Cells Definition Anatomy
A type of white blood cell that is of key importance to the immune system and is at the core of adaptive immunity the system that tailors the bodys immune response to specific pathogens. Kupffer cells in liver.
 Chapter 8 Cr Solutions Medical Terminology And Anatomy For
Chapter 8 Cr Solutions Medical Terminology And Anatomy For
Definition development anatomy and functions.
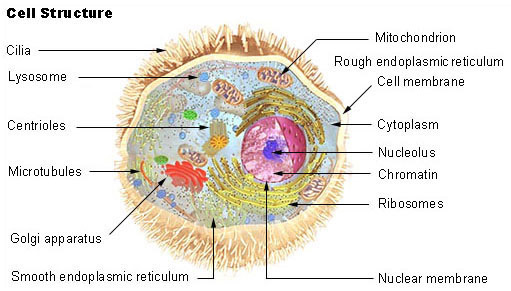
Cells definition anatomy. The nucleus is the organelle which houses chromosomes. Cell in biology the basic membrane bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. Sarcomere a unit of striated muscle tissue that contains the filaments actin and myosin.
Chromosomes consist of dna which contains heredity information and instructions for cell growth development and reproduction. A cell is the smallest unit of life. The nucleus contains the cells dna a type of nucleic acid.
It is an old science having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Cells are often called the building blocks of life. The nucleus contains a nucleolus and is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope.
Protects cell from toxic hydrogen peroxide planthelps with chemical reactions. Organ a self contained group of tissues that performs a specific function in the body. Coming from the two greek words makro.
As the level of the complexity of the organisms increase its immunity also becomes more extensive. Anatomy greek anatomē dissection is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science which deals with the structural organization of living things.
The cell is structural and functional unit of all living things. A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are cells basic unit of life differentiation process in which cells become specialized in structure and fun contains genetic information which controls functions within t the most basic unit of life surrounds the cell provides structural support. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself such as a bacterium or yeast.
The t cells are like soldiers who search out and destroy the targeted invaders. Medical definition of t cell. Related biology terms cell the basic biological unit of living things.
Meristem a. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids.
Groups of them form tissues. The major parts of a cell are the nucleus cytoplasm and cell membrane. Immature t cells termed t stem cells.
The study of cells is called cell biology cellular biology or cytology. Humans for example have various cells in the body which act to help deter the presence of pathogens.
 Prokaryotic Cells Structure Function And Definition
Prokaryotic Cells Structure Function And Definition
 Human Anatomy Blood Cells Plasma Circulation And More
Human Anatomy Blood Cells Plasma Circulation And More
 Eukaryotic Cells Definition Parts Examples And Structure
Eukaryotic Cells Definition Parts Examples And Structure
 Cells Human Anatomy Bio207 With Kelsey Stuart At State
Cells Human Anatomy Bio207 With Kelsey Stuart At State
 Active Transport In Cells Definition Examples College
Active Transport In Cells Definition Examples College
 Anatomy And Biology Of Immune Response
Anatomy And Biology Of Immune Response
 Human Brain Cell Definition Of Human Brain Cell By Medical
Human Brain Cell Definition Of Human Brain Cell By Medical
 Gland Definition Of Gland By Medical Dictionary
Gland Definition Of Gland By Medical Dictionary
 Endoneurium Definition Structure Location And Functions
Endoneurium Definition Structure Location And Functions
 Crafton Hills Anatomy Physiology Epithelial Tissues A
Crafton Hills Anatomy Physiology Epithelial Tissues A
 18 4 Leukocytes And Platelets Anatomy And Physiology
18 4 Leukocytes And Platelets Anatomy And Physiology
 Pdf Difference Between T Cells And B Cells
Pdf Difference Between T Cells And B Cells
 T Cells And Lymphokines Understanding The Immune System
T Cells And Lymphokines Understanding The Immune System
 Cell Body Definition Of Cell Body By Medical Dictionary
Cell Body Definition Of Cell Body By Medical Dictionary
 How Fat Cells Work Howstuffworks
How Fat Cells Work Howstuffworks
 Leaf Cell Definition And Types Biology Dictionary
Leaf Cell Definition And Types Biology Dictionary
 Paneth Cells Definition Functions And Role In The
Paneth Cells Definition Functions And Role In The
 Goblet Cells Definition Functions Mucus Secretion And
Goblet Cells Definition Functions Mucus Secretion And
 Structure Of The Plasma Cell Stock Vector Illustration Of
Structure Of The Plasma Cell Stock Vector Illustration Of
 Ganglion Cell Physiology By Ralph Nelson Webvision
Ganglion Cell Physiology By Ralph Nelson Webvision
 The Tissue Level Of Organization Chapter 3 Tissue
The Tissue Level Of Organization Chapter 3 Tissue
 What Are Somatic Cells With Pictures
What Are Somatic Cells With Pictures
 What Is The Cell Matrix Biology Stack Exchange
What Is The Cell Matrix Biology Stack Exchange
 The Cell Types Functions And Organelles
The Cell Types Functions And Organelles
 What Are The Functions Of Sponges Specialized Cells
What Are The Functions Of Sponges Specialized Cells



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Cells Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar