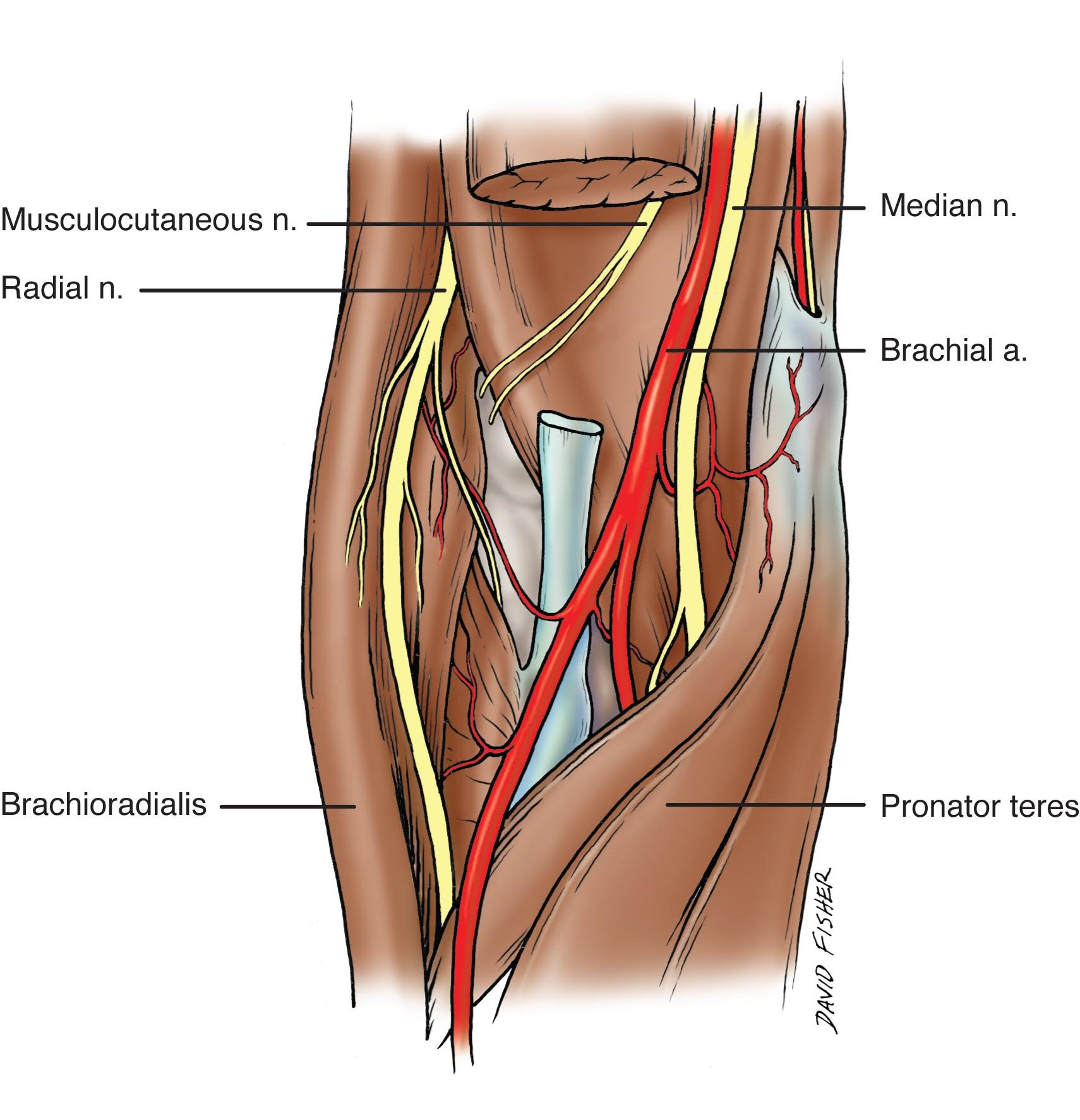 Cureus Relationship Of The Median And Radial Nerves At The
Cureus Relationship Of The Median And Radial Nerves At The
 11053 01x Normal Anatomy Of The Right Knee And Popliteal
11053 01x Normal Anatomy Of The Right Knee And Popliteal
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-pterygoideus-lateralis/bvtuf1CMQc4uAuioKUu8Q_Pterygoideus_lateralis_01.png) Infratemporal Fossa Anatomy And Contents Kenhub
Infratemporal Fossa Anatomy And Contents Kenhub
 Infratemporal Fossa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Infratemporal Fossa An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Anatomy 2 U1 L3 1 Temporal Fossa
Anatomy 2 U1 L3 1 Temporal Fossa
 Openings In The Cranial Fossa Skull Anatomy Sphenoid Bone
Openings In The Cranial Fossa Skull Anatomy Sphenoid Bone
 Olecranon Fossa Bone Anatomy Britannica
Olecranon Fossa Bone Anatomy Britannica
 Antecubital Fossa Definition Anatomy
Antecubital Fossa Definition Anatomy
 Figure Cubital Fossa Image Courtesy S Bhimji Md
Figure Cubital Fossa Image Courtesy S Bhimji Md
 Anatomy Infratemporal Fossa Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy Infratemporal Fossa Flashcards Quizlet
 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy 170 Osteology
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy 170 Osteology
 Image Result For Cranial Fossa Anatomy Anatomy Miller
Image Result For Cranial Fossa Anatomy Anatomy Miller
 The Cubital Fossa Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy
The Cubital Fossa Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy
 Pterygopalatine Fossa Wikipedia
Pterygopalatine Fossa Wikipedia
Fossa Anatomy Anatomy System Human Body Anatomy Diagram
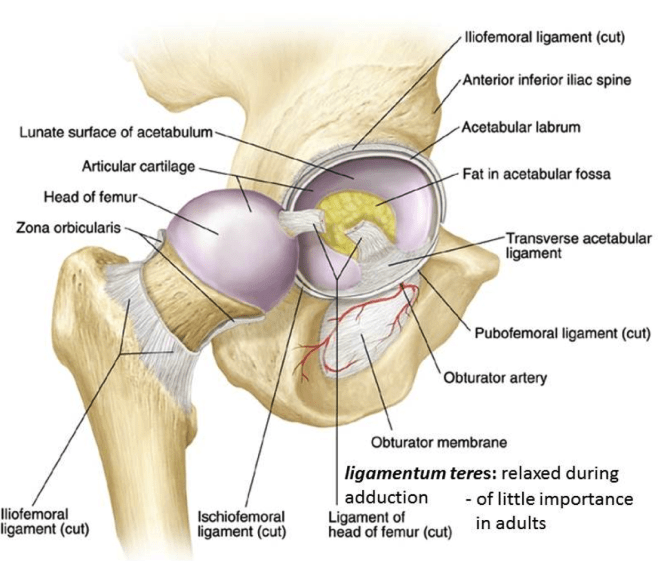 Hip Joint Anatomy Bone And Spine
Hip Joint Anatomy Bone And Spine
 The Cranial Fossae Teachmeanatomy
The Cranial Fossae Teachmeanatomy
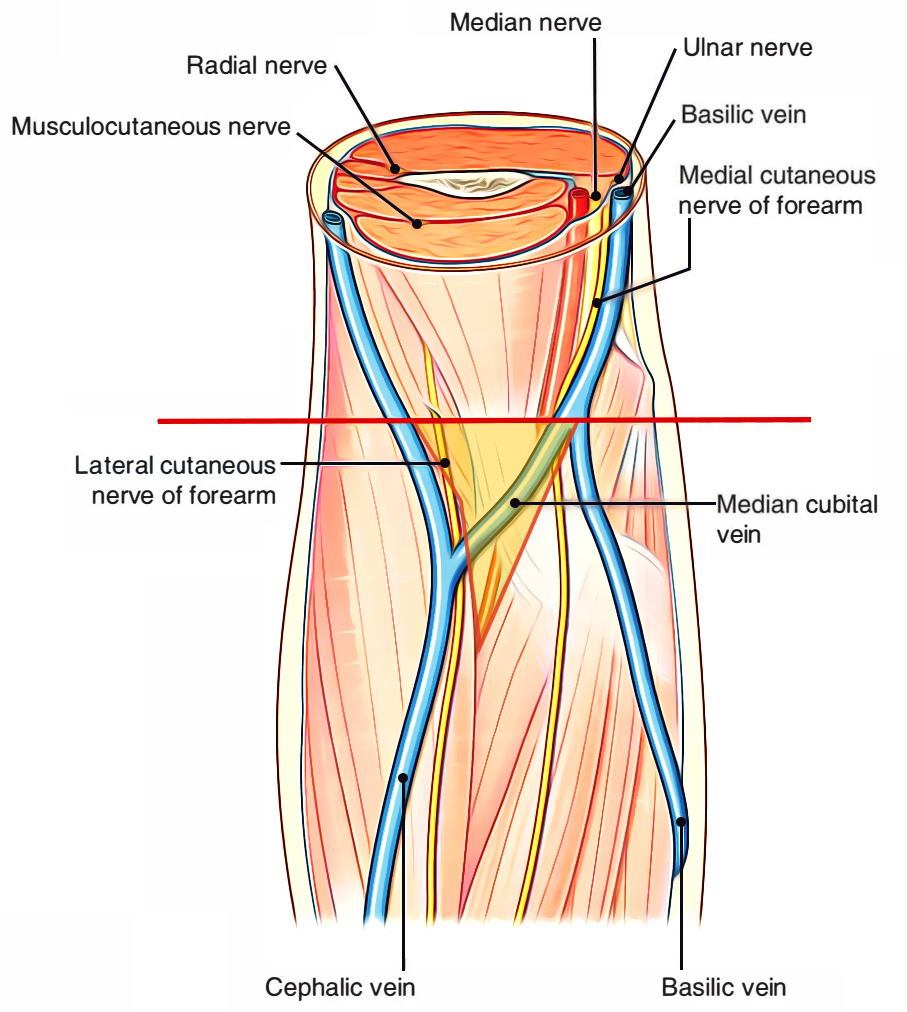 Easy Notes On Cubital Fossa Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Cubital Fossa Learn In Just 4 Minutes
 Chapter 21 Infratemporal Fossa The Big Picture Gross
Chapter 21 Infratemporal Fossa The Big Picture Gross
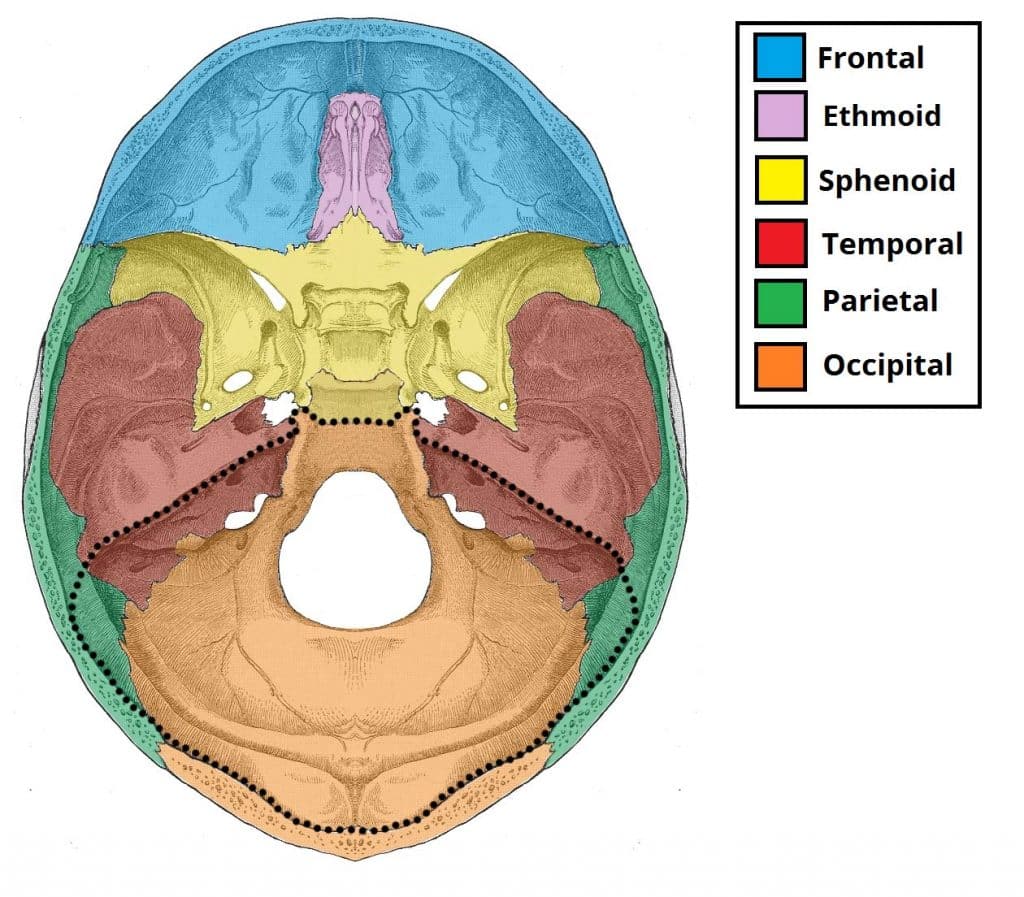 Posterior Cranial Fossa Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
Posterior Cranial Fossa Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
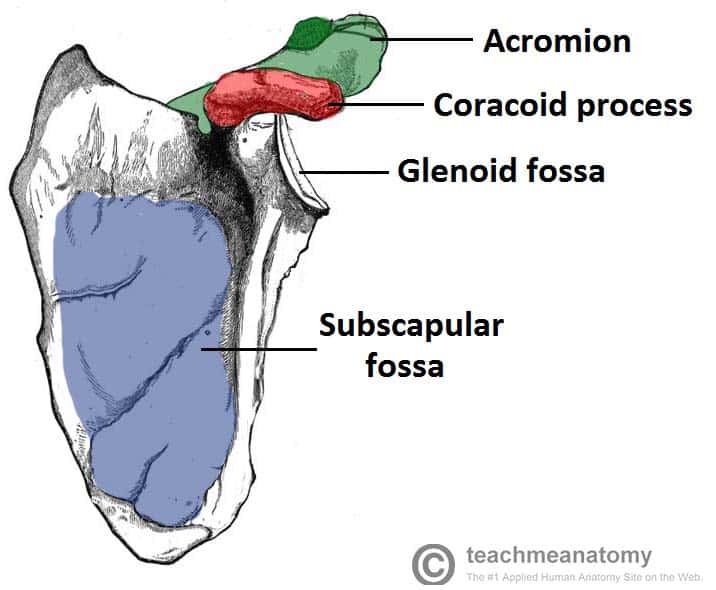 The Scapula Surfaces Fractures Winging Teachmeanatomy
The Scapula Surfaces Fractures Winging Teachmeanatomy
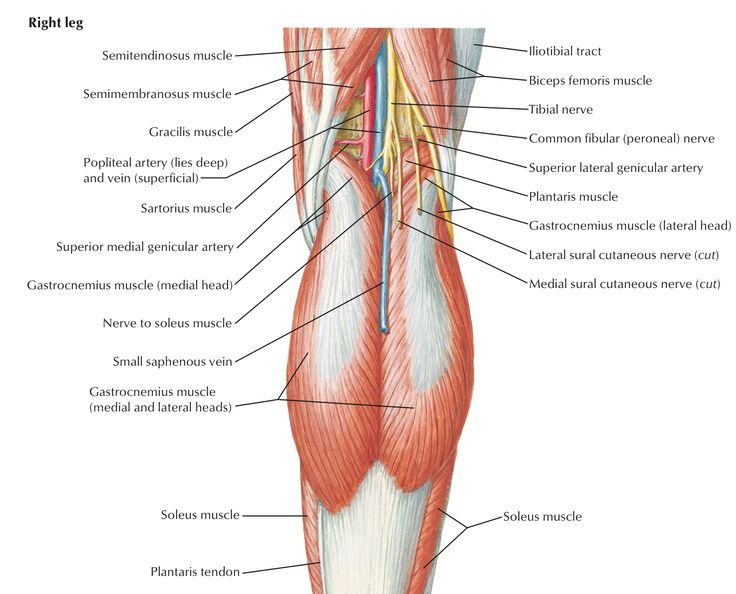 Popliteal Fossa Anatomy And Contents Bone And Spine
Popliteal Fossa Anatomy And Contents Bone And Spine
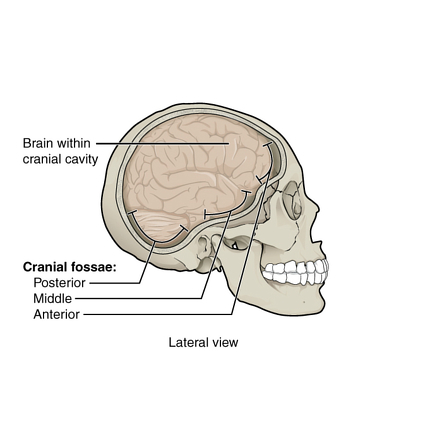 Middle Cranial Fossa Radiology Reference Article
Middle Cranial Fossa Radiology Reference Article
 What Is The Difference Between Ridge Process Fossa And
What Is The Difference Between Ridge Process Fossa And

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Fossa Anatomy"
Posting Komentar