Mandible Anatomy Radiology
The mandible can be considered as an anatomical ring of bone stabilised at each end at the temporomandibular joints. The tooth sockets called alveoli open onto this surface.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
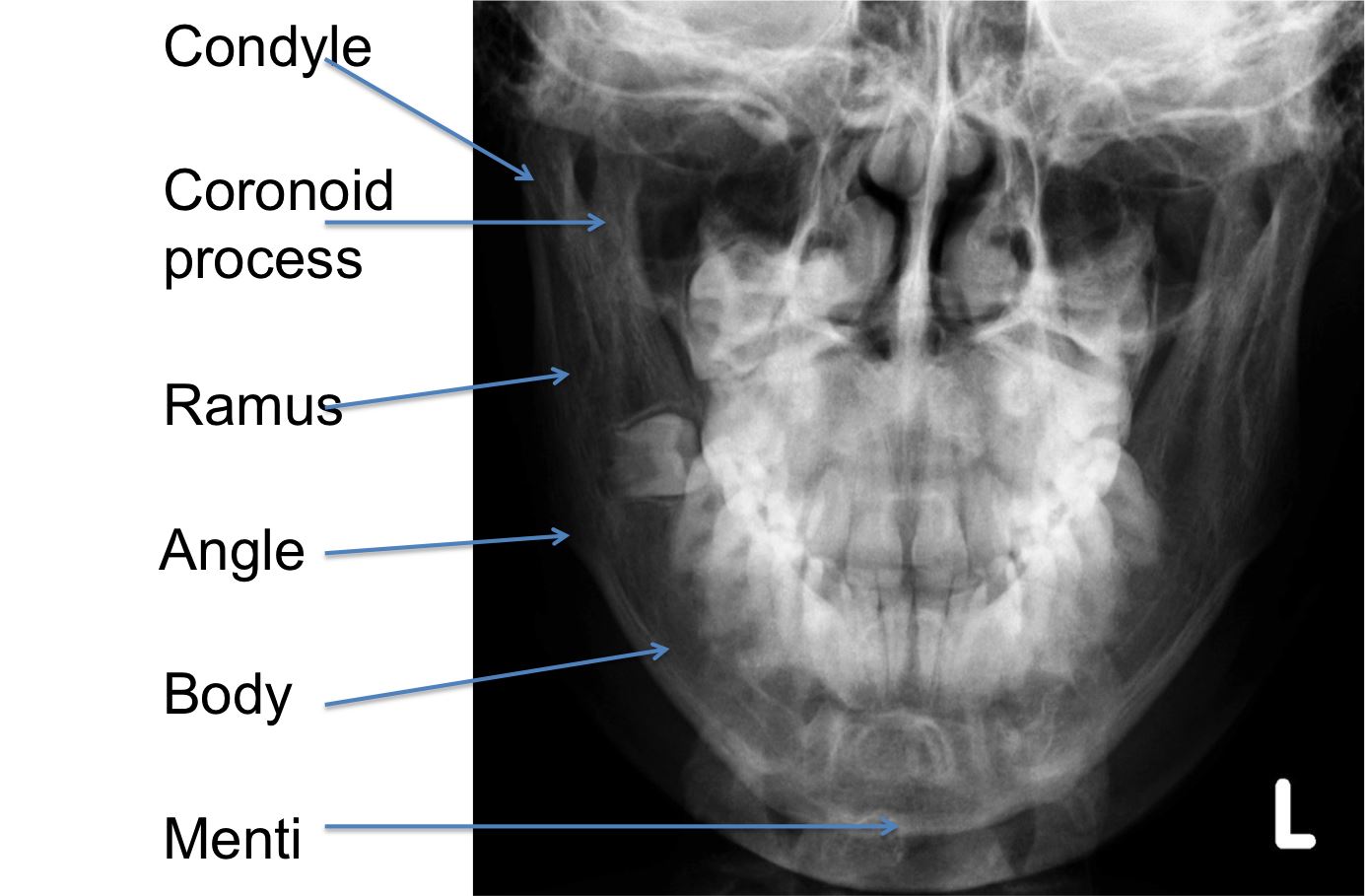
Mandible anatomy radiology. The body of the mandible anchors the lower teeth and forms the chin. The mandible is another commonly fractured bone in the head and most of these fractures are obvious on clinical exam. The range of motion is free in all directions and the condyle moves downward and forward in the articular fossa upon opening of the jaw.
It articulates with both temporal bones at the mandibular fossa at the temporomandibular joints tmj. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. Its superior border is the alveolar process.
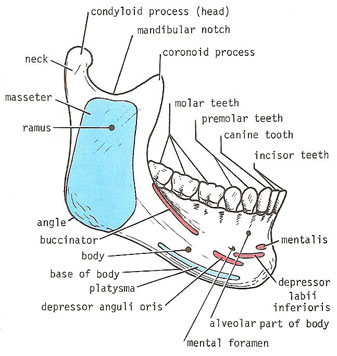
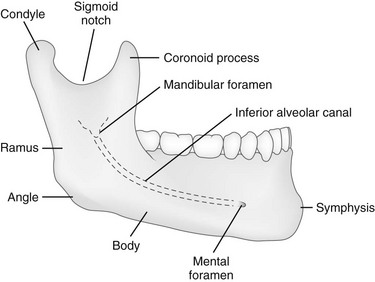
The ramus meets the body at the angle. Anteriorly the two halves of the mandible fuse at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the only freely movable bone of the face.
A break of the ring in one place will usually be accompanied by further break in the ring elsewhere. The mental protuberance at this junction forms the chin. If you see one fracture look for a second fracture or a dislocation of the temporomandibular joint.
This should mean that the mandible should fracture in two places akin to the bony pelvis making single fractures uncommon but this in fact not the case with 40 of fractures being unifocal. It consists of a curved horizontal portion the body and two perpendicular portions the rami which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles angle of the jaw. It articulates with the temporal bone in the temporomandibular fossa anterior to the external auditory canal see fig.
The lateral pterygoid at the condylar process the medial pterygoid at the posterior inferior ramus near the angle the temporalis at the coronoid process and the masseter at the ramus. The midline of the body is the mandibular symphysis fig. The buccal surface of the mandible attaches multiple muscles.
Start studying radiology normal anatomy of mandible. The mandible is comprised of a body and paired rami coronoid processes and condylar processes. Clinical findings include facial distortion malocclusion of the teeth or abnormal mobility of portions of the mandible or teeth.
Although traditionally the mandible and base of skull are thought to form a complete bony ring interrupted only by the tmjs.
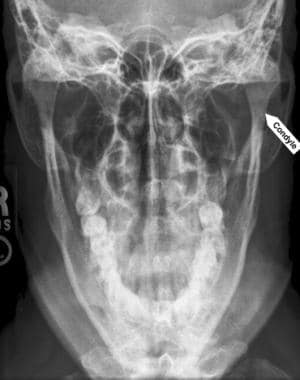 Mandibular Fracture Imaging Practice Essentials
Mandibular Fracture Imaging Practice Essentials

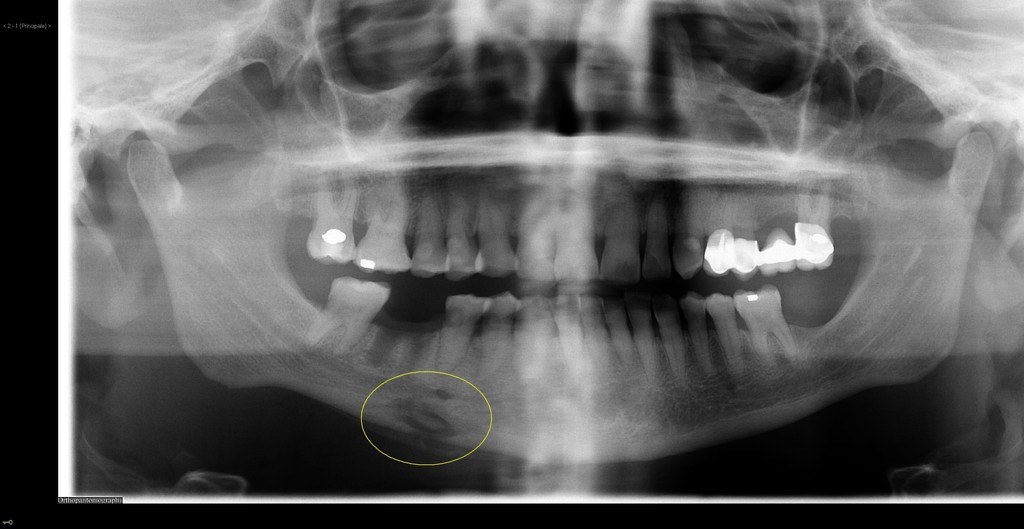 Mandibular Osteomyelitis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Mandibular Osteomyelitis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
 Radiology For Trigeminal Neuralgia Springerlink
Radiology For Trigeminal Neuralgia Springerlink
Dingman And Natvig Classification Of Mandibular Fractures
Panoramic Radiograph Wikipedia
Mandible Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography
 Facial And Mandibular Fractures
Facial And Mandibular Fractures
Evaluation Of Mandibular Asymmetry In Angle Malocclusion
 Temporomandibular Joint An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Temporomandibular Joint An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Mandible And Maxilla Oblique Radiography
Mandible And Maxilla Oblique Radiography
Mandible Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography
Anatomy On Radiographs Pantomographs Part 1 Dr G S Toothpix
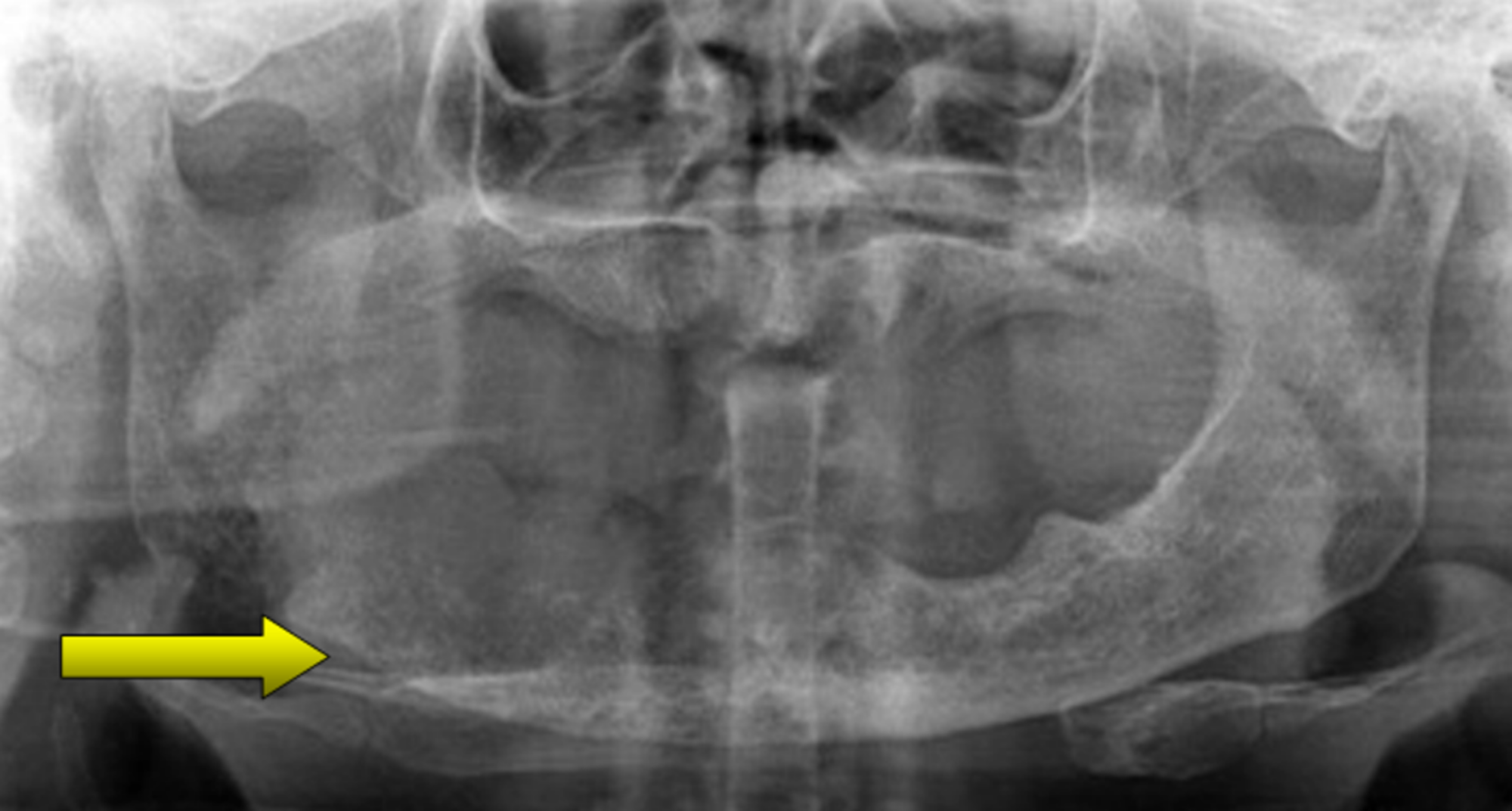 Cureus Metastatic Tumour To The Mandible A Diagnostic
Cureus Metastatic Tumour To The Mandible A Diagnostic
The Accuracy And Interobserver Reliability Of Identification
 Radiology Skull And Mandible Dogs Vetlexicon Canis From
Radiology Skull And Mandible Dogs Vetlexicon Canis From
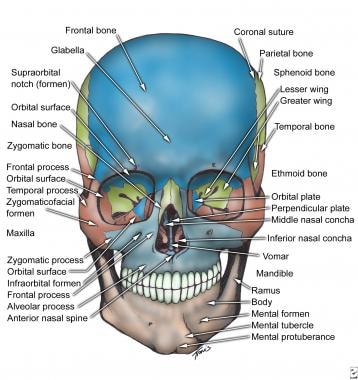 Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
 Mandible Fracture Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Mandible Fracture Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
 Normal Intraoral Radiographic Anatomy
Normal Intraoral Radiographic Anatomy
How Was That Missed Mandibular Fracture Dr G S Toothpix
 The Canine Head And Skull Ct Atlas Of Veterinary Clinical
The Canine Head And Skull Ct Atlas Of Veterinary Clinical
Masseter Muscle Hypertrophy Case Report
 Mandibular Ramus And Gonial Angle Measurements As Predictors
Mandibular Ramus And Gonial Angle Measurements As Predictors
 Scan Atlas Of Anatomy Of The Face
Scan Atlas Of Anatomy Of The Face
Comparison Between Conventional Radiography And 3d
 Radiology Skull And Mandible Dogs Vetlexicon Canis From
Radiology Skull And Mandible Dogs Vetlexicon Canis From
 Radiology Skull And Mandible Dogs Vetlexicon Canis From
Radiology Skull And Mandible Dogs Vetlexicon Canis From
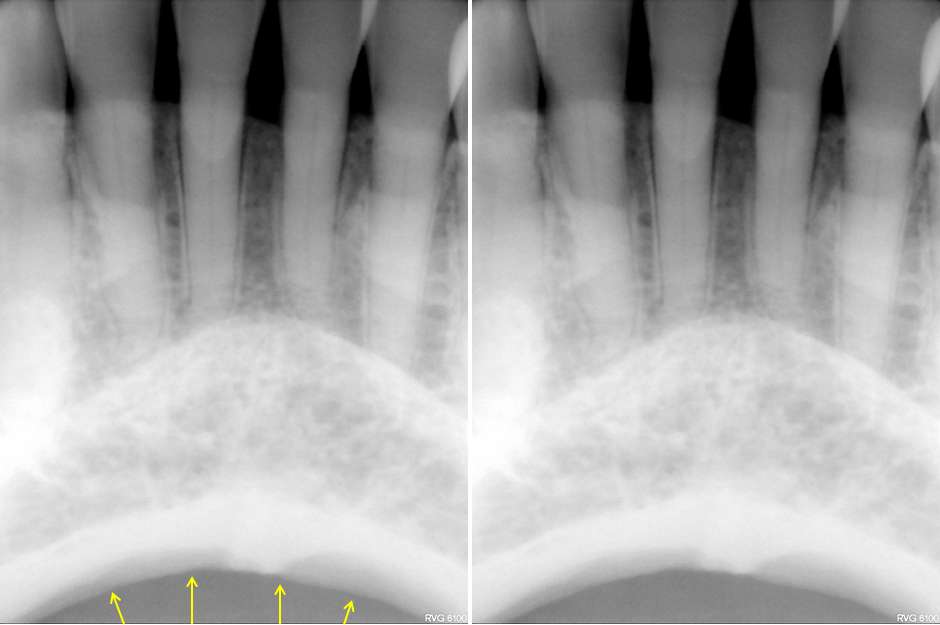 Anatomy Monday Anatomy On Mandibular Periapical Radiographs
Anatomy Monday Anatomy On Mandibular Periapical Radiographs
 The Mandible Structure Attachments Fractures
The Mandible Structure Attachments Fractures
Mandibular Fractures Opg Radiology At St Vincent S

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Mandible Anatomy Radiology"
Posting Komentar