Forearm Vein Anatomy
The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb but which in anatomy technically means only the region of the upper arm whereas the lower arm is called the forearm. Each of these potential venipuncture sites presents its own advantages and disadvantages.
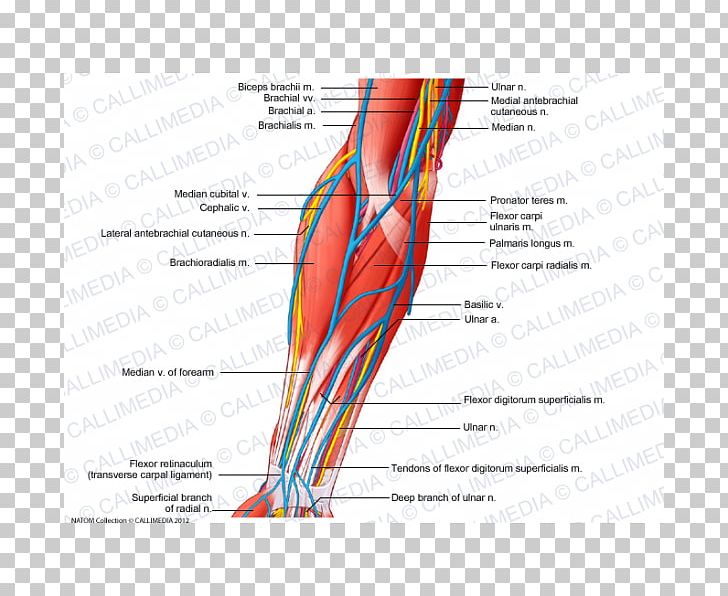 Anterior Compartment Of The Forearm Nerve Muscle Vein Png
Anterior Compartment Of The Forearm Nerve Muscle Vein Png
There are two prominent superficial veins of the upper limb.

Forearm vein anatomy. As with the veins in the calf the veins of the forearm genarally run in pairs venous commantantes. As their name implies these veins are close to the skins surface. This is the space between the upper.
Nerves the following nerves branch from the brachial plexus in the neck and travel through the arm to supply the. The muscles in the forearm rotate flex and extend the wrist. Like in the forearm the arm is drained by the brachial veins.
Veins of the upper limb hand. It can be subdivided into the superficial system and the deep system. This web of veins extends across the back of the hand.
The forearm is drained by numerous deep veins which form double venae comitantes. The major nerves and veins start in your neck and run the length of your arms often into your hands. The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist.
Extending from the shoulder to the elbow the upper arm provides pulling and lifting strength. The basilic vein is a large superficial vein of the upper limb that helps drain parts of the hand and forearm. In our descent down the arm the ventral aspect of the forearm is next followed by the dorsum of the wrist and the dorsum of the hand.
It originates on the medial ulnar side of the dorsal venous network of the hand and travels up the base of the forearm where its course is generally visible through the skin as it travels in the subcutaneous fat and fascia lying superficial to the muscles. The muscles and joints of the elbow and forearm need nervous supply and blood flow. Forearm veins radial ulna still with the patient seated on the side of the bed follow the radial and ulnar veins to the wrist confirming compressibility and flow.
It can be subdivided into the superficial system and the deep system. This hinged joint allows the arm to open up to 180 degrees at full extension. It is homologous to the region of the leg.
Dorsal metacarpal veins palmar digital veins intercapitular veins dorsal venous network palmar venous network cephalic vein basilic vein median antebrachial vein medial cephalic vein. This large vein travels through the upper arm before branching near. The forearm is the area between the wrist and the elbow.
The venous system of the upper limb drains deoxygenated blood from the arm forearm and hand. Some of the veins in the arm include.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/basilic-vein/OnAbwoqp0EDeA3qN2HLEbA_eCmnCpxyXM_Vena_basilica_2.png) Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
 Venous Lymphatic Drainage Of Upper Limb
Venous Lymphatic Drainage Of Upper Limb
 Forearm Veins Google Search In 2019 Arm Anatomy
Forearm Veins Google Search In 2019 Arm Anatomy
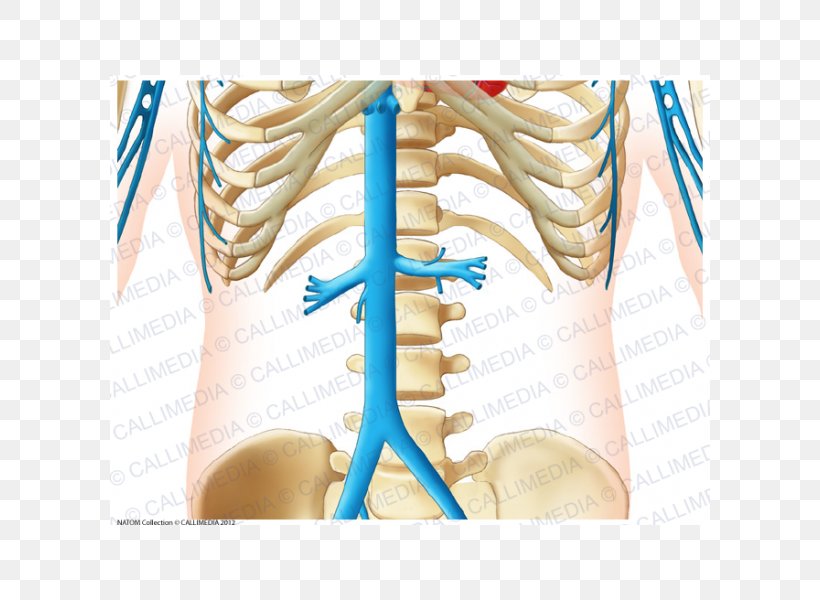 Abdomen Vein Forearm Artery Anatomy Png 600x600px
Abdomen Vein Forearm Artery Anatomy Png 600x600px
 Venous Cannulation Sites In The Arm Illustration Stock
Venous Cannulation Sites In The Arm Illustration Stock
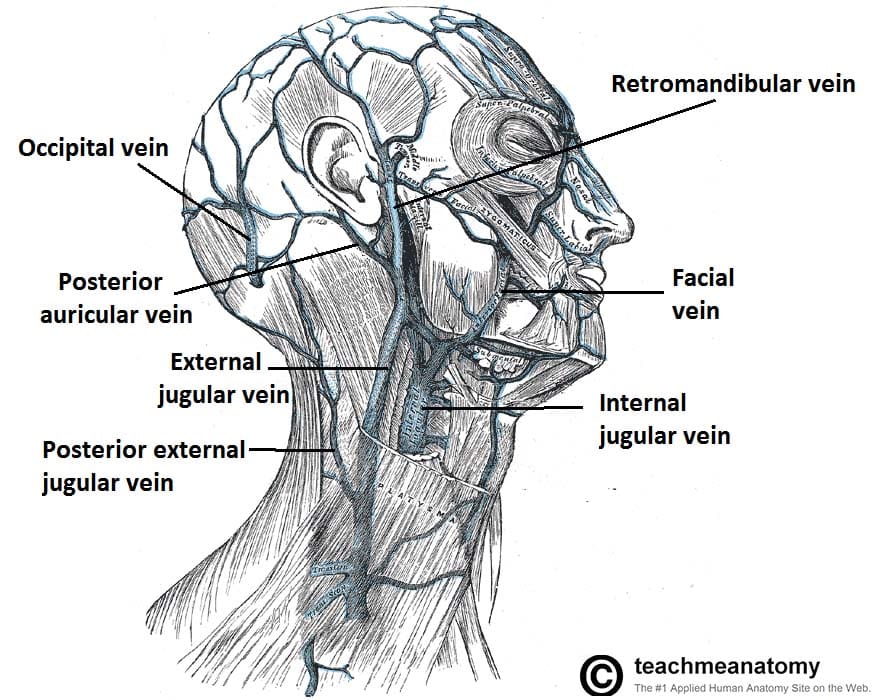 Venous Drainage Of The Head And Neck Dural Sinuses
Venous Drainage Of The Head And Neck Dural Sinuses
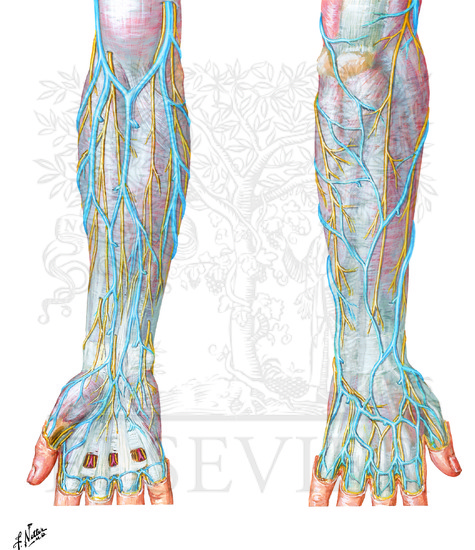 Cutaneous Nerves And Superficial Veins Of Forearm And Hand
Cutaneous Nerves And Superficial Veins Of Forearm And Hand
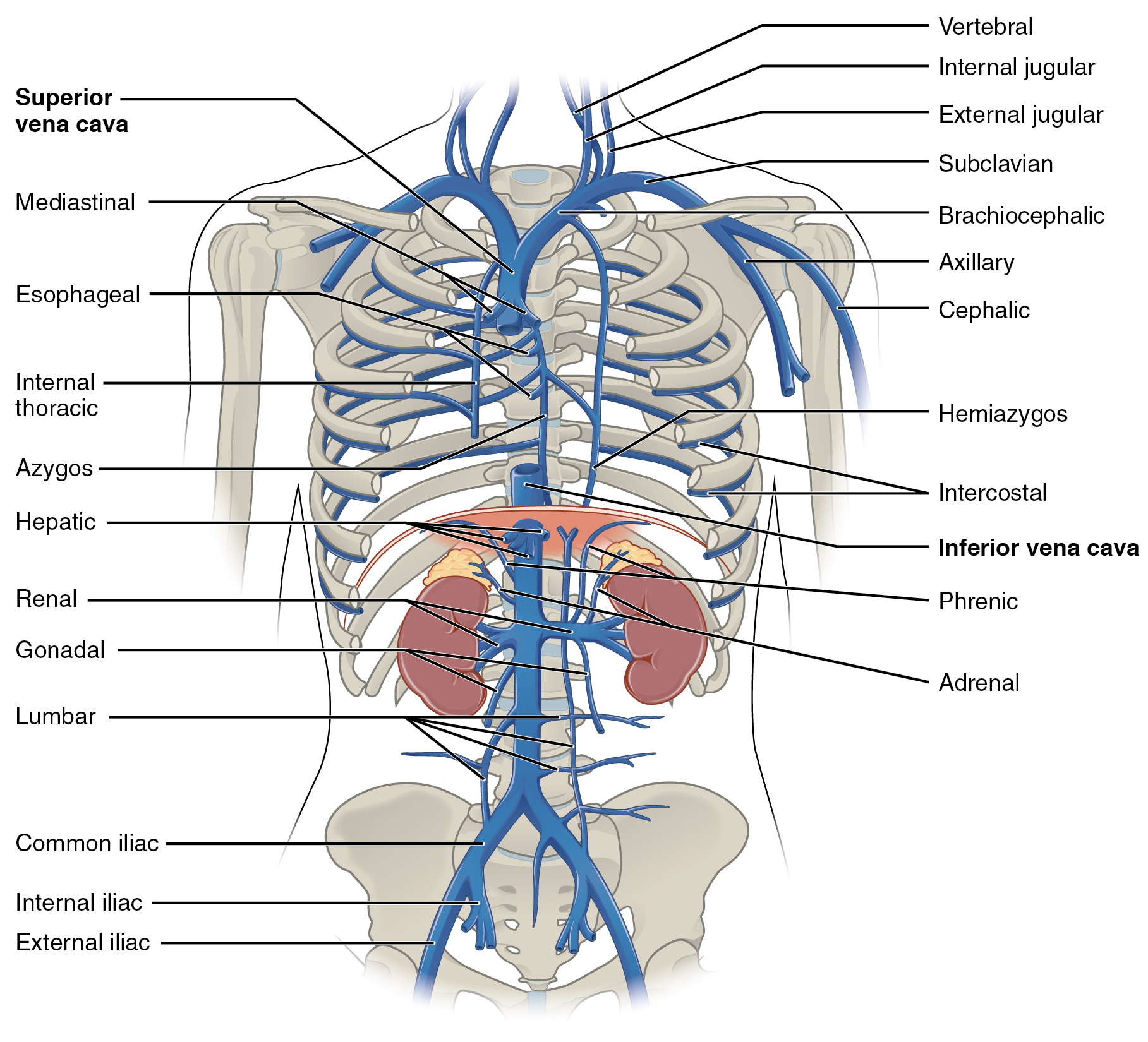 20 5 Circulatory Pathways Anatomy And Physiology
20 5 Circulatory Pathways Anatomy And Physiology

 Radial Forearm Flap Standard Technique Plastic Surgery Key
Radial Forearm Flap Standard Technique Plastic Surgery Key
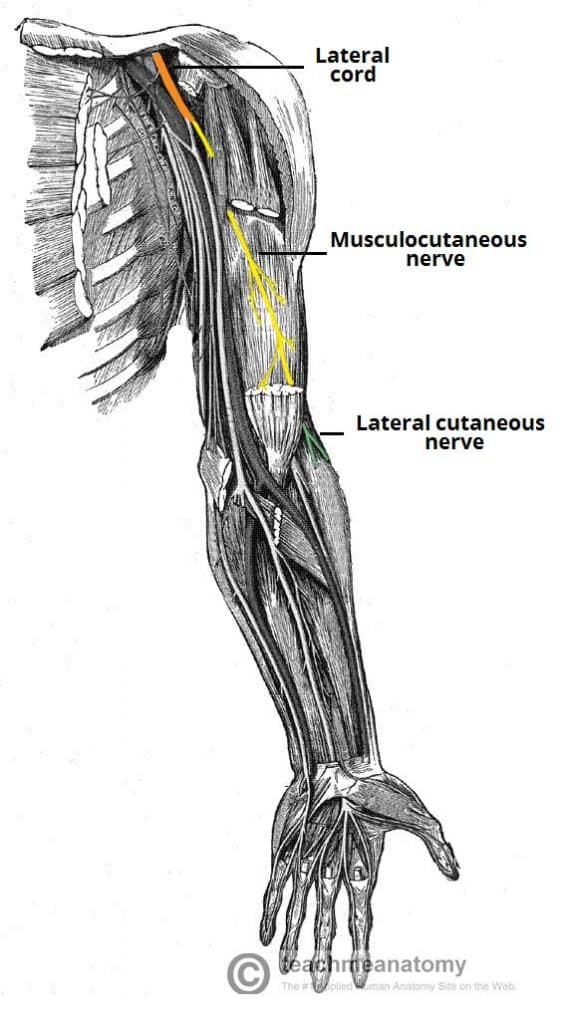 The Musculocutaneous Nerve Course Motor Sensory
The Musculocutaneous Nerve Course Motor Sensory
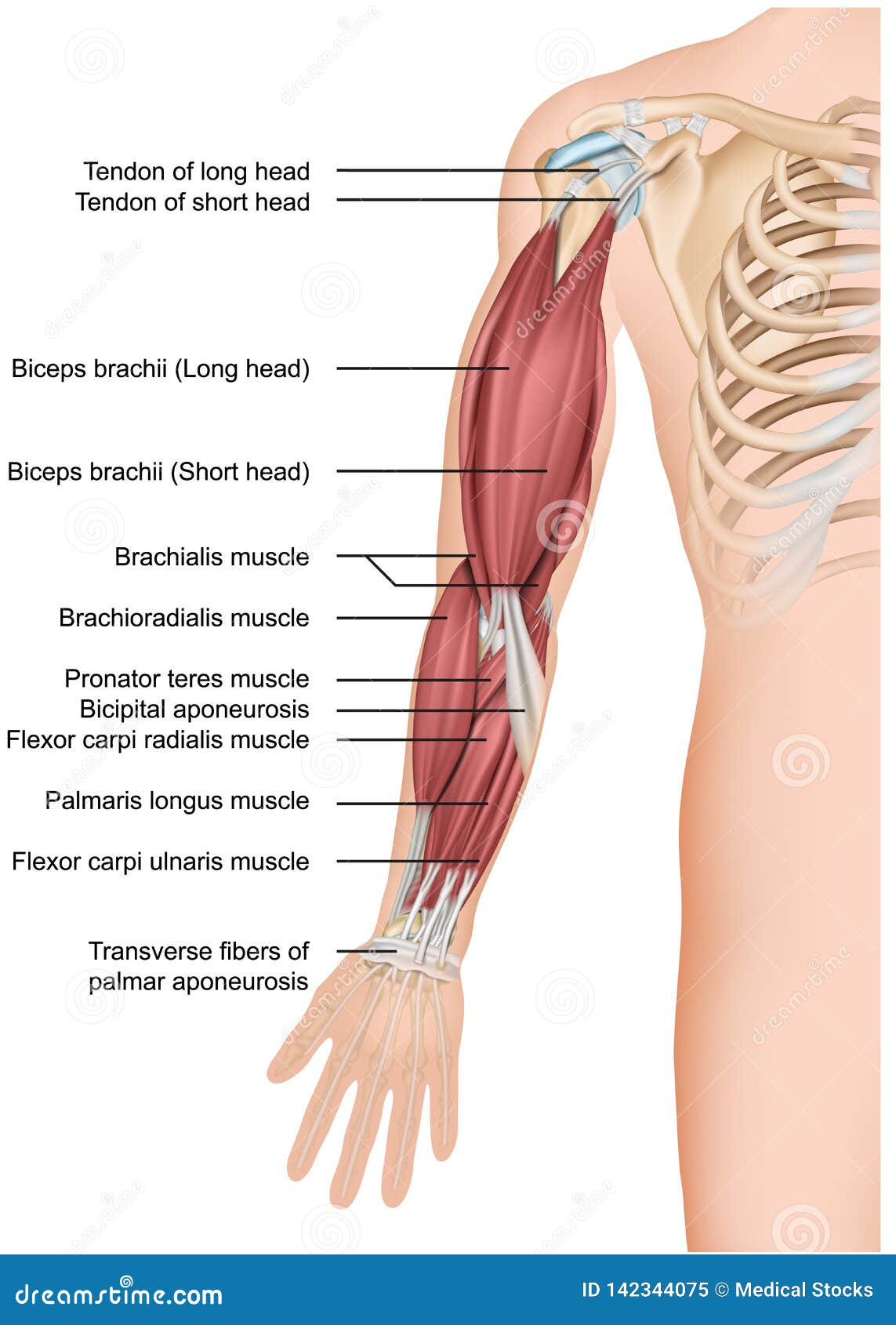 Arm Muscle Anatomy 3d Medical Illustration Forearm Stock
Arm Muscle Anatomy 3d Medical Illustration Forearm Stock
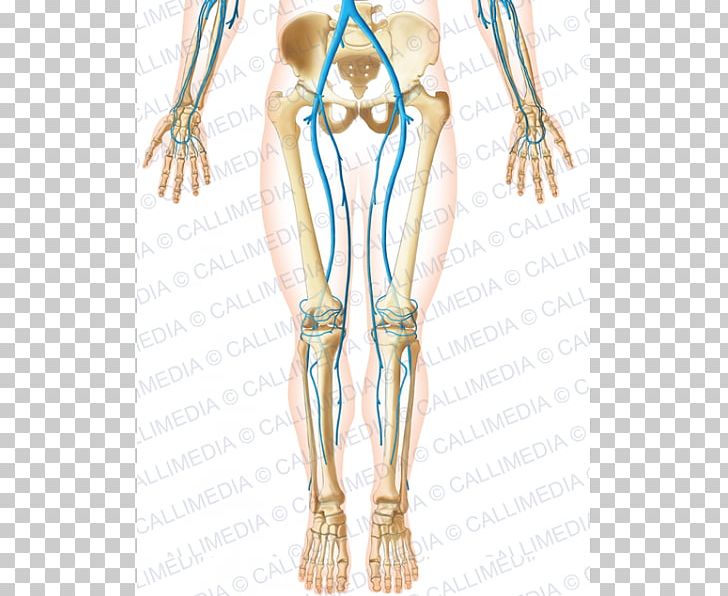 Finger Basilic Vein Forearm Png Clipart Abdomen Anatomy
Finger Basilic Vein Forearm Png Clipart Abdomen Anatomy
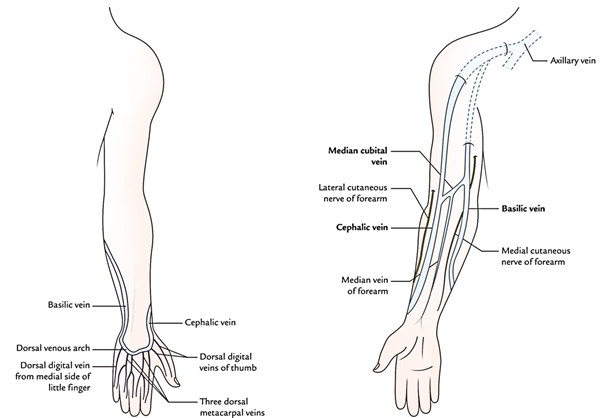 Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Upper Limb
Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Upper Limb
 Median Cubital Vein An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Median Cubital Vein An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Human Anatomy
The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Human Anatomy
 Anatomy Of Forearm Muscles Anterior View Middle Iphone Wallet
Anatomy Of Forearm Muscles Anterior View Middle Iphone Wallet
 Ultrasound Anatomy Of Peripheral Veins And Ultrasound Guided
Ultrasound Anatomy Of Peripheral Veins And Ultrasound Guided
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/cephalic-vein-of-the-forearm/nA2JBRh6FusVKzTaChI3tQ_JufzsJz8pH_Vena_cephalica_antebrachii_2.png) Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
Veins Of The Upper Limb Anatomy Kenhub
 Anatomy Veins Of The Hand And Forearm Critical Care
Anatomy Veins Of The Hand And Forearm Critical Care
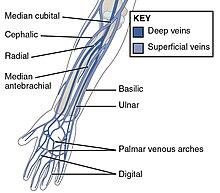
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Forearm Vein Anatomy"
Posting Komentar