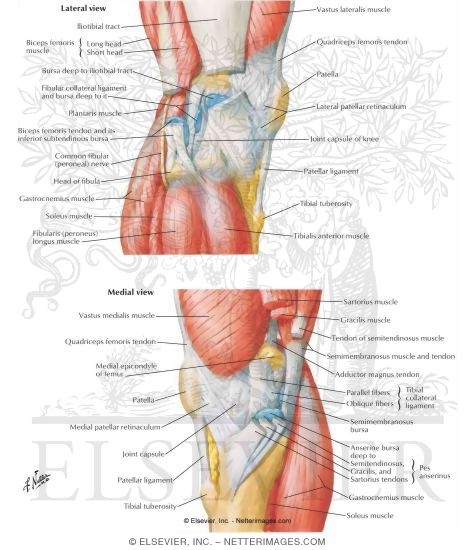
Lateral Knee Anatomy
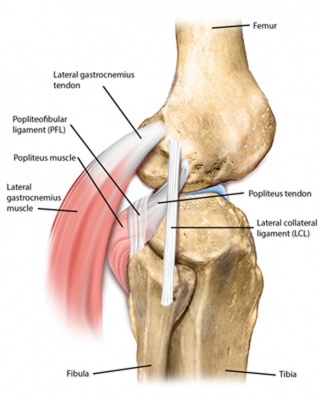
A lack of familiarity leads to hesitancy when performing approaches in these areas of the knee. At the posterior lateral corner of the knee located distally to the posterior horn fascicles is the arcuate ligament.
Anatomy Knee Restoration Center Of Indiana
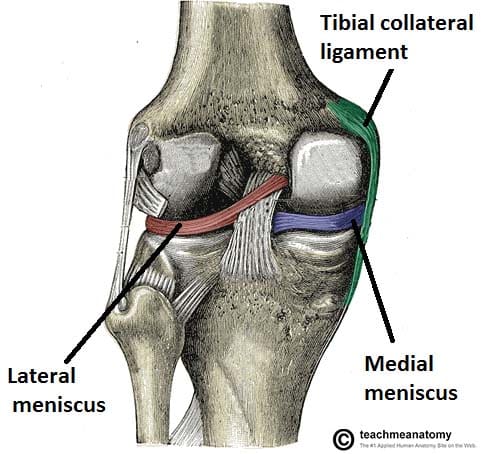
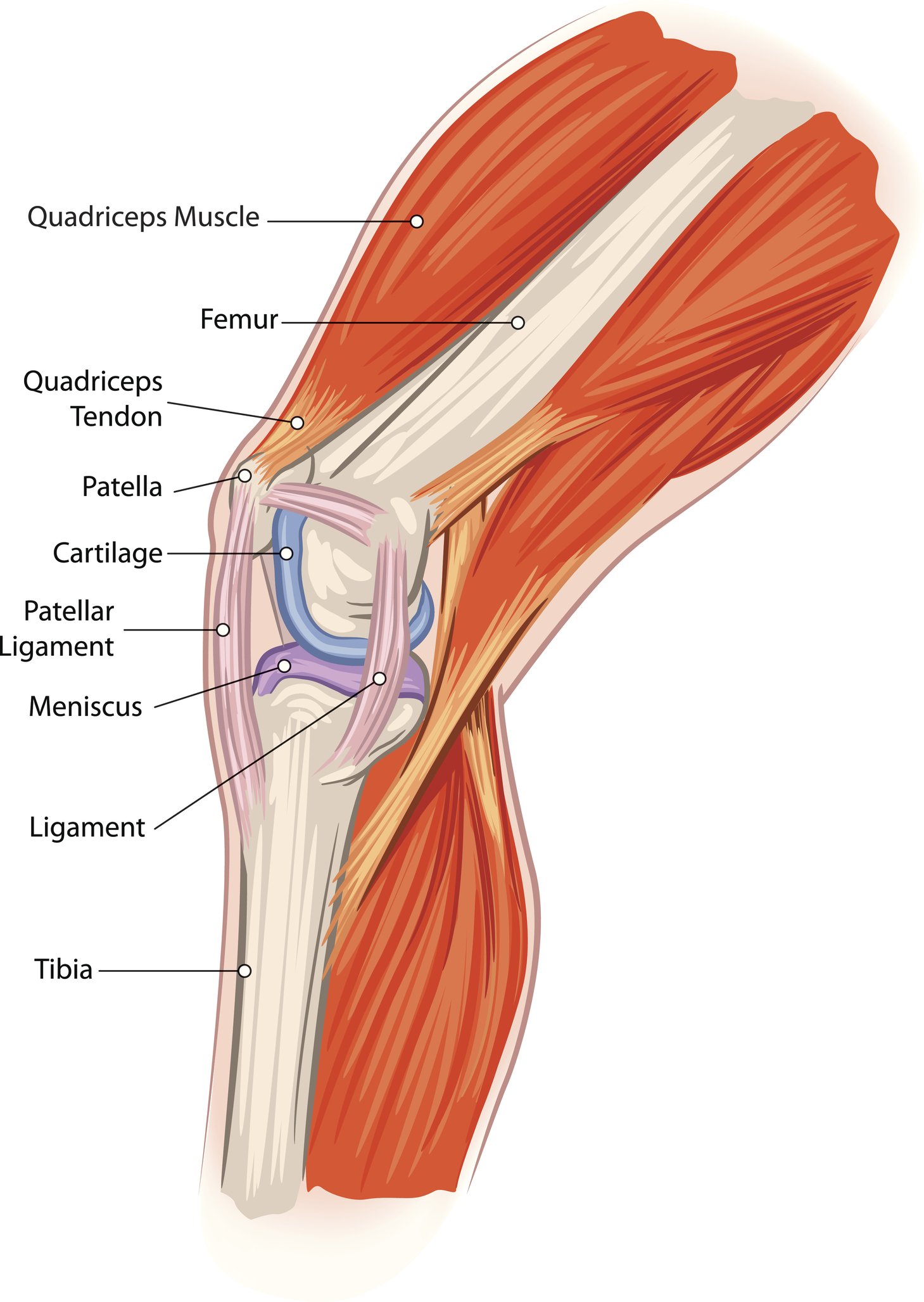
The medial and lateral menisci are fibrocartilage structures in the knee that serve two functions.
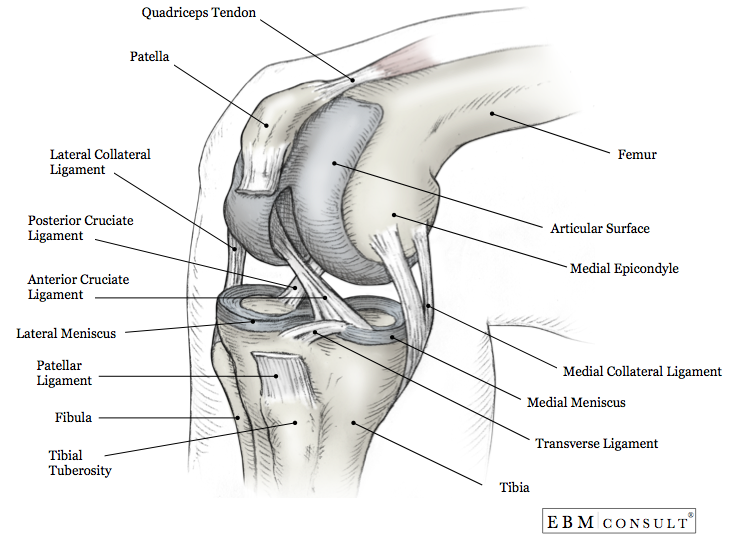
Lateral knee anatomy. A lack of familiarity leads to hesitancy when performing approaches in these areas of the knee. Ligaments are tough fibrous connective tissues which link bone to bone made of collagen. A varus thrust gait occurs as the foot strikes and the lateral compartment opens due to the forces applied on the joint.
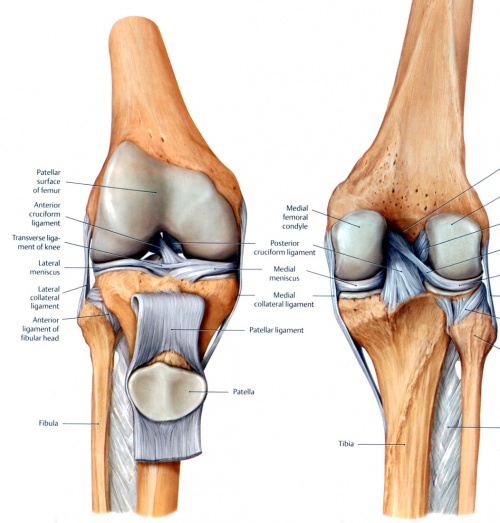
Outer knee pain may be a general ache or specific sharp pain and movement may be restricted. The 3 primary stabilizers that are com monly reconstructed surgically include the fcl pfl and plt fig. In knee joint anatomy knee ligaments are the main stabilising structures of the knee preventing excessive movements and instability.
The posterior and lateral anatomy of the knee joint presents a challenge to even the most experienced knee surgeon. In posterolateral corner injuries the lateral compartment has lost all or part of its stability and cannot maintain normal anatomic positioning when stressed. Two c shaped pieces of cartilage called the medial and lateral menisci act as shock absorbers between the femur and tibia.
Numerous bursae or fluid filled sacs help the knee move smoothly. As a result the symptoms are varied too. Anatomy of the lateral knee the lateral knee is comprised of 28 unique static and dynamic stabilizers.
It may come on gradually over time or may develop suddenly after an injury. 16 the peroneal nerve also courses through the posterolateral aspect of the knee. Lateral knee pain is pain that occurs on the outside of the knee.
This arch type ligament is composed of a medial arm and a lateral arm. As the foot makes contact with the ground the compartments of the knee should remain tight and stabilize the joint through the impact and movements of walking. Knowledge of the bony topography will result in a greater number of anatomic ligament reconstructions.
Knowledge of the bony topography will result in a greater number of anatomic ligament reconstructions. The posterior and lateral anatomy of the knee joint presents a challenge to even the most experienced knee surgeon. It may or may not be connected to a specific activity.
To deepen the articular surface of the tibia thus increasing stability of the joint. To act as shock absorbers by increasing surface area to further dissipate forces.
 Injuries To The Posterolateral Corner Of The Knee Rayner
Injuries To The Posterolateral Corner Of The Knee Rayner
 Knee And Related Knee Anatomy Images And Medical
Knee And Related Knee Anatomy Images And Medical
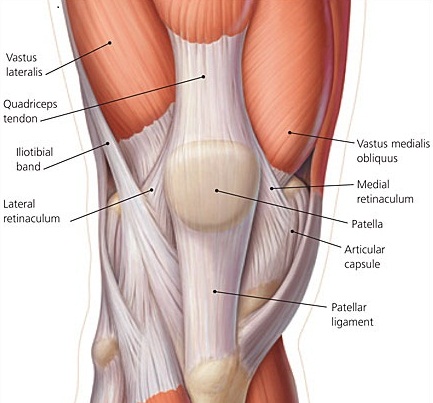 Lateral Outside Knee Pain Causes Treatment Your
Lateral Outside Knee Pain Causes Treatment Your
 Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Anatomy Of The Foot And Ankle Orthopaedia
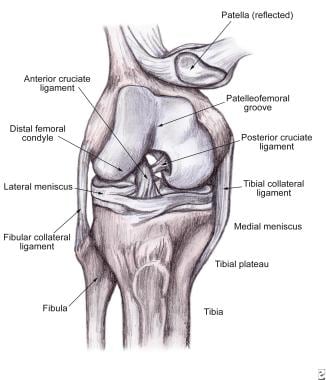 Soft Tissue Knee Injury Practice Essentials Background
Soft Tissue Knee Injury Practice Essentials Background
 Discoid Meniscus Orthoinfo Aaos
Discoid Meniscus Orthoinfo Aaos
Common Knee Injuries Orthoinfo Aaos
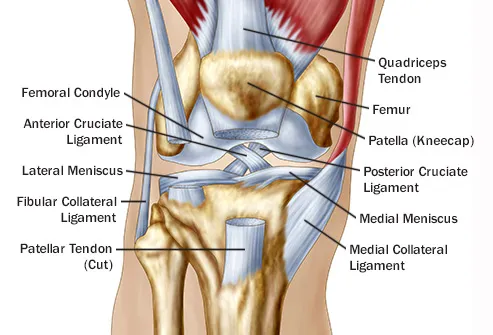 Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
Lateral Knee Radiography Wikiradiography
Anatomy Knee Restoration Center Of Indiana
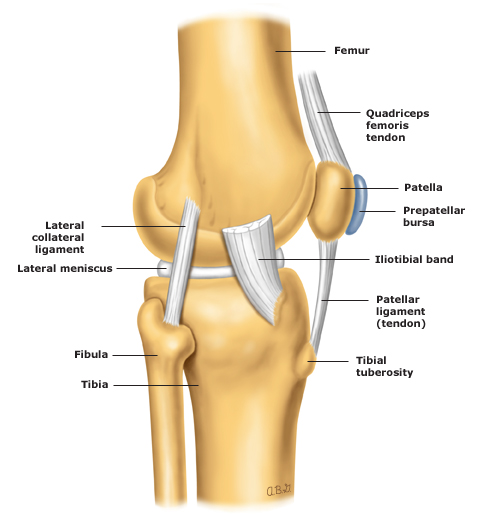 Lateral Anatomy Knee Joint Uptodate
Lateral Anatomy Knee Joint Uptodate
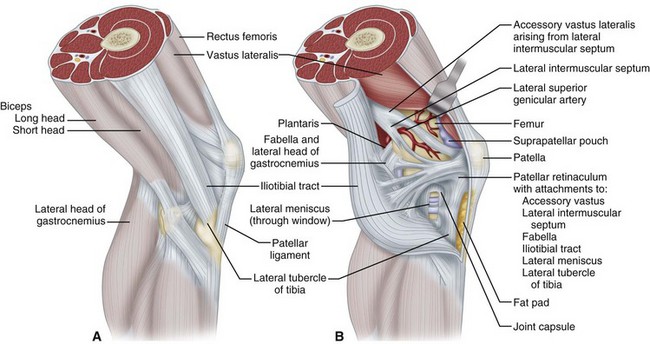 Knee Injuries Musculoskeletal Key
Knee Injuries Musculoskeletal Key
 Types Of Knee Pain Anterior Posterior Medial Lateral
Types Of Knee Pain Anterior Posterior Medial Lateral
 Lateral Medial And Posterior Knee Pain Brukner Khan S
Lateral Medial And Posterior Knee Pain Brukner Khan S
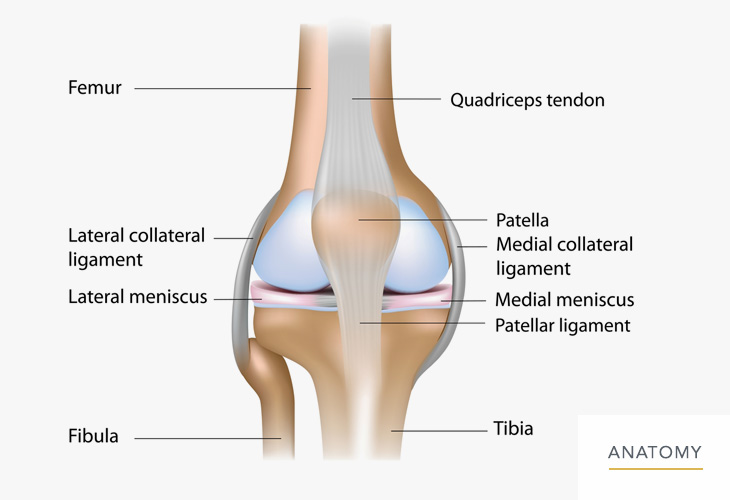 Knee Calf Orthopedic Specialist Of Northern California
Knee Calf Orthopedic Specialist Of Northern California
 How To Keep Your Knees Safe And Injury Free During A Yoga
How To Keep Your Knees Safe And Injury Free During A Yoga
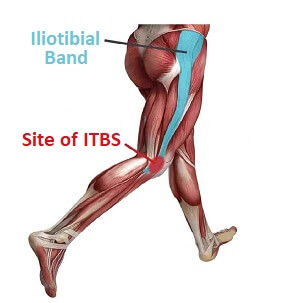 Lateral Knee Pain Pain On Outside Of Knee Knee Pain Explained
Lateral Knee Pain Pain On Outside Of Knee Knee Pain Explained
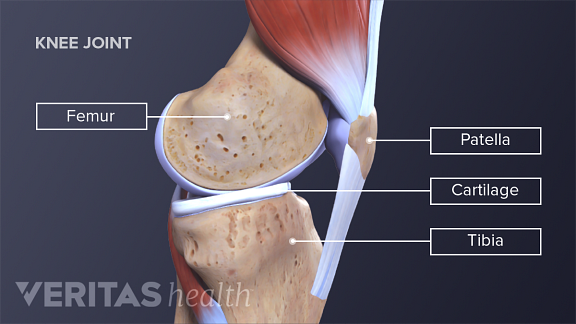
 The Knee Joint Articulations Movements Injuries
The Knee Joint Articulations Movements Injuries

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Lateral Knee Anatomy"
Posting Komentar