Equilibrium Anatomy Definition
Medical definition of equilibrium 1. Learn equilibrium anatomy physiology with free interactive flashcards.
It entails visual system vestibular system and proprioception working together to achieve balance.

Equilibrium anatomy definition. A state of balance between opposing forces or actions that is either static as in a body acted on by forces whose resultant is zero or dynamic as in a reversible chemical reaction when the velocities in both directions are equal. The maculea play an. The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant.
The state to which a system evolveseg sustained periodic oscillations. Static and dynamic equilibrium. Equilibrium receptors in the inner ear are called the what.
A macula contains numerous receptor cells called hair cells from which numerous stereocilia long microvilli and a single kinocilium a true cilium extend into a glycoprotein gel the otolithic membrane. A sensory receptor called a macula is located in the walls of the saccule and utricle the two bulblike sacs of the vestibule. Choose from 500 different sets of equilibrium anatomy physiology flashcards on quizlet.
It is a physiological sense in humans and animals to prevent them from falling over as they move or stand. Cards return to set details. Static equilibrium when a system reaches a point of stability in which no parts are still moving.
2 functions of the vestibular apparatus. Equilibrium a state of constancy in a system. Anatomy anatomy and physiology.
Several types of sensory receptors provide information to the brain for the maintenance of equilibrium. The apparently steady but actually fluctuating state which is exhibited by stable ecosystems and communities. Along with hearing the inner ear is responsible for encoding information about equilibrium the sense of balance which it does in the vestibule and semicircular canals structures that are sometimes collectively referred to as the vestibular apparatus fig.
Equilibrium a point in a reaction in which the lowest free energy exists on both sides of a chemical equation. A population might be in static equilibriumno pasa nadaie no births or deaths or in dynamic equilibriumie same numbers of births and deaths. Equilibrioception is the sense of balance.
Fluctuations occur within such systems in relation to seasons life cycles nutrient cycles energy cycles successional stages etc all within an apparently stable system.
/anatomy-of-the-brain-cerebellum-373216_final-87543856311e4c0380bd1fa616c84f41.png) Anatomy Of The Cerebellum And Its Function
Anatomy Of The Cerebellum And Its Function
 Physiology Of Equilibrium Balance
Physiology Of Equilibrium Balance
 What Is Dynamic Equilibrium Definition And Examples
What Is Dynamic Equilibrium Definition And Examples
 Equilibrium Translational Rotational
Equilibrium Translational Rotational
 Sound Properties Types Facts Britannica
Sound Properties Types Facts Britannica
 How The Inner Ear Balance System Works Labyrinth Semicircular Canals
How The Inner Ear Balance System Works Labyrinth Semicircular Canals
 Partition Coefficient Definition And Calculation
Partition Coefficient Definition And Calculation
Vestibular And Balance Disorders Explained Causes And Effects
 Physiology Of Equilibrium Balance
Physiology Of Equilibrium Balance
The Gibbs Donnan Effect Deranged Physiology
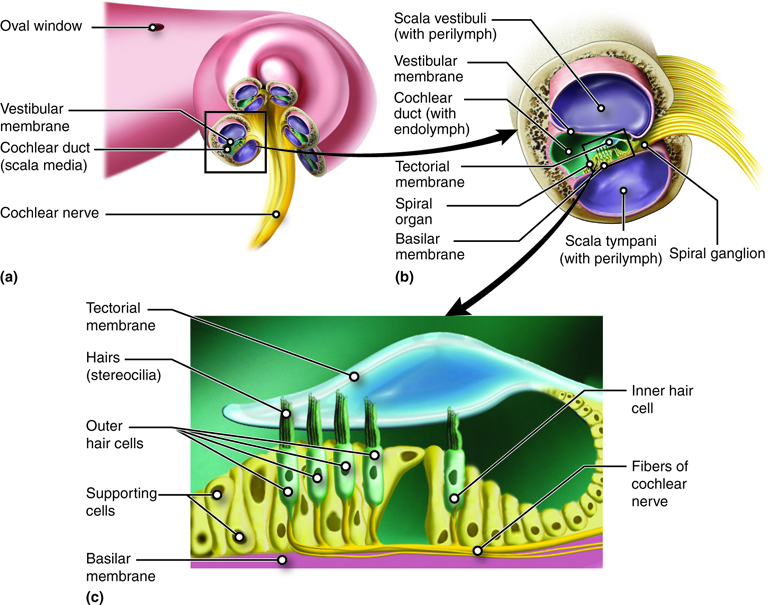 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Vestibular And Balance Disorders Explained Causes And Effects
 Exergonic Reaction Definition Examples And Quiz Biology
Exergonic Reaction Definition Examples And Quiz Biology
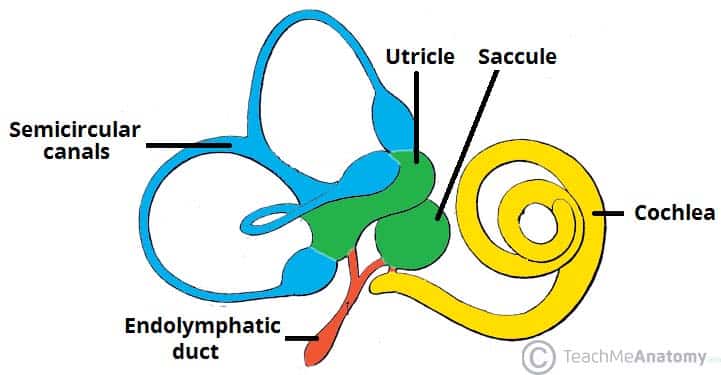 The Vestibulocochlear Nerve Cn Viii Balance Hearing
The Vestibulocochlear Nerve Cn Viii Balance Hearing
Dynamic Equilibrium Definition Function Examples Video
Net Magnetization Questions And Answers In Mri
 Punctuated Equilibrium Definition Theory Examples
Punctuated Equilibrium Definition Theory Examples
 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
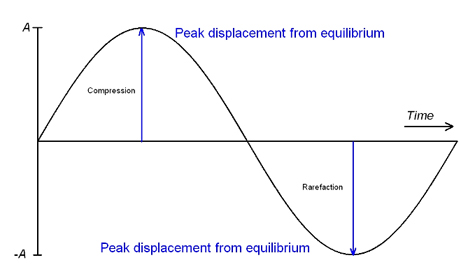 Understanding Sound What Is Sound Pro Audio Files
Understanding Sound What Is Sound Pro Audio Files
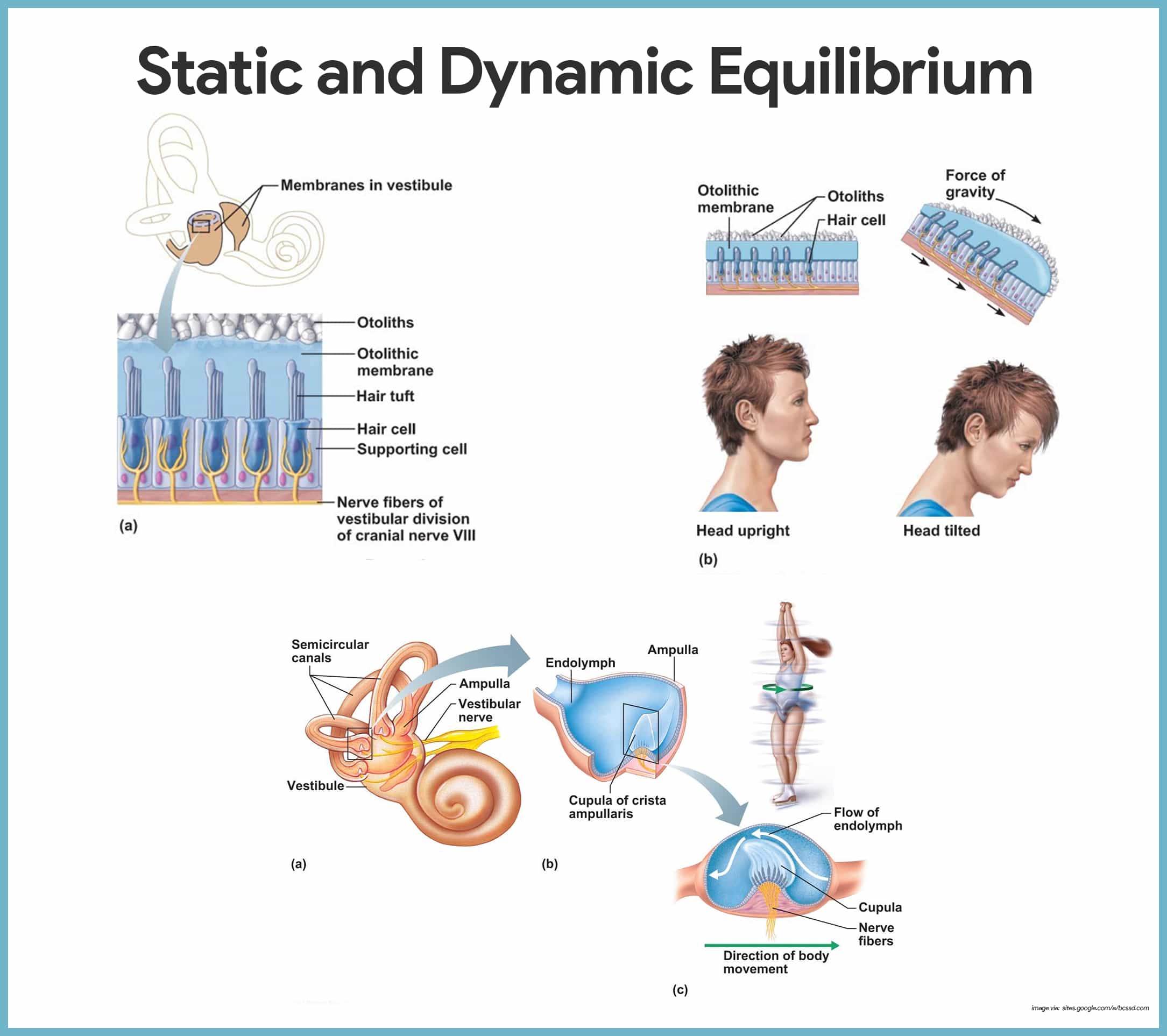 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica
Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica
 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Equilibrium Anatomy Definition"
Posting Komentar