Physiology And Anatomy Of Eye
Conjunctiva cornea iris lens macula retina optic nerve vitreous and extraocular muscles. Anatomy of the eye.
 Physiology Of Vision Online Biology Notes
Physiology Of Vision Online Biology Notes
Eye anatomy how the eye works.
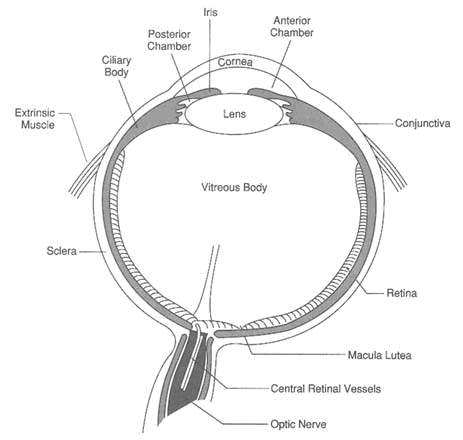
Physiology and anatomy of eye. Nerve signals that contain visual information are transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain. Interior of the ball 1 anterior cavity 2 vitreous chamber 3 lens b. The eye is contained within the bony orbit of the head.
The anterior cavity and the posterior cavity. A tapetum is a mirror type membrane that is reflective on the back of the eye activating the rod gives better night vision vitreous humor posterior portion of eye filled with jelly like substance. Anatomy parts and structure.
Anatomy of the eye. Last week we discussed vision from a historical perspective in order to understand how johannes kepler rené descartes and bishop berkeley discovered the importance of the mind in effecting vision. Watch an animation on how vision works.
Human eye is spherical about 25 cm in diameter. Learn about the anatomy of the eye with this free multiple choice quiz with links to over 200 other anatomy physiology and pathology quizzes. The eye is surrounded by the orbital bones and is cushioned by pads of fat within the orbital socket.
The eye a guide to the many parts of the human eye how and why vision works and functions. Anatomy physiology pathology of the human eye included are descriptions functions and problems of the major structures of the human eye. There are 6 sets of muscles attached to outer surface of eye ball which helps to rotate it in different direction.
It is situated on an orbit of skull and is supplied by optic nerve. It is continuous with the temporal bone and the pterygopalatine fossa caudally. Sight begins when light rays from an object enter the eye through the cornea the clear front window of the eyeball.
The bony orbit is a cavity comprising parts of the lacrimal bone includes fossa for nasolacrimal duct and the maxilla includes caudal foramen of infraorbital canal. The eye is also divided into two cavities. The innermost layer of the eye is the neural tunic or retina which contains the nervous tissue responsible for photoreception.
Physiology of vision 3. The eye is the photo receptor organ. Physiology of the eye 1.
Eye ball structures 1 fibrous tunic 2 vascular tunic 3 nervous tunic 3. The anterior cavity is the space between the cornea and lens including the iris and ciliary body. Development anatomy and physiology of the eye the word perspective comes from the latin per through and specere look at.
They have more rods. Extraocular muscles help move the eye in different directions.
 Free Anatomy Coloring Pages Eye Anatomy Anatomy Coloring
Free Anatomy Coloring Pages Eye Anatomy Anatomy Coloring
 Anatomy And Physiology Of Vision
Anatomy And Physiology Of Vision
 Ppt Learning Target Human Eye Anatomy Physiology
Ppt Learning Target Human Eye Anatomy Physiology
Eye Anatomy And Physiology How The Eye And Vision Work
 Outlines Of The Comparative Physiology And Morphology Of
Outlines Of The Comparative Physiology And Morphology Of
 The Clinical Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Rila
The Clinical Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Rila
 Vision Anatomy And Physiology I
Vision Anatomy And Physiology I
 Sense Organs Anatomy And Physiology
Sense Organs Anatomy And Physiology
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Video Anatomy Osmosis
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Video Anatomy Osmosis
Eye Anatomy And Vision Course Hero
 8 Ocular Effects Of Mustard Agents And Lewisite Veterans
8 Ocular Effects Of Mustard Agents And Lewisite Veterans
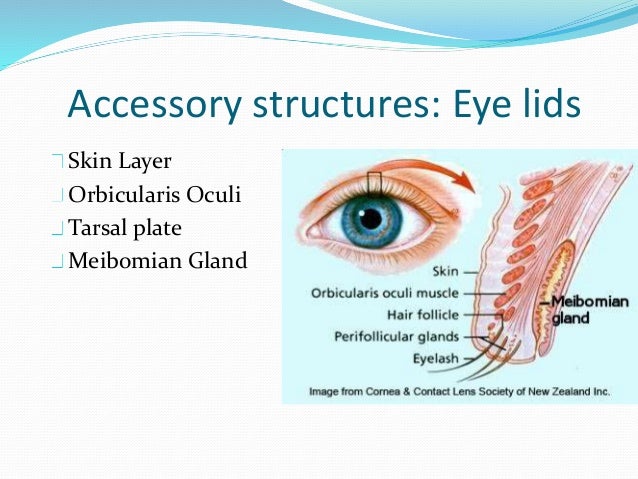 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye
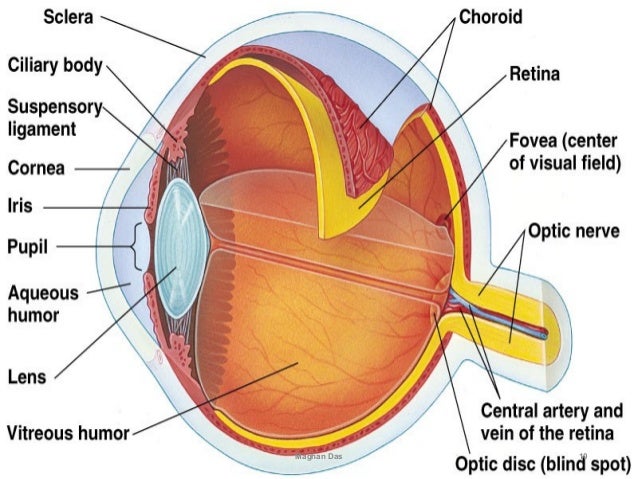 Anatomy And Physiology Of Eye By Maghan Das
Anatomy And Physiology Of Eye By Maghan Das
Min Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye Eyeball And
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Medical Estudy
 Medical Surgical Eye Disorders Brilliant Nurse
Medical Surgical Eye Disorders Brilliant Nurse
 Anatomy And Physiology Special Senses The Eyes Nursing Crib
Anatomy And Physiology Special Senses The Eyes Nursing Crib
 The Eye The Physiology Of Vision Anatomy Of The Eye Ppt
The Eye The Physiology Of Vision Anatomy Of The Eye Ppt
 Structure Of Human Eye Anatomy Cross Section Stock Vector
Structure Of Human Eye Anatomy Cross Section Stock Vector
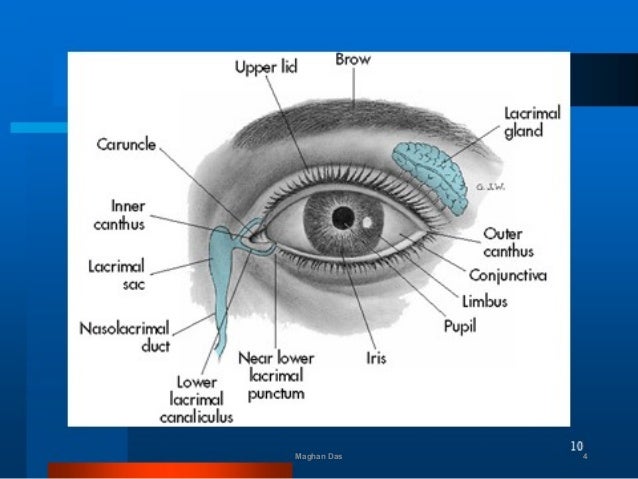 Anatomy And Physiology Of Eye By Maghan Das
Anatomy And Physiology Of Eye By Maghan Das
Understanding Eye Structure Fiteyes Com
 Eye Care Anatomy And Physiology Metro Technology Centers
Eye Care Anatomy And Physiology Metro Technology Centers
 Anatomy Physiology Of The Eye To Include Ocular Immune Cells
Anatomy Physiology Of The Eye To Include Ocular Immune Cells
 Amazon Com Semtomn Gaming Mouse Pad Blue Components Of
Amazon Com Semtomn Gaming Mouse Pad Blue Components Of

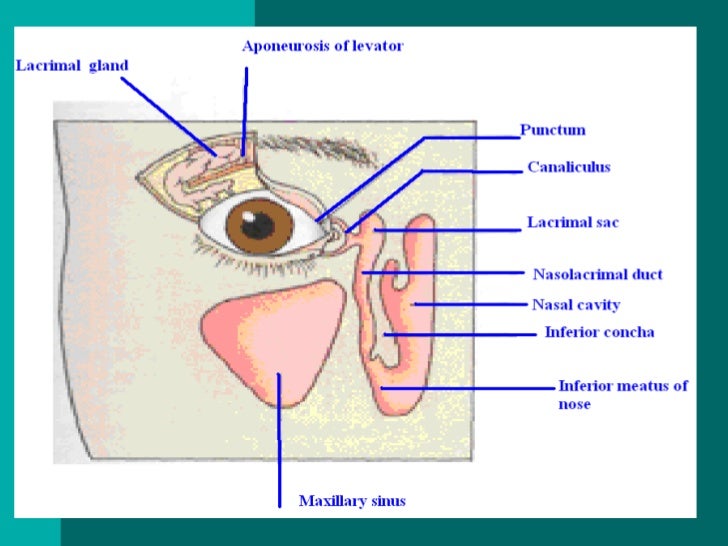
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Physiology And Anatomy Of Eye"
Posting Komentar