Anatomy And Physiology Of Kidney
The primary roles of the kidneys are to remove metabolic wastes maintain fluid and electrolyte balance and help achieve acidbase balance. This illustration demonstrates the normal kidney physiology showing where some types of diuretics act and what they do.
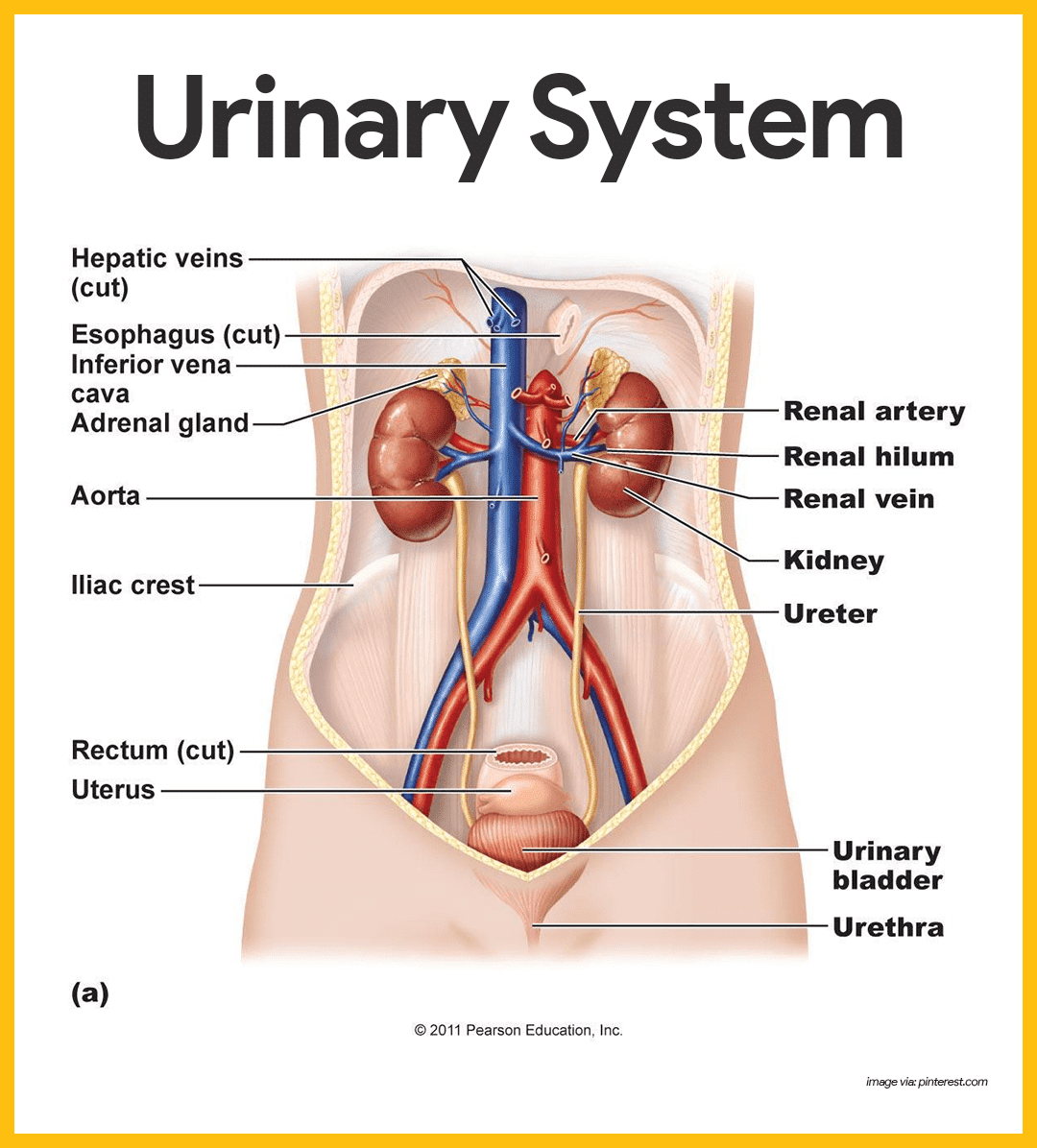 Urinary System Anatomy And Physiology Study Guide For Nurses
Urinary System Anatomy And Physiology Study Guide For Nurses
Anatomy and physiology of the kidneys.
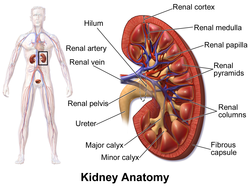
Anatomy and physiology of kidney. A frontal section through the kidney reveals an outer region called the renal cortex and an inner region called the medulla figure 2. Hormones produced by the kidneys have an important role in blood pressure control red blood cell production and bone metabolism. Kidney anatomy and physiology.
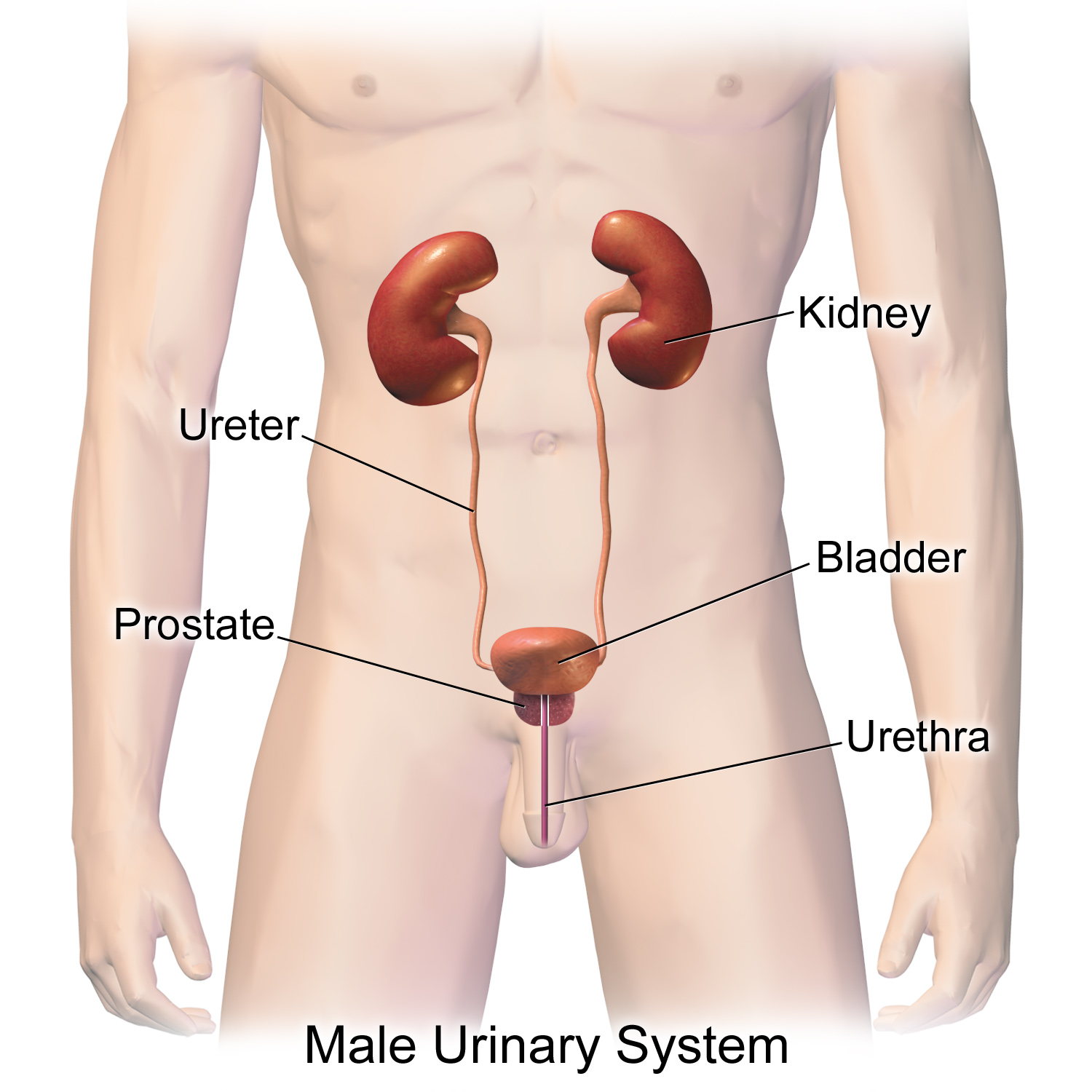
Anatomy of the urinary system. Location of the kidneys there are two kidneys which lie retroperioneally in the lumbar area. Kidney anatomy and physiology.
The basic anatomy and physiology of the kidney how kidney function changes through life. Connective tissue anchors the kidneys to surrounding structures and helps maintain their normal position. The kidneys are surrounded by a layer of adipose that holds them in place and protects them from physical damage.
In this chapter we explain. In species where the right kidney is most cranial it lies in a small fossa of the caudate liver lobe. Discover the worlds research.
The renal columns are connective tissue extensions that radiate downward from the cortex through the medulla to separate the most characteristic features of the medulla. This also often contains a large quantity of fat to cushion and protect the kidneys from the pressure of other organs the right kidney is most cranial in all species except the pig and grasscutter. The kidneys are 11 centimeters long paired reddish brown organs situated on the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity one on each side of the vertebral column and capped by the adrenal gland.
Due to the presence of the liver the right kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney. The kidneys alone perform the functions just described and manufacture urine in the process while the other organs of the urinary system provide temporary storage reservoirs for urine or serve as transportation channels to carry it from one body region to another. Glomerular filtration glomerular filtration is the renal process whereby fluid in the blood is filtered across the capillaries of the glomerulus.
The right kidney is lower than the left due to displacement by the liver. The kidneys unlike the other organs of the abdominal cavity are located posterior to the peritoneum and touch the muscles of the back.
 Urinary System Anatomy Archives Page 11 Of 12 Anatomy Note
Urinary System Anatomy Archives Page 11 Of 12 Anatomy Note
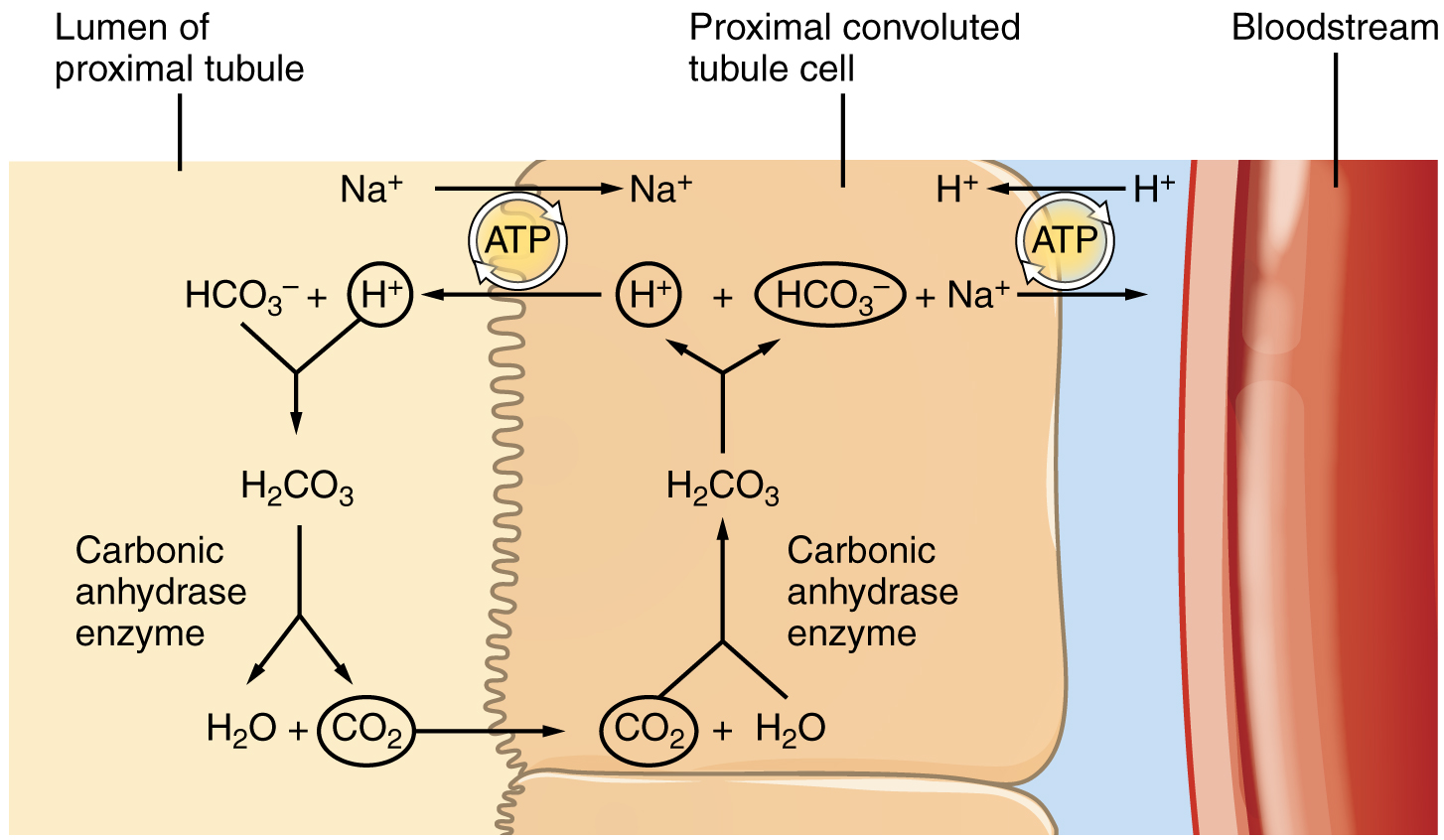 25 6 Tubular Reabsorption Anatomy And Physiology
25 6 Tubular Reabsorption Anatomy And Physiology
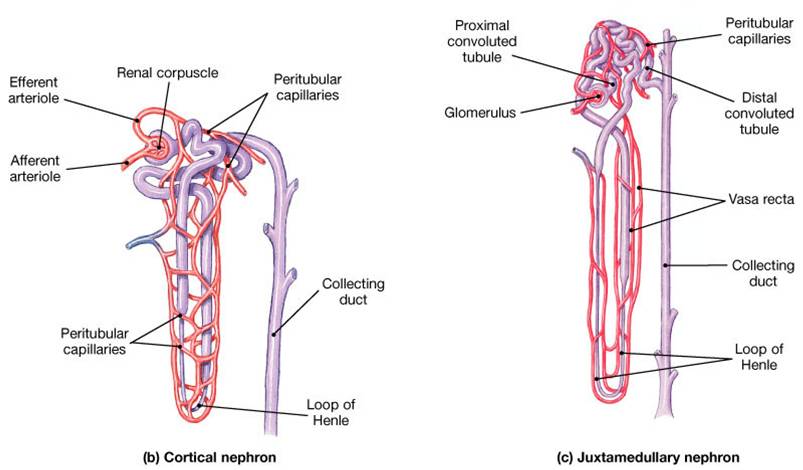 Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review
 Urinary System Kidney Anatomy Arteries Anatomy Kidney
Urinary System Kidney Anatomy Arteries Anatomy Kidney
 Kidneys Anatomy And Physiology
Kidneys Anatomy And Physiology
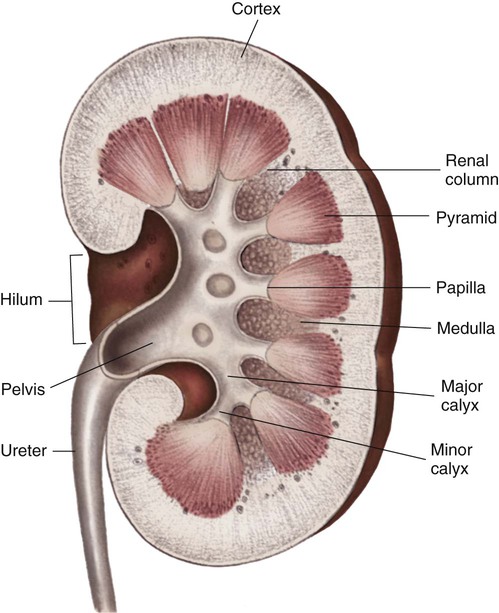 Kidney Anatomy And Physiology Nurse Key
Kidney Anatomy And Physiology Nurse Key
 Microscopic Anatomy Of The Kidney Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Microscopic Anatomy Of The Kidney Anatomy And Physiology Ii
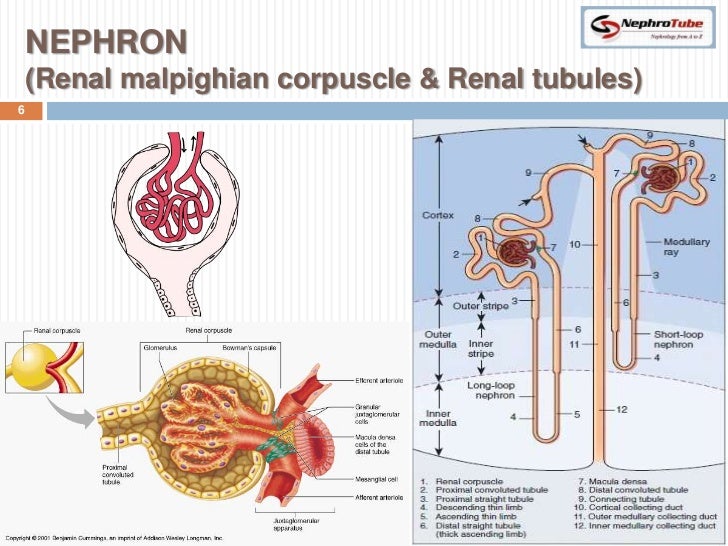 Renal Physiology I Kidney Function Physiological Anatomy
Renal Physiology I Kidney Function Physiological Anatomy
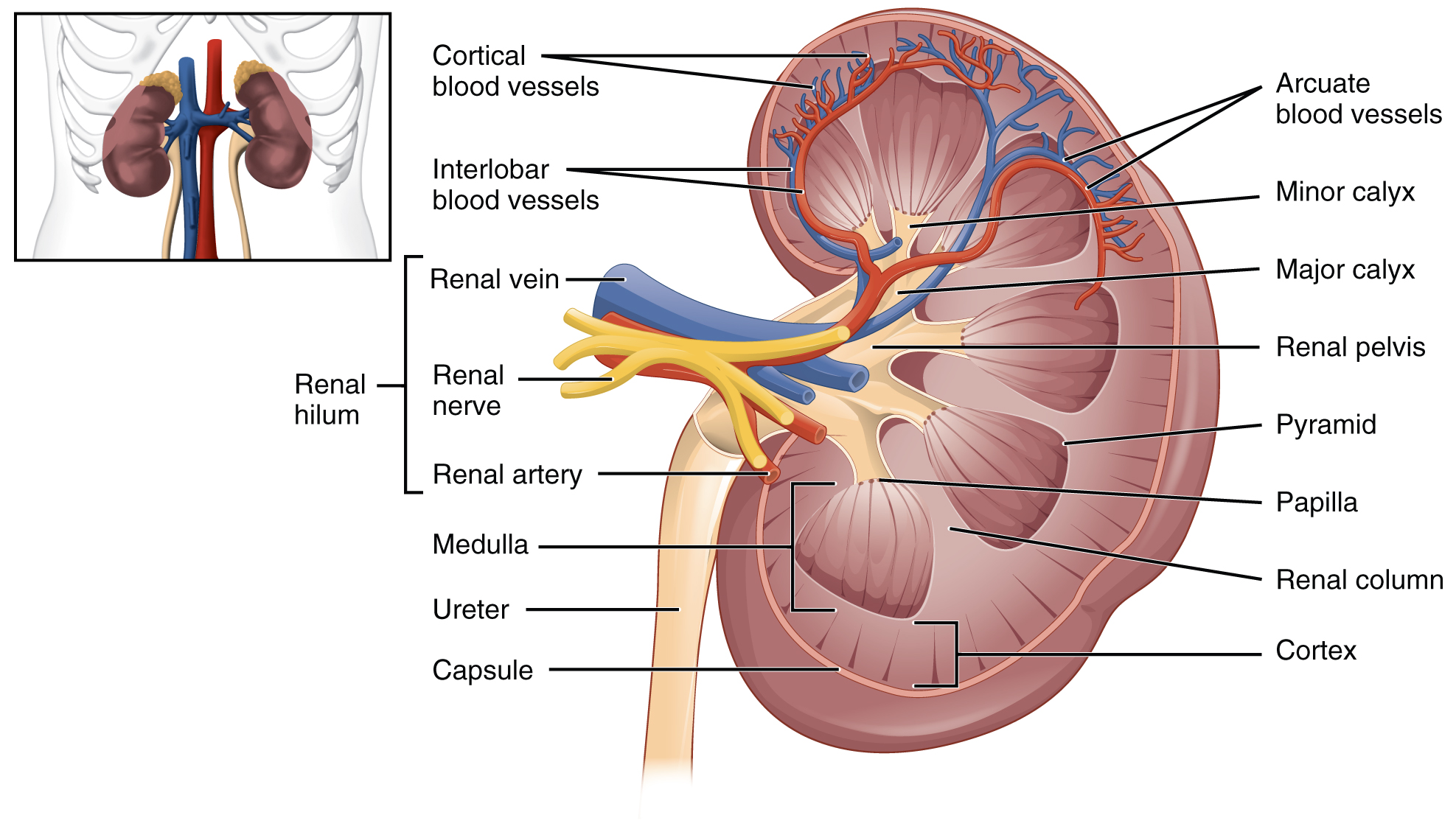 25 3 Gross Anatomy Of The Kidney Anatomy And Physiology
25 3 Gross Anatomy Of The Kidney Anatomy And Physiology
Anatomy And Physiology Ii Kidney Model 2 Renal
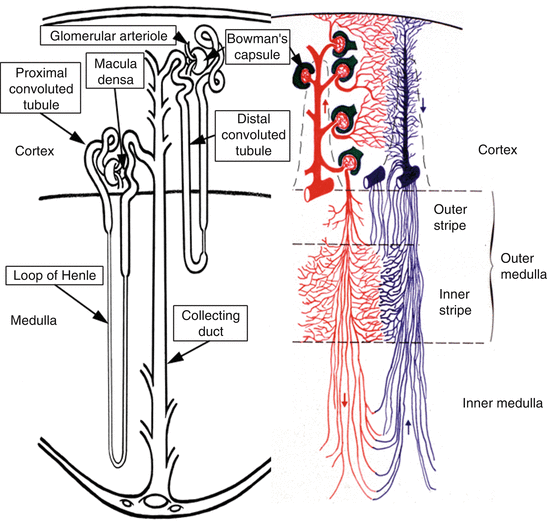 Kidney Anatomy And Physiology Springerlink
Kidney Anatomy And Physiology Springerlink
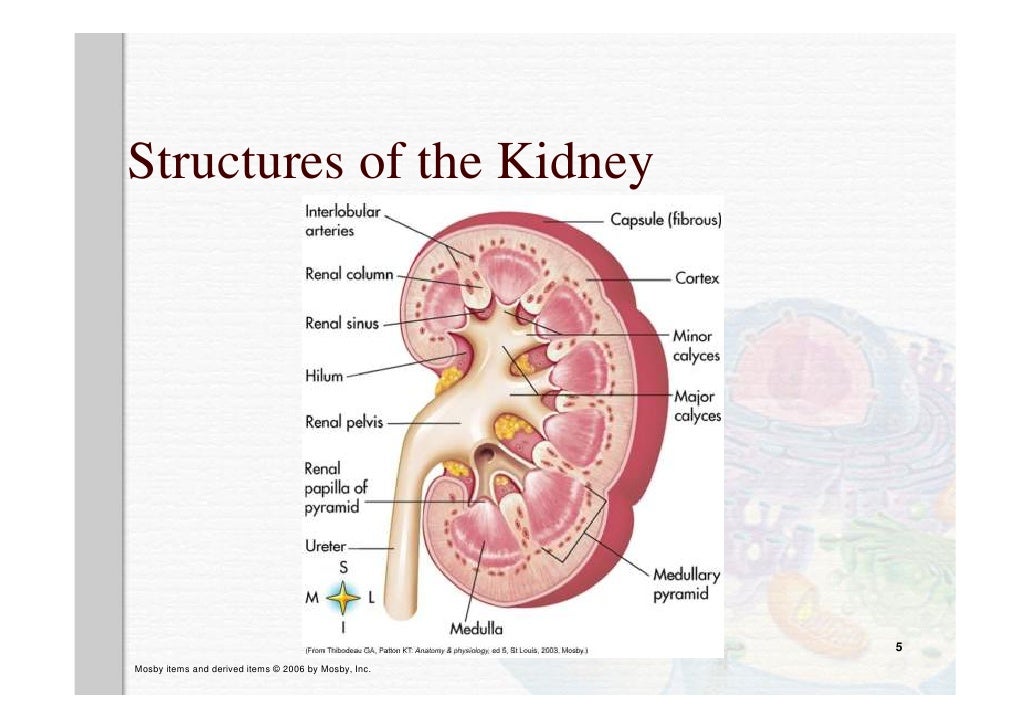 Review Anatomy And Physiology Kidney
Review Anatomy And Physiology Kidney
 Kidney Anatomy And Filtration Diagram Stock Image C043
Kidney Anatomy And Filtration Diagram Stock Image C043
 Kidney Structure Anatomy And Function Online Biology Notes
Kidney Structure Anatomy And Function Online Biology Notes
 The Internal Anatomy Of The Kidney Diagram Quizlet
The Internal Anatomy Of The Kidney Diagram Quizlet
 The Urinary System Ross And Wilson Anatomy And Physiology
The Urinary System Ross And Wilson Anatomy And Physiology
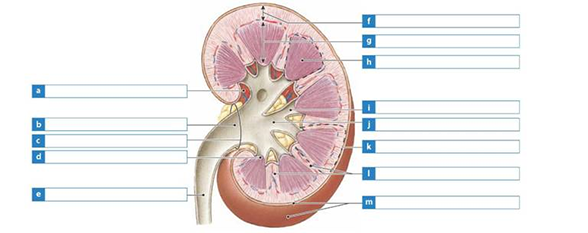 Solved Label The Kidney Structures In The Following Diagram
Solved Label The Kidney Structures In The Following Diagram
 Pin By Lisa Harris Mcdermid On Urinary System Renal
Pin By Lisa Harris Mcdermid On Urinary System Renal
 Pdf Kidney Anatomy And Physiology
Pdf Kidney Anatomy And Physiology
Kidneys Anatomy And Physiology
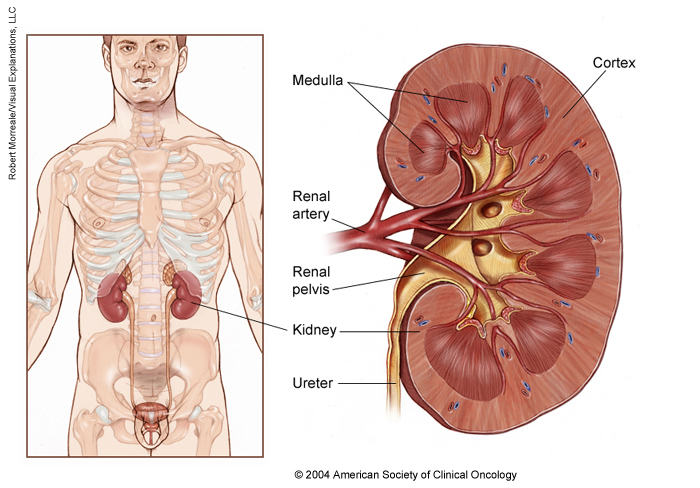 Kidney Cancer Medical Illustrations Cancer Net
Kidney Cancer Medical Illustrations Cancer Net
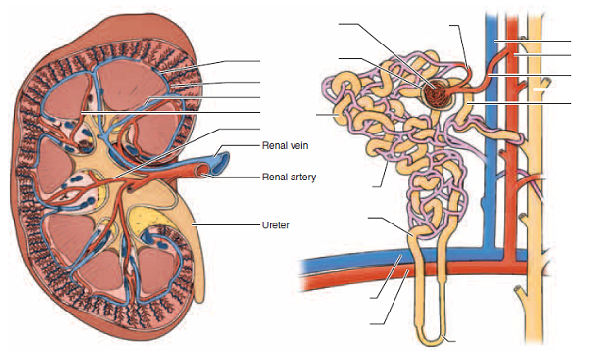 Functional Microscopic Anatomy Of The Kidney And Bladde
Functional Microscopic Anatomy Of The Kidney And Bladde
 Urology Nephrology Sections Anatomy And Physiology
Urology Nephrology Sections Anatomy And Physiology
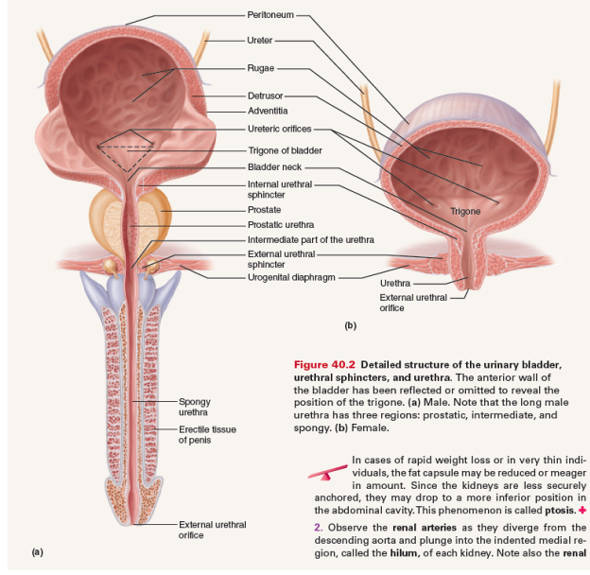 Chapter 40 Solutions Human Anatomy Physiology Laboratory
Chapter 40 Solutions Human Anatomy Physiology Laboratory
Blood Flow Through The Kidney Course Hero
 Structure Of The Kidney Anatomy And Physiology Doctor
Structure Of The Kidney Anatomy And Physiology Doctor
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy And Physiology Of Kidney"
Posting Komentar