Acetylcholine Definition Anatomy
Acetylcholine is the chief neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system the part of the autonomic nervous system. A neurotransmitter released by nerves that is essential for communication between the nerves and muscles.
 Pharmacology Cholinergic Drugs Made Easy
Pharmacology Cholinergic Drugs Made Easy
Twisted around actin filaments and covver the acin binding sites.

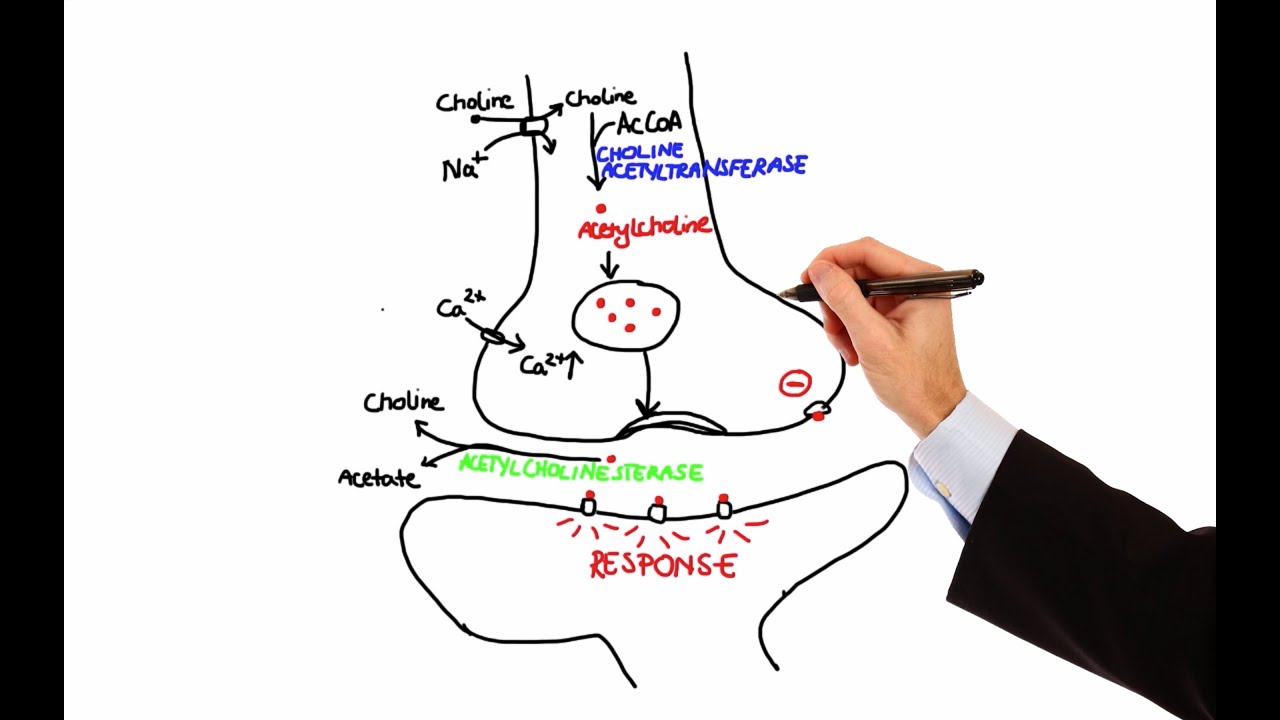
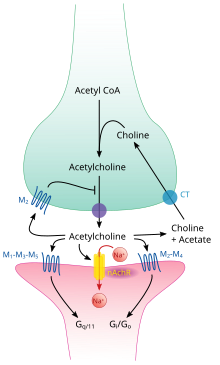
Acetylcholine definition anatomy. Acetylcholine ach is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals and humans as a neurotransmitter a chemical message released by nerve cells to send signals to other cells such as neurons muscle cells and gland cells. Residents cannot receive their mail until he or she comes and delivers it to the mailbox. Acetylcholine is synthesized and liberated by the action of the enzyme choline acetyltranferase from the compounds choline and acetyl coenzyme a acetyl coa which occurs in all cholinergic neurons.
Acetylcholine definition is a neurotransmitter c7h16no2 released at autonomic synapses and neuromuscular junctions and formed enzymatically in the tissues from choline. When activated it causes the contraction of skeletal muscles and activates glandular functions in the endocrine system. Acetylcholine is a chemical that is found between the nerve synapses or gaps between nerve cells.
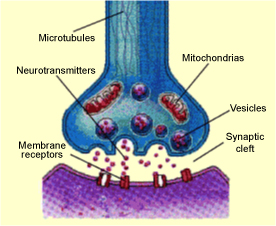
Acetylcholine an ester of choline and acetic acid that serves as a transmitter substance of nerve impulses within the central and peripheral nervous systems. Medical definition of acetylcholinesterase. An enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the synaptic cleft the space between two nerve cells so the next nerve impulse can be transmitted across the synaptic gap.
Pesticides of the organophosphate and carbamate types act to paralyze. Acetylcholine receptor anatomy the acetylcholine receptor achr is a membrane protein that binds to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine ach. Think of acetylcholine as a mailperson.
These receptors can be divided into two main types of distinct receptors nicotinic and muscarinic. Acetylcholine definition the acetic acid ester of choline c7h17no3 released and hydrolyzed during nerve conduction and causing muscle action by transmitting nerve impulses across synapses. A protein attached to trypomyosinn and binds to ca altering its configuration which results in pulling the tropomyosin away from the actin binding sites which allows myosin to come in and bind to it contraction.
 Neuromuscular Junction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Neuromuscular Junction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
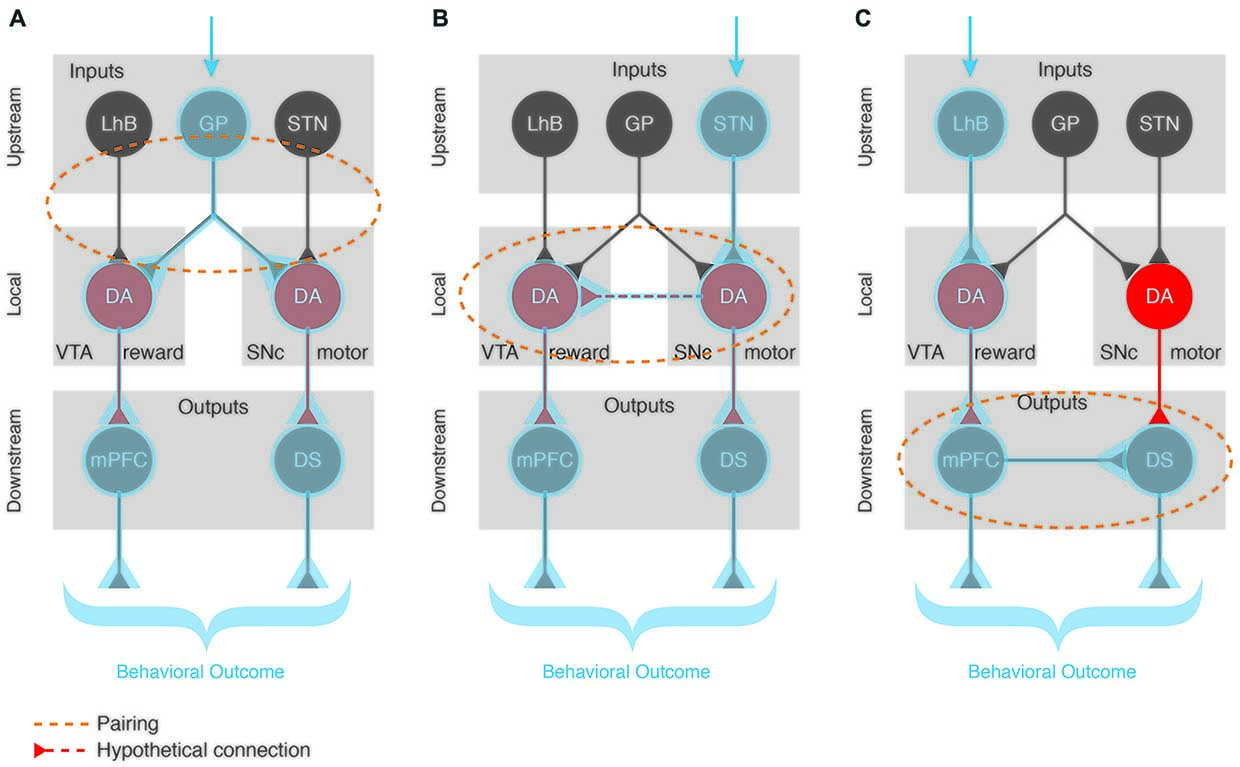 Frontiers Dopamine And Acetylcholine A Circuit Point Of
Frontiers Dopamine And Acetylcholine A Circuit Point Of
 Ib Psychology Bloa Cognitions Emotions Psychology
Ib Psychology Bloa Cognitions Emotions Psychology
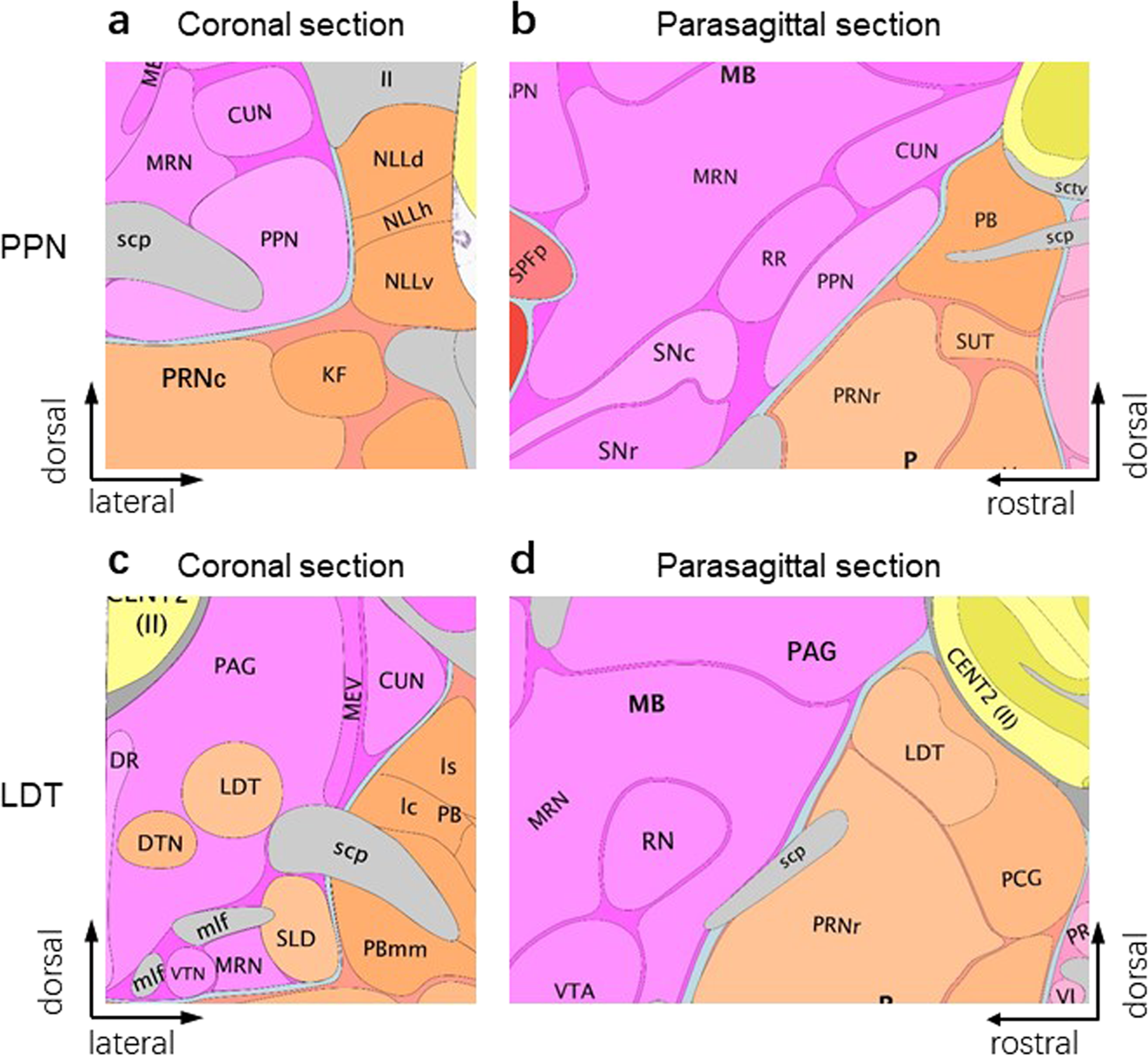 Neural Circuits And Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
Neural Circuits And Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
 What Are The Differences Between Muscarinic And Nicotinic
What Are The Differences Between Muscarinic And Nicotinic
 Sympathetic Vs Parasympathetic Nervous System Includes
Sympathetic Vs Parasympathetic Nervous System Includes
 What Is Neuromuscular Junction Definition Structure
What Is Neuromuscular Junction Definition Structure
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/synapse-103018523-59c7f273054ad9001175c403.jpg) Neurotransmitters Definition And List
Neurotransmitters Definition And List
 Neuromuscular Junctions And Muscle Contractions Anatomy
Neuromuscular Junctions And Muscle Contractions Anatomy
 Why Introverts And Extroverts Are Different The Science
Why Introverts And Extroverts Are Different The Science
 Sympathetic Nervous System Definition Function Examples
Sympathetic Nervous System Definition Function Examples
 Neuromuscular Junctions And Muscle Contractions Anatomy
Neuromuscular Junctions And Muscle Contractions Anatomy
 Acetylcholine Definition Function Facts Britannica
Acetylcholine Definition Function Facts Britannica
 Neurotransmitters What They Are Functions And Psychology
Neurotransmitters What They Are Functions And Psychology
 Autonomic Pharmacology Pharmacology Education Project
Autonomic Pharmacology Pharmacology Education Project
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11686/Neurotransmitters.jpeg) Neurotransmitters Types Functions And Disorders Kenhub
Neurotransmitters Types Functions And Disorders Kenhub
 Acetylcholine Definition Function Facts Britannica
Acetylcholine Definition Function Facts Britannica
 Neurotransmitters And Its Mechanism Of Action
Neurotransmitters And Its Mechanism Of Action
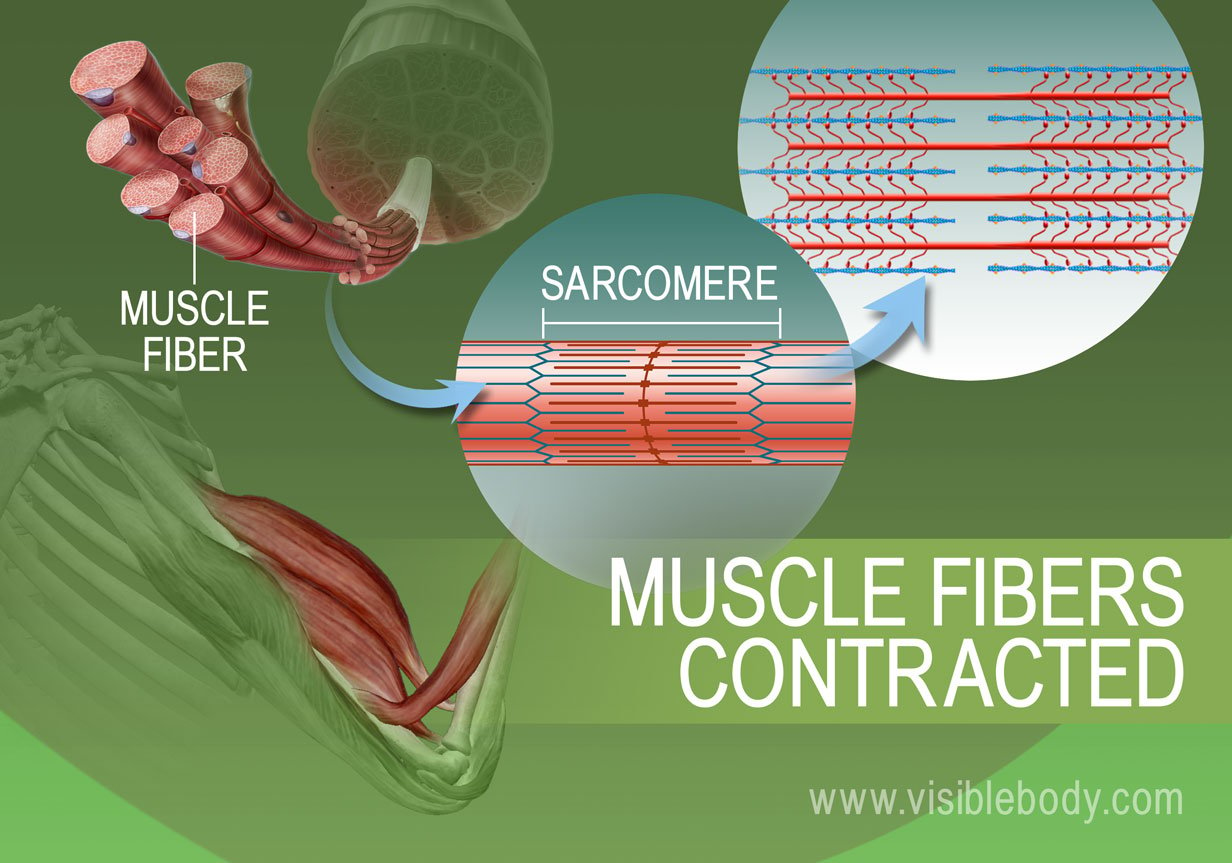 Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
Acetylcholine Choline Deficiency In Chronic Illness The
 Arousal In Psychology Definition
Arousal In Psychology Definition
 Overview Of Nervous System Parasympathetic Responses Ppt
Overview Of Nervous System Parasympathetic Responses Ppt
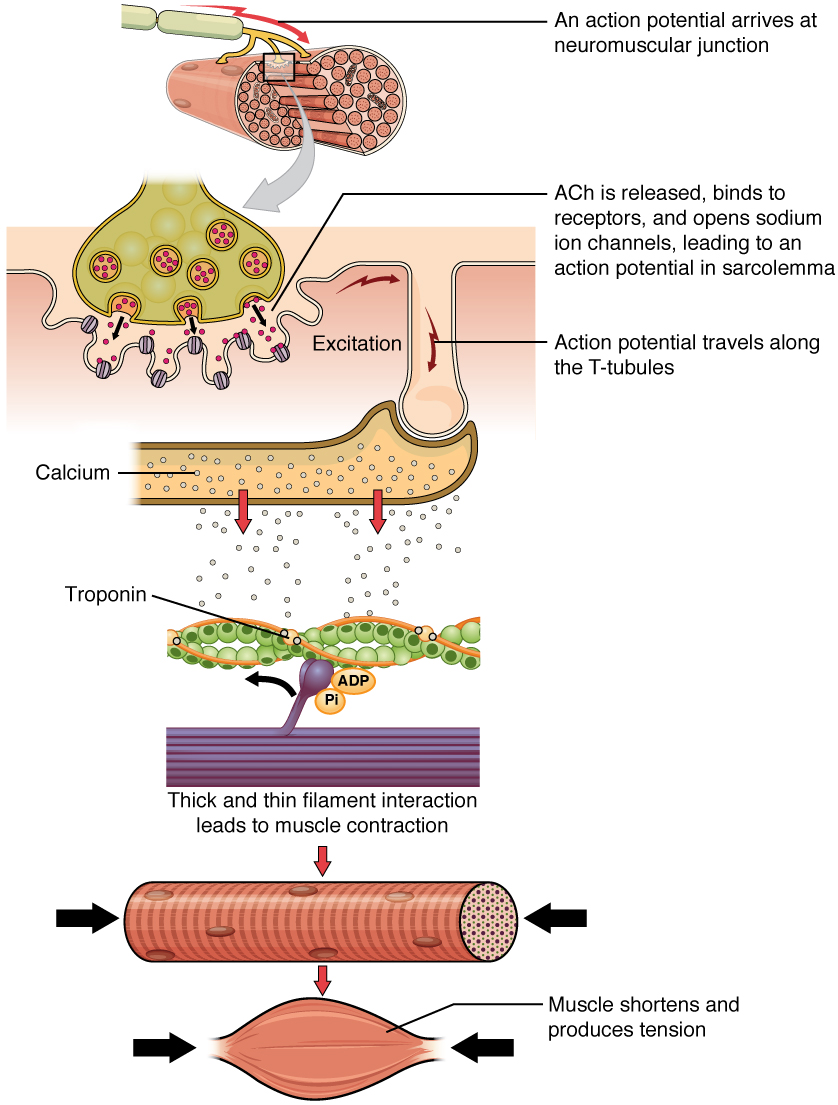 10 3 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
10 3 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
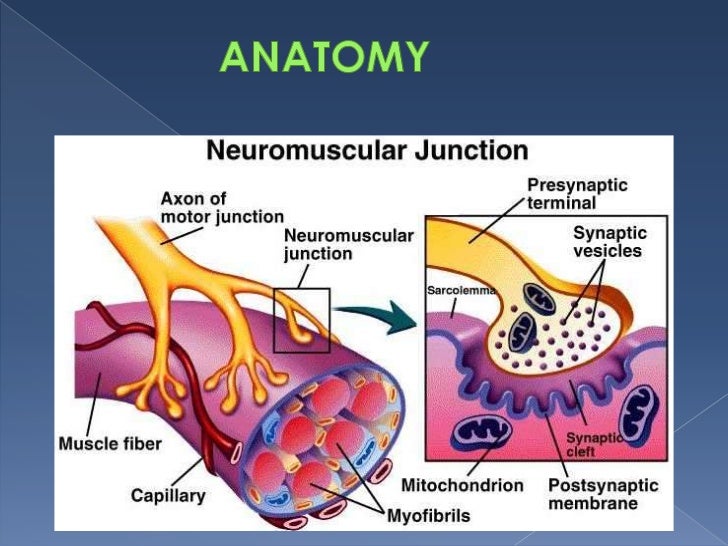 Neuromuscular Junction And Its Physiology
Neuromuscular Junction And Its Physiology



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Acetylcholine Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar