Anatomy Of The Kneecap
The medial and lateral. An inside look at the structure of the knee.
 Total Joint Anatomy Lakeshore Orthopaedics
Total Joint Anatomy Lakeshore Orthopaedics
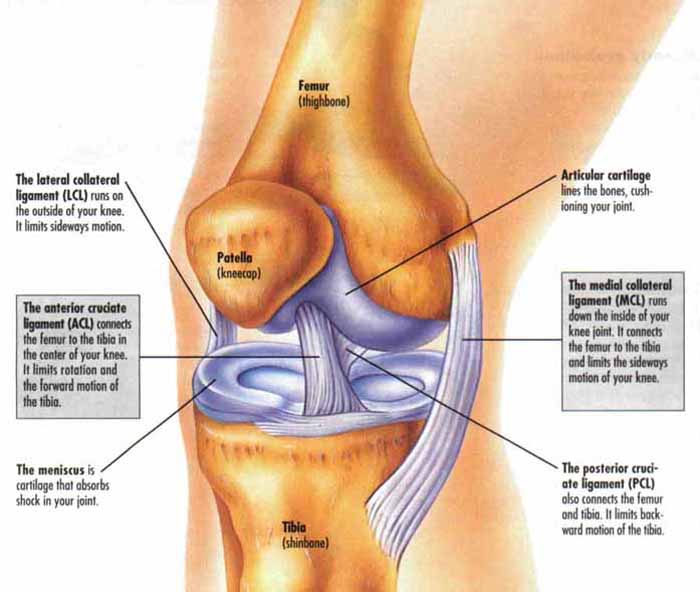
Ligaments of the knee.

Anatomy of the kneecap. They act like strong ropes to connect bones. Tendons connect the knee bones to the leg muscles that move the knee joint. Anatomy of the knee bones around the knee.
Medial collateral ligament mcl anterior cruciate ligament acl posterior cruciate ligament pcl two groups of muscles support the knee. This long bone runs between the hip and the knee. The knee joins the thigh bone femur to the shin bone tibia.
These are crescent shaped discs that act as a cushion. Ligaments are structures that connect two bones together. Tendons at the knee.
Patella kneecap a semi flat triangular bone that is able to move as the knee bends. The tibia and fibula which are the leg bones between the knee and ankle. Muscles tendons and ligaments connect the knee bones.
The kneecap glides in a groove in the thighbone and adds leverage to the thigh muscles which are used to extend the leg. The smaller bone that runs alongside the tibia fibula and the kneecap patella are the other bones that make the knee joint. They are they soft tissues found at the end of muscles which link the muscle to bone.
The apex of the patella gives rise to the patellar ligament which inserts onto the tibial tuberosity on the anterior surface of the tibia. And the patella which is sometimes called the kneecap. Its main function is to increase the force generated by the quadriceps muscle which straightens or extends the knee.
Another bone the patella kneecap is at the center of the knee. The knee is one of the largest and most complex joints in the body. The knee cap actually sits inside the patellar tendon.
There are three bones that come together at the knee joint. Cartilage of the knee. Tendons are often overlooked as part of knee joint anatomy.
Hamstrings muscles on the back of the thigh which run from the hip to just below the knee and work. There are two types of cartilage of the knee joint. Two concave pads of cartilage strong flexible tissue called menisci minimize the friction created at the meeting of the ends of the tibia and femur.
These tough bands of soft tissue. The femur thigh bone tibia shin bone and patella. The middle third of the patella has various vascular openings that allow for arteries to penetrate and supply the bone.
The thigh bone and shine bone come together at the knee joint and move on one another when bending or straightening the leg. There are also several key ligaments a type of fibrous connective tissue that connect these bones. The bones of the knee and the leg include the femur which is the large thigh bone.
Ligaments are tough and fibrous tissues. The main tendon found at the knee is the patellar tendon which links the quads muscles to the shin bone.
 The Knee Anatomy Injuries Treatment And Rehabilitation
The Knee Anatomy Injuries Treatment And Rehabilitation
 Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
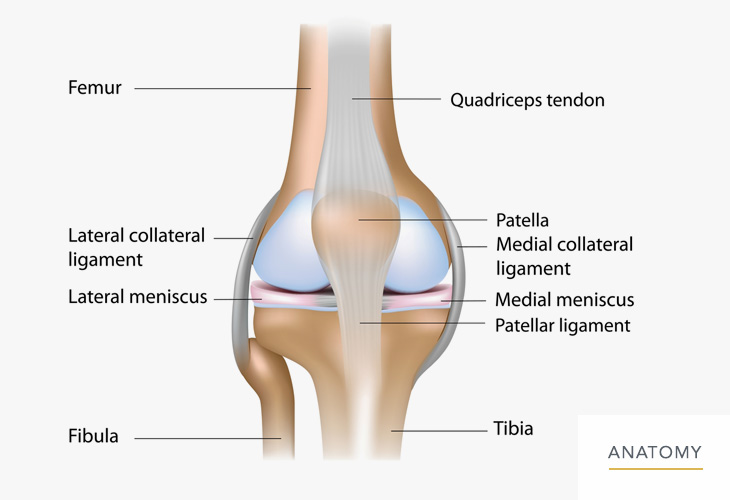 Knee Calf Orthopedic Specialist Of Northern California
Knee Calf Orthopedic Specialist Of Northern California
 Osgood Schlatter Disease Knee Pain Orthoinfo Aaos
Osgood Schlatter Disease Knee Pain Orthoinfo Aaos
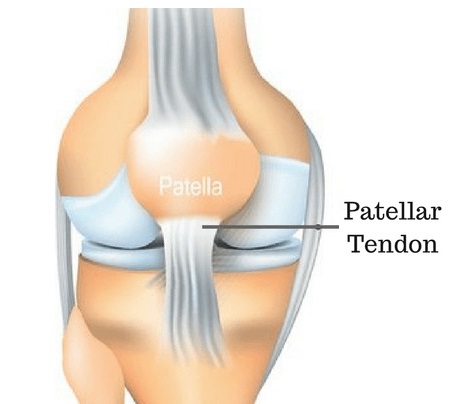 Knee Joint Anatomy Motion Knee Pain Explained
Knee Joint Anatomy Motion Knee Pain Explained
 Anatomy Of The Knee For Dancers Dance Work Balance
Anatomy Of The Knee For Dancers Dance Work Balance

Patellofemoral Arthritis Orthoinfo Aaos
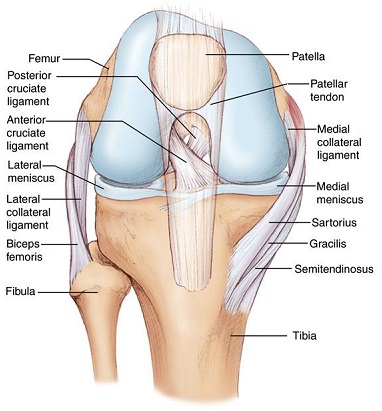 Knee Surgeon Chicago Prp Treatment Chicago Patellar
Knee Surgeon Chicago Prp Treatment Chicago Patellar
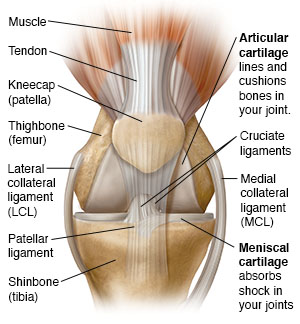
 Patellar Fractures Broken Kneecap Orthoinfo Aaos
Patellar Fractures Broken Kneecap Orthoinfo Aaos
Anatomy Knee Restoration Center Of Indiana
Knee Advanced Orthopedics Sports Medicine
 Patellar Tendinitis Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Patellar Tendinitis Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Knee Surgeon Chicago Illinois Steven Chudik Md
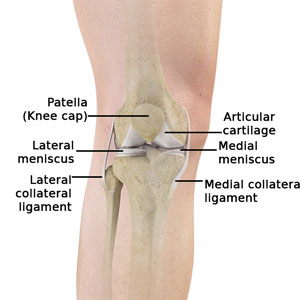 Knee Pain Treatment Atlanta Ga Knee Fracture Treatment
Knee Pain Treatment Atlanta Ga Knee Fracture Treatment
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/5748/RmVeyFNbCOffPwvE60F4A_1Hb654x3CC_Arteria_superior_medialis_genus_2.png-2.jpeg) Patella Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Patella Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
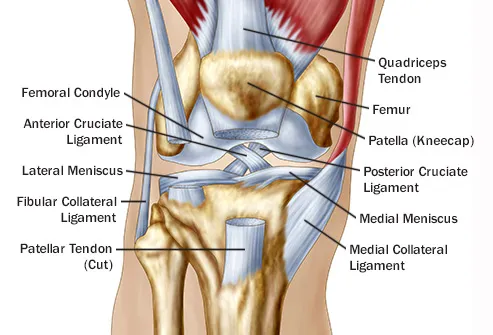 Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
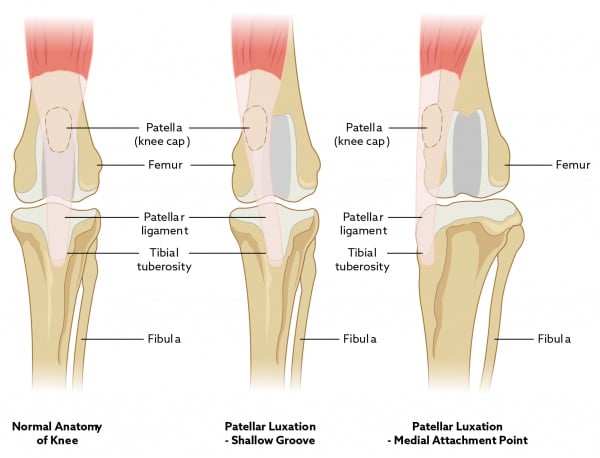 Luxating Patella In Cats Vca Animal Hospital
Luxating Patella In Cats Vca Animal Hospital
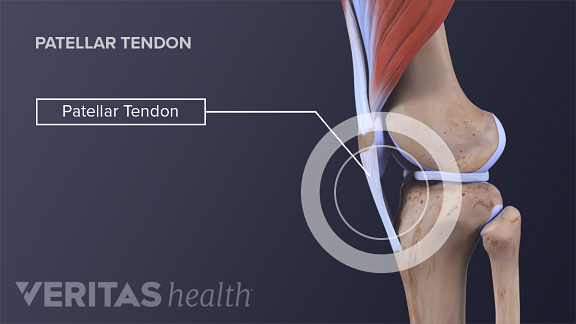


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of The Kneecap"
Posting Komentar